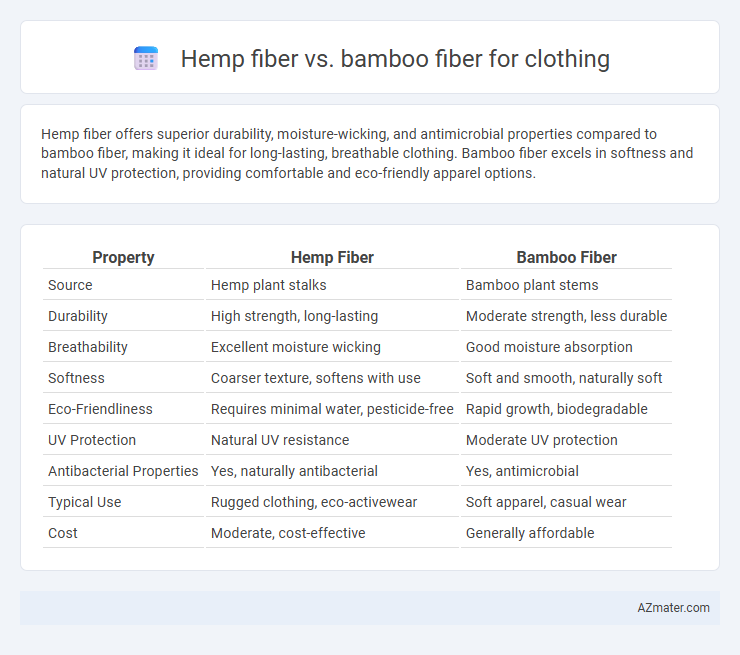
Hemp fiber offers superior durability, moisture-wicking, and antimicrobial properties compared to bamboo fiber, making it ideal for long-lasting, breathable clothing. Bamboo fiber excels in softness and natural UV protection, providing comfortable and eco-friendly apparel options.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hemp Fiber | Bamboo Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Hemp plant stalks | Bamboo plant stems |
| Durability | High strength, long-lasting | Moderate strength, less durable |
| Breathability | Excellent moisture wicking | Good moisture absorption |
| Softness | Coarser texture, softens with use | Soft and smooth, naturally soft |
| Eco-Friendliness | Requires minimal water, pesticide-free | Rapid growth, biodegradable |
| UV Protection | Natural UV resistance | Moderate UV protection |
| Antibacterial Properties | Yes, naturally antibacterial | Yes, antimicrobial |
| Typical Use | Rugged clothing, eco-activewear | Soft apparel, casual wear |
| Cost | Moderate, cost-effective | Generally affordable |
Introduction to Hemp and Bamboo Fibers
Hemp fiber, derived from the stalk of the Cannabis sativa plant, is renowned for its high tensile strength, durability, and natural resistance to UV rays and mold, making it ideal for sustainable clothing. Bamboo fiber, extracted from the bamboo plant through mechanical or chemical processes, offers exceptional softness, moisture-wicking properties, and antibacterial benefits, enhancing wearer comfort. Both fibers are eco-friendly alternatives to conventional textiles, with hemp excelling in robustness and bamboo standing out for its breathable, gentle texture.
Environmental Impact: Hemp vs Bamboo
Hemp fiber production requires significantly less water and pesticides compared to bamboo, making it a more eco-friendly choice for sustainable clothing. While bamboo grows quickly and aids in carbon sequestration, its manufacturing process often involves chemical-intensive methods that can harm the environment. Hemp's natural resistance to pests and ability to improve soil health contribute to its lower environmental footprint relative to bamboo fiber.
Cultivation and Sustainability Differences
Hemp fiber cultivation requires less water, pesticides, and herbicides compared to bamboo, making it a more sustainable choice for eco-friendly clothing production. While bamboo grows rapidly and can be harvested frequently, the processing of bamboo into textiles often involves chemically intensive methods that reduce its environmental benefits. Hemp's ability to improve soil health and its lower resource demand contribute to its superior sustainability profile in textile cultivation.
Processing Methods for Hemp and Bamboo
Hemp fiber undergoes a retting process, where microbial action breaks down the pectin holding the fibers together, followed by decortication to separate the strong bast fibers used in clothing. Bamboo fiber production varies: mechanical processing involves crushing bamboo and using natural enzymes, resulting in eco-friendly fiber, while chemical processing typically uses harsh solvents to create bamboo viscose or rayon with smoother texture but lower sustainability. The distinct processing methods significantly impact the texture, durability, and environmental footprint of clothing made from hemp and bamboo fibers.
Fiber Strength and Durability Comparison
Hemp fiber exhibits superior strength and durability compared to bamboo fiber, offering a tensile strength approximately 20-30% higher, which translates to longer-lasting garments resistant to wear and tear. The densely packed cellulose in hemp fibers provides robust structural integrity, making hemp clothing ideal for heavy-use and outdoor apparel. Bamboo fiber, while softer and more flexible, tends to have lower abrasion resistance and can degrade faster under repeated stress, limiting its longevity compared to hemp-based textiles.
Comfort and Breathability in Clothing
Hemp fiber offers excellent moisture-wicking properties and durability, making it highly breathable and comfortable for clothing in warm weather. Bamboo fiber, known for its softness and natural antibacterial qualities, provides a smoother texture and superior comfort against the skin. Both fibers excel in breathability, but bamboo's finer yarn tends to create lighter, silkier fabrics, while hemp delivers more robust, long-lasting garments.
Moisture-Wicking and Antibacterial Properties
Hemp fiber outperforms bamboo fiber in moisture-wicking due to its superior breathability and ability to absorb and release sweat quickly, making it ideal for activewear. Bamboo fiber features natural antibacterial properties from its viscose processing, reducing odor-causing bacteria for fresher garments. Combining hemp's durability and moisture management with bamboo's antibacterial benefits creates advanced clothing materials optimized for comfort and hygiene.
Dyeing and Color Retention Abilities
Hemp fiber exhibits strong dye absorption due to its porous structure, resulting in vibrant and long-lasting colors that resist fading over time, especially when natural dyes are used. Bamboo fiber, while soft and breathable, tends to have a smoother surface that can cause dyes to sit more on the surface, often leading to less intense color and reduced retention after multiple washes. Both fibers benefit from eco-friendly dyeing processes, but hemp stands out for superior color durability and enhanced dye compatibility in sustainable apparel production.
Cost and Availability in the Market
Hemp fiber generally costs more than bamboo fiber due to its longer processing time and lower production scale, but it offers superior durability and breathability for clothing. Bamboo fiber is more widely available and affordable in the market, benefiting from faster-growing plants and established manufacturing processes in regions like China and Southeast Asia. Despite price differences, both fibers are eco-friendly alternatives, with hemp requiring less water and pesticides, influencing long-term sustainability costs.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Hemp and Bamboo Fiber
Hemp fiber offers exceptional durability, breathability, and natural resistance to UV rays and mold, making it ideal for long-lasting, eco-friendly clothing. Bamboo fiber excels in softness, moisture-wicking, and antibacterial properties, suited for comfortable, breathable garments. Selecting between hemp and bamboo fibers depends on prioritizing durability and sustainability versus softness and moisture management in clothing applications.
Infographic: Hemp fiber vs Bamboo fiber for Clothing
 azmater.com
azmater.com