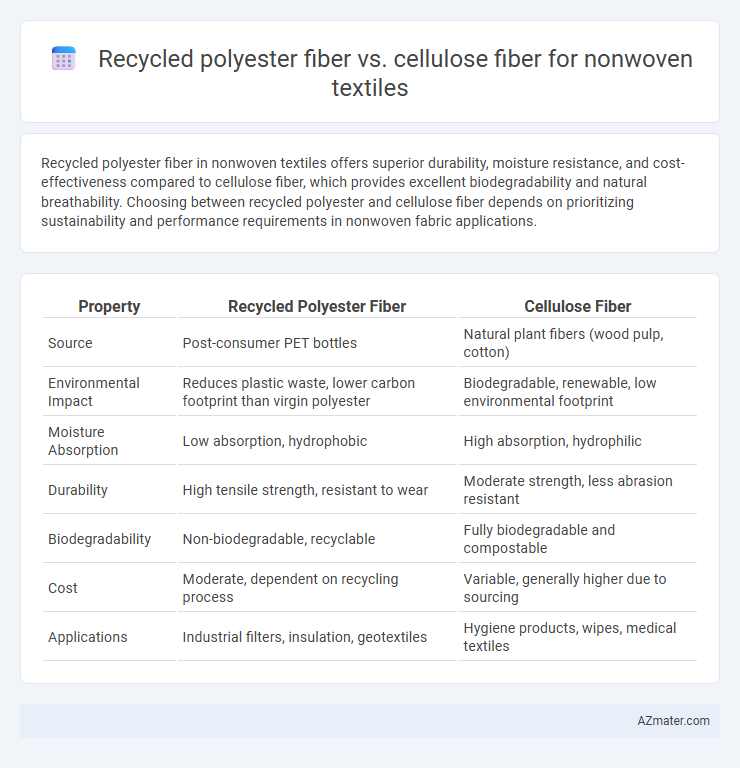
Recycled polyester fiber in nonwoven textiles offers superior durability, moisture resistance, and cost-effectiveness compared to cellulose fiber, which provides excellent biodegradability and natural breathability. Choosing between recycled polyester and cellulose fiber depends on prioritizing sustainability and performance requirements in nonwoven fabric applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Recycled Polyester Fiber | Cellulose Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Post-consumer PET bottles | Natural plant fibers (wood pulp, cotton) |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces plastic waste, lower carbon footprint than virgin polyester | Biodegradable, renewable, low environmental footprint |
| Moisture Absorption | Low absorption, hydrophobic | High absorption, hydrophilic |
| Durability | High tensile strength, resistant to wear | Moderate strength, less abrasion resistant |
| Biodegradability | Non-biodegradable, recyclable | Fully biodegradable and compostable |
| Cost | Moderate, dependent on recycling process | Variable, generally higher due to sourcing |
| Applications | Industrial filters, insulation, geotextiles | Hygiene products, wipes, medical textiles |
Introduction to Nonwoven Textile Fibers
Recycled polyester fiber and cellulose fiber are prominent materials in nonwoven textile production, each offering unique benefits in sustainability and performance. Recycled polyester fiber, derived from post-consumer plastic waste, provides high strength, durability, and moisture resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring long-lasting nonwoven fabrics. Cellulose fiber, sourced from natural plant-based materials like wood pulp, ensures excellent biodegradability, breathability, and softness, catering to environmentally conscious products such as hygiene and medical textiles.
Overview of Recycled Polyester Fiber
Recycled polyester fiber, derived from post-consumer plastic bottles or industrial polyester waste, offers sustainable advantages for nonwoven textiles by reducing landfill waste and conserving petroleum resources. This fiber exhibits excellent durability, moisture resistance, and dimensional stability, making it suitable for applications in filtration, geotextiles, and hygiene products. Compared to cellulose fiber, recycled polyester provides superior tensile strength and hydrophobic properties, enhancing the performance and longevity of nonwoven materials.
Understanding Cellulose Fiber
Cellulose fiber, derived from natural sources like wood pulp and cotton, offers biodegradability and breathability, making it a sustainable choice for nonwoven textiles. It provides excellent moisture absorption and comfort compared to synthetic alternatives such as recycled polyester fiber, which is derived from PET plastic and focuses on durability and water resistance. Understanding cellulose fiber's renewable origin and eco-friendly degradation highlights its increasing importance in environmentally conscious nonwoven textile applications.
Environmental Impact: Recycled Polyester vs Cellulose
Recycled polyester fiber significantly reduces reliance on virgin petroleum resources and lowers greenhouse gas emissions by repurposing plastic waste into textile applications, contributing to waste diversion from landfills and oceans. Cellulose fibers, derived from renewable plant sources like wood pulp, offer biodegradability and a lower carbon footprint but require intensive water and chemical use during harvesting and processing, impacting overall environmental sustainability. The choice between recycled polyester and cellulose fibers for nonwoven textiles hinges on balancing pollutant emissions, resource consumption, and end-of-life biodegradability to optimize ecological outcomes.
Performance and Durability Comparison
Recycled polyester fiber demonstrates superior tensile strength and abrasion resistance compared to cellulose fiber in nonwoven textiles, resulting in enhanced durability under mechanical stress. Cellulose fiber offers better moisture absorption and biodegradability but tends to degrade faster when exposed to UV light and repeated washing cycles. Overall, recycled polyester fibers provide longer-lasting performance in industrial and technical applications, while cellulose fibers are preferable for eco-friendly, low-durability products.
Cost Analysis and Market Trends
Recycled polyester fiber in nonwoven textiles offers cost advantages due to lower raw material expenses and energy-efficient production compared to cellulose fiber, which requires more intensive processing of natural sources like wood pulp. Market trends show increasing demand for recycled polyester driven by sustainability initiatives and corporate commitments to circular economy practices, while cellulose fiber maintains steady growth fueled by biodegradable and eco-friendly product preferences. Price volatility in cellulose fiber is influenced by raw material availability and environmental regulations, whereas recycled polyester benefits from scalability and integration within established PET recycling infrastructures.
Sustainability Considerations
Recycled polyester fiber for nonwoven textiles reduces reliance on virgin petroleum resources and diverts plastic waste from landfills, contributing to a lower carbon footprint and energy consumption compared to virgin polyester. Cellulose fibers, derived from renewable plant sources, offer biodegradability and lower environmental impact during degradation but may involve intensive water and chemical use in cultivation and processing. Evaluating sustainability involves balancing the circular economy benefits of recycled polyester with the renewable, compostable nature of cellulose fibers and their respective production footprints.
Applications in Nonwoven Industries
Recycled polyester fiber offers high durability, moisture resistance, and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for nonwoven applications in geotextiles, automotive interiors, and filtration media. Cellulose fiber excels in biodegradability, softness, and breathability, which suits it for hygiene products, medical nonwovens, and wipes. The choice between recycled polyester and cellulose fibers in the nonwoven industry depends on performance requirements, environmental impact goals, and end-use applications.
Challenges in Processing and Manufacturing
Recycled polyester fiber poses challenges in nonwoven textile manufacturing due to variability in fiber quality and potential contamination, affecting fiber bonding and fabric strength. Cellulose fibers often face difficulties related to moisture content control and fiber flammability, which can complicate thermal bonding and require specialized processing equipment. Both fiber types demand precise control over fiber orientation and bonding methods to ensure consistent fabric performance and durability in nonwoven applications.
Future Outlook and Innovations
Recycled polyester fiber in nonwoven textiles is rapidly advancing with innovations in chemical recycling and biodegradable additives, promoting sustainability and reducing landfill waste. Cellulose fiber, derived from renewable sources like wood pulp, is gaining traction due to its biodegradability and enhanced filtration properties when engineered at the micro or nano-scale. Future outlooks emphasize hybrid nonwovens combining recycled polyester's durability with cellulose fiber's eco-friendliness to meet stringent environmental regulations and performance demands in medical and hygiene applications.
Infographic: Recycled polyester fiber vs Cellulose fiber for Nonwoven textile
 azmater.com
azmater.com