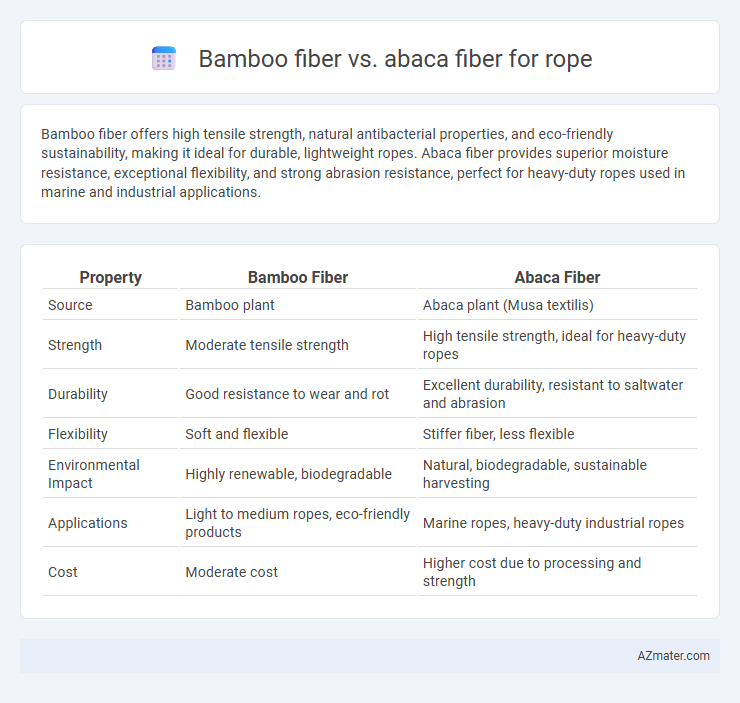
Bamboo fiber offers high tensile strength, natural antibacterial properties, and eco-friendly sustainability, making it ideal for durable, lightweight ropes. Abaca fiber provides superior moisture resistance, exceptional flexibility, and strong abrasion resistance, perfect for heavy-duty ropes used in marine and industrial applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bamboo Fiber | Abaca Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Bamboo plant | Abaca plant (Musa textilis) |
| Strength | Moderate tensile strength | High tensile strength, ideal for heavy-duty ropes |
| Durability | Good resistance to wear and rot | Excellent durability, resistant to saltwater and abrasion |
| Flexibility | Soft and flexible | Stiffer fiber, less flexible |
| Environmental Impact | Highly renewable, biodegradable | Natural, biodegradable, sustainable harvesting |
| Applications | Light to medium ropes, eco-friendly products | Marine ropes, heavy-duty industrial ropes |
| Cost | Moderate cost | Higher cost due to processing and strength |
Introduction to Bamboo and Abaca Fibers
Bamboo fiber, derived from bamboo plants, is known for its strength, flexibility, and eco-friendly properties, making it an innovative material in rope manufacturing. Abaca fiber, extracted from the leaf stalks of the abaca plant native to the Philippines, is prized for its exceptional tensile strength, resistance to saltwater, and durability, especially in marine ropes. Both fibers offer sustainable alternatives to traditional materials, with bamboo providing softness and biodegradability, while abaca excels in toughness and longevity under harsh conditions.
Botanical Origins and Cultivation
Bamboo fiber derived from the fast-growing subfamily Bambusoideae thrives in tropical and subtropical climates, offering sustainable cultivation due to its rapid renewable nature and minimal pesticide requirements. Abaca fiber, sourced from Musa textilis, a banana relative native to the Philippines, requires well-drained soil and humid conditions for optimal growth and is harvested primarily for its strong, lustrous fibers ideal for rope making. Both fibers possess distinct botanical origins influencing their cultivation practices and fiber qualities, with bamboo emphasizing rapid biomass production and abaca focusing on fiber strength and durability.
Physical and Mechanical Properties Comparison
Bamboo fiber exhibits high tensile strength and excellent flexibility, making it ideal for durable ropes that require resistance to wear and tear. Abaca fiber offers superior moisture resistance and greater abrasion resistance, which enhances rope longevity in wet or marine environments. Both fibers provide strong mechanical performance, but bamboo fiber is generally lighter and more elastic, while abaca fiber ensures enhanced durability under humid conditions.
Eco-Friendliness and Sustainability
Bamboo fiber and Abaca fiber both offer eco-friendly options for rope production, but Bamboo fiber is highly renewable due to its rapid growth rate, enabling multiple harvests annually without replanting. Abaca fiber, derived from the leaf stalks of the Musa textilis plant, is biodegradable and sourced from sustainable plantations, especially in the Philippines, where it supports biodiversity and local economies. Both fibers contribute to reducing reliance on synthetic ropes, but Bamboo's lower water and pesticide requirements make it a more sustainable choice in large-scale manufacturing.
Rope-Making Processes: Bamboo vs Abaca
Bamboo fiber for rope-making involves mechanical extraction through crushing and retting, producing finer, flexible fibers ideal for lightweight ropes but requiring intensive processing to enhance strength. Abaca fiber, derived from the leaf stalks of the Musa textilis plant, undergoes traditional stripping and drying methods, yielding coarse, highly durable fibers valued for heavy-duty ropes and marine applications. The rope-making process for abaca is more straightforward and less resource-intensive, offering superior tensile strength and resistance to saltwater compared to the more delicate, eco-friendly bamboo fiber ropes.
Strength and Durability of Fiber Ropes
Abaca fiber, derived from the Musa textilis plant, exhibits superior tensile strength and abrasion resistance compared to bamboo fiber, making it ideal for heavy-duty rope applications. Bamboo fiber, while eco-friendly and flexible, tends to be less durable and more susceptible to moisture-related degradation than abaca. The enhanced strength and longevity of abaca fiber ropes result from their natural lignin and cellulose composition, providing increased resistance to wear and environmental factors.
Resistance to Moisture, Rot, and UV Exposure
Bamboo fiber exhibits excellent resistance to moisture and UV exposure, making it suitable for outdoor rope applications where durability under sun and rain is essential. Abaca fiber offers superior resistance to rot due to its natural lignin content, which protects the rope from fungal decay and prolonged damp conditions. While both fibers withstand environmental stress well, abaca's enhanced rot resistance provides an advantage in consistently wet or marine environments.
Applications in Various Industries
Bamboo fiber offers superior flexibility and moisture resistance, making it ideal for eco-friendly textile ropes in fashion and home decor industries. Abaca fiber is known for its exceptional strength and durability, widely used in marine, construction, and industrial sectors for heavy-duty ropes and cordage. Both fibers provide sustainable alternatives, with bamboo favored in lightweight applications and abaca preferred where tensile strength and abrasion resistance are critical.
Cost and Market Availability
Bamboo fiber offers a cost-effective alternative for rope production due to its rapid growth and abundant availability in Asia, leading to lower raw material expenses compared to abaca fiber. Abaca fiber, derived from the banana plant native to the Philippines, commands a higher market price because of its superior strength, durability, and limited supply constrained by geographic and climatic factors. Market availability of bamboo fiber is more widespread and scalable, while abaca remains a niche fiber primarily used in specialty ropes requiring exceptional tensile strength.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Fiber for Rope
Bamboo fiber offers superior flexibility and resistance to mildew, making it ideal for ropes used in wet or humid environments, while Abaca fiber provides exceptional strength and abrasion resistance suited for heavy-duty applications requiring durability. Selecting the right fiber depends on the rope's intended use: Bamboo fibers excel in lightweight, eco-friendly ropes, whereas Abaca fibers are preferred for high-tensile, industrial-grade ropes. Evaluating factors like environmental conditions, load requirements, and sustainability goals ensures optimal performance and lifespan for rope products.
Infographic: Bamboo fiber vs Abaca fiber for Rope
 azmater.com
azmater.com