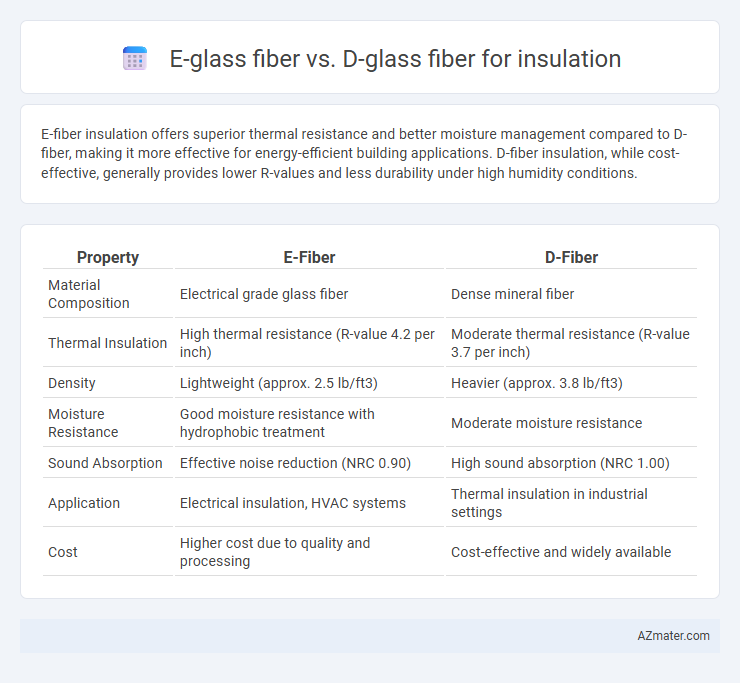
E-fiber insulation offers superior thermal resistance and better moisture management compared to D-fiber, making it more effective for energy-efficient building applications. D-fiber insulation, while cost-effective, generally provides lower R-values and less durability under high humidity conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | E-Fiber | D-Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Electrical grade glass fiber | Dense mineral fiber |
| Thermal Insulation | High thermal resistance (R-value 4.2 per inch) | Moderate thermal resistance (R-value 3.7 per inch) |
| Density | Lightweight (approx. 2.5 lb/ft3) | Heavier (approx. 3.8 lb/ft3) |
| Moisture Resistance | Good moisture resistance with hydrophobic treatment | Moderate moisture resistance |
| Sound Absorption | Effective noise reduction (NRC 0.90) | High sound absorption (NRC 1.00) |
| Application | Electrical insulation, HVAC systems | Thermal insulation in industrial settings |
| Cost | Higher cost due to quality and processing | Cost-effective and widely available |
Introduction to Fiberglass Insulation Types
E-fiber and D-fiber represent two primary types of fiberglass insulation fibers used in construction, with E-fiber characterized by its fine diameter and superior thermal resistance, making it ideal for high-performance insulation applications. D-fiber, featuring thicker strands, offers greater durability and soundproofing capabilities but with slightly reduced insulating efficiency compared to E-fiber. Selection between E-fiber and D-fiber impacts the overall R-value, moisture resistance, and acoustic properties of fiberglass insulation, crucial factors in optimizing building energy efficiency and comfort.
What is E-Fiber?
E-fiber, also known as electrical fiber glass, is a type of glass fiber specifically designed for insulation in electrical applications due to its excellent dielectric properties and high tensile strength. It is composed mainly of silica and alumina, providing superior resistance to heat and corrosion compared to D-fiber, which is primarily used for mechanical reinforcement. E-fiber's fine filament diameter and uniform composition make it ideal for producing insulating materials in transformers, motors, and other electrical devices.
What is D-Fiber?
D-fiber is a type of synthetic fiber characterized by its strong tensile strength and excellent resistance to moisture and chemicals, making it ideal for insulation applications where durability and performance are critical. Unlike E-fiber, typically known as E-glass fiber with high electrical resistivity and thermal stability, D-fiber offers enhanced mechanical robustness and flexibility. These properties enable D-fiber to provide superior protection against heat, impact, and environmental degradation in insulation materials.
Composition and Manufacturing Differences
E-fiber insulation primarily consists of alumina and silica, offering superior electrical resistance and thermal stability due to its low iron content, while D-fiber contains higher levels of iron oxides, impacting its dielectric properties. Manufacturing E-fiber involves precise control of melting and fiberizing processes to reduce impurities and iron content, enhancing its insulation performance, whereas D-fiber production is less stringent, resulting in coarser fibers with reduced electrical characteristics. These compositional and manufacturing distinctions make E-fiber ideal for high-performance electrical insulation applications, whereas D-fiber is suited for general-purpose thermal insulation.
Thermal Insulation Performance: E-Fiber vs D-Fiber
E-fiber insulation exhibits superior thermal insulation performance compared to D-fiber due to its lower thermal conductivity, typically around 0.03 W/m*K versus 0.04 W/m*K for D-fiber. The fine diameter and higher density of E-fiber create more effective air pockets, reducing heat transfer and enhancing energy efficiency in applications such as building insulation and HVAC systems. E-fiber's improved thermal resistance translates to better temperature regulation and reduced energy consumption in industrial and residential settings.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
E-fiber glass insulation exhibits superior mechanical strength and durability compared to D-fiber due to its higher tensile strength and better resistance to environmental degradation. The enhanced structural integrity of E-fiber results from its alumino-borosilicate composition, which retains stability under thermal and mechanical stress. D-fiber, composed mainly of high-silica content, offers good chemical resistance but falls short in toughness and long-term durability for demanding insulation applications.
Moisture and Chemical Resistance
E-fiber insulation offers superior moisture resistance due to its low water absorption properties, making it ideal for environments exposed to humidity or water. D-fiber insulation, while cost-effective, tends to absorb more moisture, which can compromise its thermal performance and durability over time. Chemically, E-fiber exhibits enhanced resistance to acids and alkalis, whereas D-fiber is more susceptible to degradation when exposed to harsh chemical environments.
Cost and Availability
E-fiber insulation, made from recycled polyethylene terephthalate (PET), offers a cost-effective solution due to the abundance of recycled materials, making it widely available in the market. D-fiber insulation, derived from natural cellulose fibers, often comes at a higher price point because of processing costs and limited supply, affecting its availability in some regions. Choosing between E-fiber and D-fiber insulation depends on project budget constraints and local material accessibility.
Common Applications of E-Fiber and D-Fiber Insulation
E-fiber insulation is commonly used in electrical equipment such as transformers and motors due to its high dielectric strength and thermal stability, ensuring efficient electrical performance. D-fiber insulation is frequently applied in automotive and construction industries where enhanced mechanical durability and flame resistance are critical for safety and longevity. Both fibers offer specialized properties tailored to distinct insulation needs, with E-fiber prioritizing electrical insulation and D-fiber emphasizing robustness and fire resistance.
Choosing the Right Fiber for Your Insulation Needs
E-fiber, or E-glass fiber, offers superior electrical insulation and high tensile strength, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and moisture resistance. D-fiber, also known as dielectric fiber, excels in thermal insulation with excellent dielectric properties, suited for environments where heat resistance is critical. Selecting the right fiber depends on specific insulation demands such as electrical performance, thermal stability, and environmental exposure.
Infographic: E-fiber vs D-fiber for Insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com