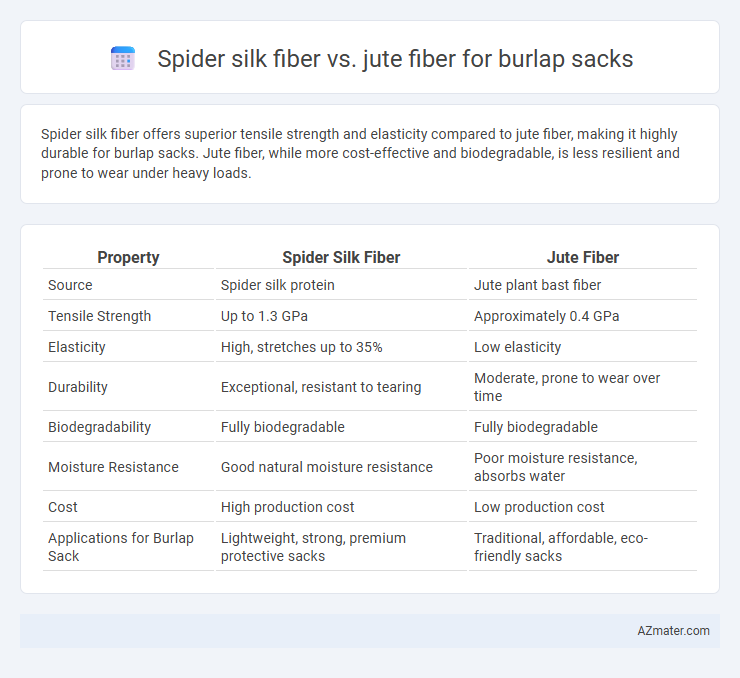
Spider silk fiber offers superior tensile strength and elasticity compared to jute fiber, making it highly durable for burlap sacks. Jute fiber, while more cost-effective and biodegradable, is less resilient and prone to wear under heavy loads.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Spider Silk Fiber | Jute Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Spider silk protein | Jute plant bast fiber |
| Tensile Strength | Up to 1.3 GPa | Approximately 0.4 GPa |
| Elasticity | High, stretches up to 35% | Low elasticity |
| Durability | Exceptional, resistant to tearing | Moderate, prone to wear over time |
| Biodegradability | Fully biodegradable | Fully biodegradable |
| Moisture Resistance | Good natural moisture resistance | Poor moisture resistance, absorbs water |
| Cost | High production cost | Low production cost |
| Applications for Burlap Sack | Lightweight, strong, premium protective sacks | Traditional, affordable, eco-friendly sacks |
Introduction to Spider Silk Fiber and Jute Fiber
Spider silk fiber, renowned for its exceptional tensile strength and elasticity, is a natural protein fiber produced by spiders, offering superior durability and lightweight properties compared to conventional materials. Jute fiber, derived from the Corchorus plant, is a long, soft, and shiny bast fiber widely used in making burlap sacks due to its affordability, breathability, and biodegradability. While spider silk fiber provides enhanced strength and flexibility, jute remains favored for its cost-effectiveness and environmental sustainability in traditional sack manufacturing.
Origins and Natural Sources
Spider silk fiber originates from orb-weaving spiders, specifically species like Nephila and Araneus, producing protein-based filaments renowned for their exceptional strength and elasticity; it is naturally harvested through spider farming or biomimetic synthesis techniques. Jute fiber derives from the stems of Corchorus plants, primarily Corchorus olitorius and Corchorus capsularis, cultivated extensively in South Asia, especially Bangladesh and India, for its coarse, durable cellulosic fiber ideal for burlap sacks. While spider silk is a proteinaceous material sourced in limited quantities from arachnids, jute is a lignocellulosic bast fiber obtained from terrestrial plants, making jute more commercially viable for large-scale burlap production.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Spider silk fiber exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to jute fiber, with tensile strength reaching up to 1.3 GPa, significantly higher than jute's typical range of 200-400 MPa. The elasticity and toughness of spider silk allow it to absorb and dissipate energy effectively, making burlap sacks made from spider silk more resistant to tearing and deformation under heavy loads. In contrast, jute fiber, while strong and sustainable, has lower elongation at break and less resilience, limiting its durability for high-stress applications.
Durability and Longevity
Spider silk fiber exhibits exceptional durability and longevity due to its superior tensile strength and elasticity, outperforming traditional jute fiber used in burlap sacks. Jute fiber, while widely used for its cost-effectiveness and biodegradability, tends to degrade faster under environmental stress and repeated wear. The molecular structure of spider silk provides higher resistance to stretching, tearing, and environmental factors, making it a more sustainable choice for long-lasting burlap sacks.
Biodegradability and Environmental Impact
Spider silk fiber exhibits exceptional biodegradability, breaking down naturally without releasing harmful substances, making it an eco-friendly alternative to conventional fibers. Jute fiber, widely used for burlap sacks, is also biodegradable and renewable but has a higher environmental footprint due to intensive water usage and pesticide application during cultivation. Comparing both, spider silk fiber offers superior environmental benefits with minimal ecological impact, while jute remains a sustainable yet more resource-intensive option.
Weight and Flexibility Differences
Spider silk fiber exhibits exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, making burlap sacks lighter yet more durable compared to those made from jute fiber, which tends to be heavier due to its coarse and dense structure. In terms of flexibility, spider silk fibers are highly elastic and can stretch up to five times their original length without breaking, enhancing the sack's ability to withstand dynamic loads, whereas jute fibers are more rigid and prone to fraying under stress. These differences highlight spider silk's superior performance in applications requiring lightweight, flexible, and strong materials.
Cost and Production Feasibility
Spider silk fiber offers exceptional strength and elasticity compared to jute fiber, but its high production cost and complex farming requirements limit its commercial use for burlap sacks. Jute fiber remains the preferred material due to its low cost, abundant availability, and established large-scale cultivation and processing infrastructure. Production feasibility heavily favors jute, enabling widespread use in burlap sacks without incurring the premium expenses associated with spider silk.
Applications in Burlap Sack Manufacturing
Spider silk fiber demonstrates exceptional tensile strength and elasticity, making it ideal for high-performance burlap sacks that require durability and resistance to wear. Jute fiber, widely used in traditional burlap sack manufacturing, offers affordability, biodegradability, and excellent breathability, suitable for packaging agricultural products. Combining spider silk's mechanical properties with jute's cost-effectiveness can lead to innovative, sustainable burlap sacks with enhanced strength and environmental benefits.
Challenges and Limitations
Spider silk fiber exhibits superior tensile strength and elasticity compared to jute fiber, but its high production cost and scalability issues limit its use in burlap sack manufacturing. Jute fiber, while cost-effective and widely available, suffers from lower durability and moisture resistance, making burlap sacks less durable under harsh environmental conditions. Both materials face challenges in balancing performance properties with economic feasibility, hindering widespread adoption for commercial packaging solutions.
Future Prospects and Innovations
Spider silk fiber offers superior tensile strength, elasticity, and biodegradability compared to jute fiber, positioning it as a highly promising alternative for burlap sacks. Innovations in bioengineering and synthetic spider silk production are driving scalability and cost-effectiveness, potentially revolutionizing the sustainable packaging industry. The future of burlap sack manufacturing may see a significant shift toward spider silk composites, enhancing durability while reducing environmental impact.
Infographic: Spider silk fiber vs Jute fiber for Burlap sack
 azmater.com
azmater.com