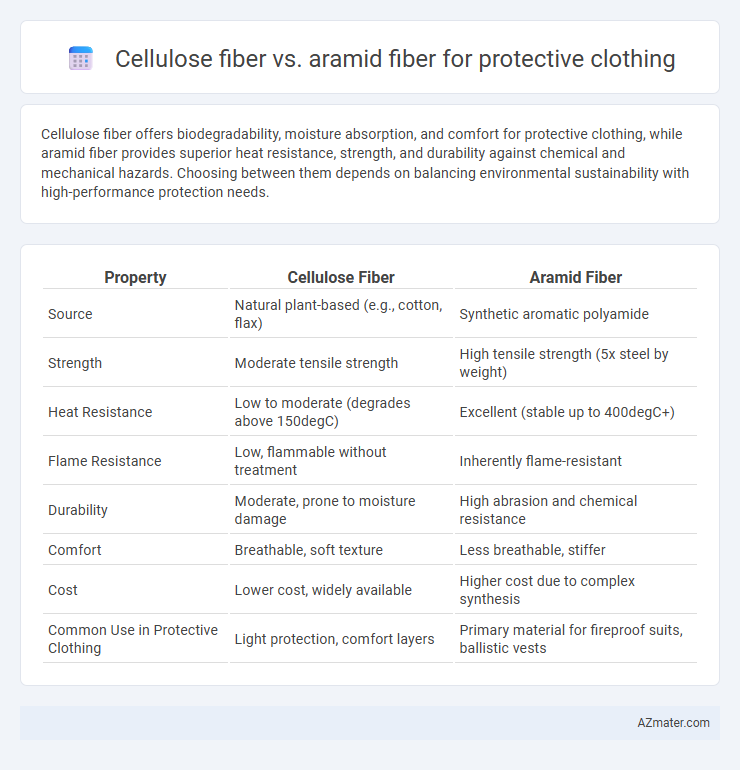
Cellulose fiber offers biodegradability, moisture absorption, and comfort for protective clothing, while aramid fiber provides superior heat resistance, strength, and durability against chemical and mechanical hazards. Choosing between them depends on balancing environmental sustainability with high-performance protection needs.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Cellulose Fiber | Aramid Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural plant-based (e.g., cotton, flax) | Synthetic aromatic polyamide |
| Strength | Moderate tensile strength | High tensile strength (5x steel by weight) |
| Heat Resistance | Low to moderate (degrades above 150degC) | Excellent (stable up to 400degC+) |
| Flame Resistance | Low, flammable without treatment | Inherently flame-resistant |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to moisture damage | High abrasion and chemical resistance |
| Comfort | Breathable, soft texture | Less breathable, stiffer |
| Cost | Lower cost, widely available | Higher cost due to complex synthesis |
| Common Use in Protective Clothing | Light protection, comfort layers | Primary material for fireproof suits, ballistic vests |
Introduction to Cellulose and Aramid Fibers
Cellulose fibers, derived from natural sources like cotton and flax, offer biodegradability and comfort, making them valuable for protective clothing applications focused on breathability and sustainability. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar and Nomex, are synthetic polymers known for exceptional heat resistance, high tensile strength, and chemical stability, providing superior protection against flames and mechanical hazards. The distinct molecular structures--cellulose's polysaccharide chains versus aramid's aromatic polyamide polymers--define their performance characteristics and suitability across various protective clothing needs.
Material Composition and Structure
Cellulose fiber, derived from natural polymers like cotton and viscose, consists primarily of glucose units forming linear polysaccharide chains with hydrogen bonding that provides moderate tensile strength and moisture absorbency. Aramid fiber, a synthetic polyamide characterized by aromatic rings linked by amide bonds, possesses a rigid rod-like molecular structure that delivers exceptional tensile strength, thermal stability, and resistance to abrasion and chemicals. The inherent molecular arrangement and chemical composition of aramid fibers result in superior durability and protective performance compared to cellulose fibers, which are more breathable but less resistant to heat and mechanical stress.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Cellulose fiber exhibits moderate tensile strength and excellent moisture absorption, enhancing comfort but limiting durability in protective clothing applications. Aramid fiber outperforms cellulose with superior tensile strength, high abrasion resistance, and exceptional thermal stability, making it ideal for impact and heat protection. The combination of these fibers can optimize mechanical performance by balancing strength, flexibility, and moisture management in protective garments.
Thermal and Flame Resistance
Cellulose fibers offer moderate thermal insulation but have limited flame resistance, as they tend to ignite and burn quickly under high heat. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, provide superior thermal stability and flame resistance, maintaining structural integrity and protecting against heat exposure. The high char yield and low flammability of aramid fibers make them ideal for protective clothing in high-temperature and fire-prone environments.
Comfort and Breathability
Cellulose fibers in protective clothing offer superior moisture absorption and natural breathability, enhancing wearer comfort during prolonged use. Aramid fibers provide exceptional strength and heat resistance but tend to be less breathable and can retain heat, potentially reducing comfort. Combining cellulose with aramid fibers in fabric blends can optimize protective performance while maintaining effective moisture management and thermal comfort.
Chemical Resistance and Durability
Aramid fiber exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to cellulose fiber, effectively withstanding exposure to acids, alkalis, and solvents, making it ideal for harsh chemical environments in protective clothing. Durability of aramid fiber surpasses cellulose fiber due to its high tensile strength, thermal stability, and resistance to abrasion, ensuring long-lasting protective performance under strenuous conditions. Cellulose fiber, while biodegradable and comfortable, lacks the chemical and wear resistance necessary for prolonged protection against hazardous substances.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Cellulose fiber, derived from renewable plant sources like cotton and hemp, offers biodegradability and a lower carbon footprint compared to synthetic fibers, making it a more sustainable option for protective clothing. Aramid fiber, known for high strength and heat resistance, is petroleum-based and non-biodegradable, contributing to greater environmental impact through resource-intensive production and long-term waste persistence. Choosing cellulose fiber enhances environmental sustainability by reducing reliance on fossil fuels and supporting circular economy principles in protective textile manufacturing.
Cost-Effectiveness and Availability
Cellulose fiber offers cost-effective and readily available material for protective clothing, making it suitable for applications requiring affordability and basic protection. Aramid fiber, while significantly more expensive, provides superior strength, heat resistance, and durability, essential for high-risk environments. The choice between cellulose and aramid fibers depends on balancing budget constraints with performance requirements in safety gear manufacturing.
Applications in Protective Clothing
Cellulose fiber offers excellent moisture absorption and comfort, making it ideal for protective clothing in hot and humid environments such as firefighting and industrial workwear. Aramid fiber provides exceptional heat resistance, high tensile strength, and durability, widely used in ballistic vests, firefighting suits, and military uniforms for superior protection against flames and ballistic threats. Protective clothing often combines cellulose and aramid fibers to balance comfort, thermal protection, and mechanical strength for enhanced wearer safety.
Choosing the Right Fiber for Safety Apparel
Cellulose fiber offers natural breathability and moisture-wicking properties, making it ideal for comfort in protective clothing, while aramid fiber provides exceptional heat resistance and high tensile strength essential for flame-resistant apparel. Selecting the right fiber depends on the work environment: cellulose fibers suit tasks requiring comfort and moderate protection, whereas aramid fibers excel in environments with high heat, flames, or potential mechanical hazards. Balancing durability, thermal protection, and wearer comfort is crucial when choosing fibers for safety apparel.
Infographic: Cellulose fiber vs Aramid fiber for Protective clothing
 azmater.com
azmater.com