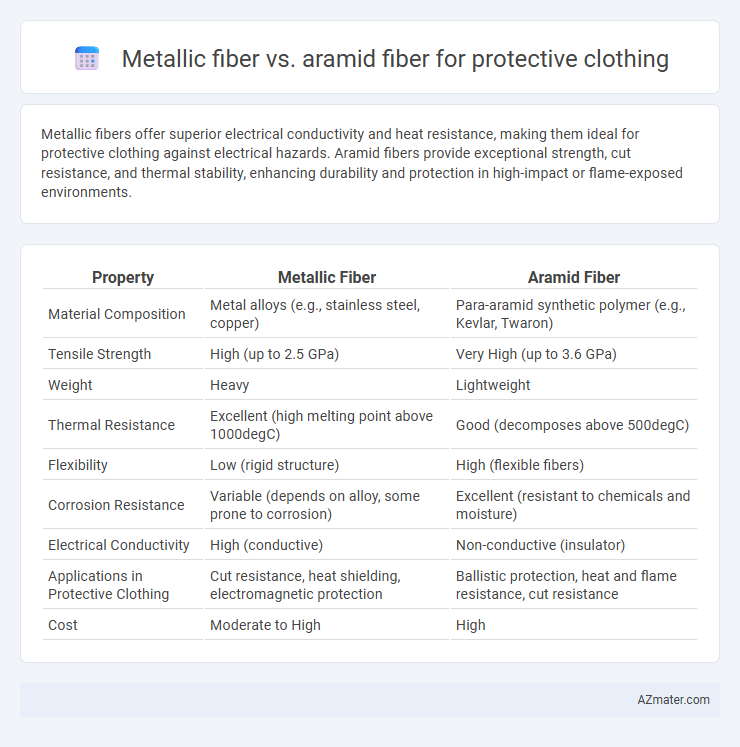
Metallic fibers offer superior electrical conductivity and heat resistance, making them ideal for protective clothing against electrical hazards. Aramid fibers provide exceptional strength, cut resistance, and thermal stability, enhancing durability and protection in high-impact or flame-exposed environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Metallic Fiber | Aramid Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Metal alloys (e.g., stainless steel, copper) | Para-aramid synthetic polymer (e.g., Kevlar, Twaron) |
| Tensile Strength | High (up to 2.5 GPa) | Very High (up to 3.6 GPa) |
| Weight | Heavy | Lightweight |
| Thermal Resistance | Excellent (high melting point above 1000degC) | Good (decomposes above 500degC) |
| Flexibility | Low (rigid structure) | High (flexible fibers) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Variable (depends on alloy, some prone to corrosion) | Excellent (resistant to chemicals and moisture) |
| Electrical Conductivity | High (conductive) | Non-conductive (insulator) |
| Applications in Protective Clothing | Cut resistance, heat shielding, electromagnetic protection | Ballistic protection, heat and flame resistance, cut resistance |
| Cost | Moderate to High | High |
Introduction to Protective Clothing Materials
Metallic fibers offer high conductivity and excellent thermal resistance, making them ideal for protective clothing against electric arcs and electromagnetic hazards. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar and Nomex, provide superior strength, heat resistance, and cut protection, widely used for flame-resistant garments and ballistic armor. Combining both materials enhances durability, thermal protection, and impact resistance in advanced protective clothing systems.
Overview of Metallic Fibers
Metallic fibers, commonly made from stainless steel, aluminum, or copper, offer exceptional heat resistance, electrical conductivity, and durability in protective clothing applications. Their integration enhances protection against electromagnetic interference, cuts, and sparks, outperforming traditional fibers in high-risk industrial environments. Compared to aramid fibers known for flame resistance and high tensile strength, metallic fibers provide superior conductivity and abrasion resistance, making them ideal for specialized safety gear requiring multimodal protection.
Overview of Aramid Fibers
Aramid fibers, known for their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and thermal stability, are widely used in protective clothing to provide heat and abrasion resistance. These synthetic fibers, such as Kevlar and Nomex, offer high tensile strength and excellent resistance to flames and chemicals, making them ideal for firefighters, military personnel, and industrial workers. Compared to metallic fibers, aramid fibers maintain flexibility and comfort while delivering superior protection against mechanical and thermal hazards.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Metallic fibers exhibit superior tensile strength and high impact resistance, making them effective for puncture and cut protection in protective clothing. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, offer exceptional tensile strength combined with high flexibility and excellent resistance to abrasion and heat, allowing for better wearability and comfort. When comparing mechanical strength, metallic fibers provide enhanced durability against sharp forces, while aramid fibers deliver a balanced strength-to-weight ratio ideal for prolonged use in hazardous environments.
Thermal and Fire Resistance Properties
Metallic fibers exhibit superior thermal conductivity and enhanced resistance to radiant heat, making them effective for protective clothing exposed to high temperatures and molten metal splashes. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar and Nomex, offer exceptional thermal stability, flame resistance, and low thermal shrinkage, maintaining integrity under direct flame and intense heat conditions without melting. Combining metallic fibers with aramid fibers can optimize thermal protection by leveraging conductive heat dissipation alongside the inherent fire resistance and durability of aramid materials.
Chemical Resistance: Metallic vs Aramid Fibers
Metallic fibers exhibit excellent chemical resistance to acids, bases, and solvents due to their inert metal surfaces, making them highly effective in corrosive environments. Aramid fibers, while strong and heat-resistant, can degrade when exposed to strong acids or alkalis, limiting their chemical resistance compared to metallic fibers. Protective clothing incorporating metallic fibers provides superior durability and longer service life in chemically aggressive workplaces.
Comfort and Wearability Factors
Metallic fibers offer excellent heat and cut resistance but tend to be heavier and less flexible, which can reduce overall comfort and breathability in protective clothing. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, provide a superior balance of lightweight durability, high tensile strength, and moisture-wicking properties, enhancing wearability and long-term comfort during extended use. The seamless integration of aramid fibers in protective garments optimizes mobility and reduces thermal discomfort, making them more suitable for demanding work environments requiring sustained protection.
Application Areas in Protective Clothing
Metallic fibers are widely used in protective clothing for electromagnetic shielding, heat resistance, and static dissipation, making them ideal for applications in firefighting gear, military uniforms, and industrial outfits exposed to high heat and electrical hazards. Aramid fibers, known for their exceptional strength, flame resistance, and lightweight properties, dominate in ballistic protection, cut-resistant gloves, and helmets used by law enforcement, military personnel, and first responders. Both fibers contribute uniquely to protective clothing, with metallic fibers enhancing thermal and electrical safety while aramid fibers ensure impact and abrasion resistance in high-risk environments.
Cost and Sustainability Considerations
Metallic fibers, derived mainly from aluminum or stainless steel, tend to be more expensive due to energy-intensive manufacturing and limited recyclability, whereas aramid fibers like Kevlar offer a cost-effective option with high durability and better lifecycle sustainability through lower environmental impact during production. Aramid fibers excel in thermal resistance and strength-to-weight ratio, making them sustainable for long-term use and reducing material waste compared to the heavier, resource-demanding metallic fibers. The choice between metallic and aramid fibers in protective clothing balances upfront cost against long-term environmental benefits, with aramid fibers generally favored for sustainable, cost-efficient protective solutions.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Fiber
Metallic fibers offer excellent electromagnetic shielding and heat resistance, making them ideal for environments with high thermal or electrical hazards. Aramid fibers provide superior tensile strength, cut resistance, and flame retardancy, proving best for ballistic and fire protective clothing. Selecting the right fiber depends on the specific protection requirements, balancing thermal, mechanical, and chemical resistance for optimal safety and performance.
Infographic: Metallic fiber vs Aramid fiber for Protective clothing
 azmater.com
azmater.com