Bamboo fiber offers superior moisture-wicking and antibacterial properties, making it ideal for breathable textiles. Nettle fiber provides exceptional durability and environmental sustainability, suitable for producing strong, eco-friendly fabrics.
Table of Comparison
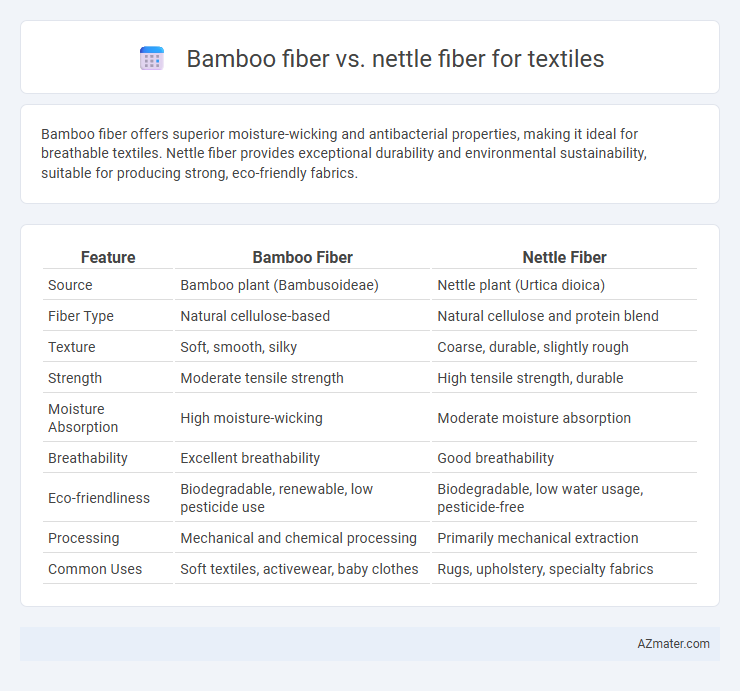
| Feature | Bamboo Fiber | Nettle Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Bamboo plant (Bambusoideae) | Nettle plant (Urtica dioica) |
| Fiber Type | Natural cellulose-based | Natural cellulose and protein blend |
| Texture | Soft, smooth, silky | Coarse, durable, slightly rough |
| Strength | Moderate tensile strength | High tensile strength, durable |
| Moisture Absorption | High moisture-wicking | Moderate moisture absorption |
| Breathability | Excellent breathability | Good breathability |
| Eco-friendliness | Biodegradable, renewable, low pesticide use | Biodegradable, low water usage, pesticide-free |
| Processing | Mechanical and chemical processing | Primarily mechanical extraction |
| Common Uses | Soft textiles, activewear, baby clothes | Rugs, upholstery, specialty fabrics |
Overview of Bamboo and Nettle Fibers
Bamboo fiber is derived from the pulp of bamboo plants and is valued for its softness, durability, and natural antibacterial properties, making it ideal for textile applications such as clothing and home textiles. Nettle fiber, extracted from the stalks of the stinging nettle plant, offers high tensile strength, breathability, and eco-friendly attributes, often used in sustainable fashion and upholstery. Both fibers are biodegradable and renewable, but bamboo fiber stands out for its smoother texture, while nettle fiber is recognized for its robust and coarse characteristics.
Historical Uses in Textiles
Bamboo fiber has been historically valued in East Asian textiles for its antimicrobial properties and softness, often used in traditional clothing and household fabrics. Nettle fiber, dating back to ancient Europe, was prized for its durability and strength, frequently woven into coarse fabrics for everyday wear and utilitarian textiles. Both fibers played significant roles in sustainable fabric production, with bamboo favored for luxury garments and nettle utilized in rugged, long-lasting textile applications.
Fiber Extraction Methods
Bamboo fiber extraction primarily involves mechanical processing or chemical treatments such as the viscose method, where bamboo pulp is chemically dissolved and regenerated into fibers suitable for textiles. Nettle fiber extraction relies on retting, a natural biodegradation process that separates fibers from stalks, followed by mechanical decortication to produce coarse but strong textile fibers. The chemical processing of bamboo allows for smoother, softer fibers ideal for fine garments, while nettle's retting method yields durable fibers favored for eco-friendly, rustic textiles.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Bamboo fiber is praised for its rapid growth and minimal need for pesticides, making it a highly renewable resource, but its conventional processing often involves chemical-intensive methods that can harm the environment. Nettle fiber, derived from stinging nettle plants, requires less water and fewer chemicals during cultivation and processing, resulting in a lower environmental footprint and enhanced biodegradability. Both fibers offer sustainable textile alternatives compared to conventional cotton, with nettle fiber emerging as a more eco-friendly option due to its minimal resource demands and natural cultivation process.
Physical Properties Comparison
Bamboo fiber exhibits superior moisture-wicking capabilities and natural antibacterial properties, making it highly breathable and ideal for activewear textiles. Nettle fiber offers greater tensile strength and abrasion resistance, contributing to enhanced durability and longevity in fabric applications. Both fibers demonstrate eco-friendly attributes, but bamboo's softness contrasts with nettle's coarser texture, influencing their suitability for different textile products.
Softness and Comfort
Bamboo fiber excels in softness and moisture-wicking properties, making it ideal for comfortable, breathable textiles suitable for sensitive skin. Nettle fiber, while slightly coarser, offers durability and natural antibacterial qualities, which enhance comfort for long-term wear despite a firmer texture. Both fibers provide sustainable alternatives, with bamboo favored for softness and nettle for robust comfort in eco-friendly fabrics.
Durability and Longevity
Bamboo fiber offers exceptional durability due to its natural antimicrobial properties and high tensile strength, making it resistant to wear and tear over time. Nettle fiber, known for its strong cellulose content, provides excellent durability that rivals hemp and linen, ensuring long-lasting textile quality. Both fibers excel in longevity, but nettle fiber often surpasses bamboo in maintaining fabric integrity through repeated use and washing cycles.
Breathability and Moisture Management
Bamboo fiber exhibits superior breathability due to its naturally porous structure, allowing enhanced air circulation and moisture evaporation, which helps keep the wearer cool and dry. Nettle fiber also offers excellent moisture management properties, efficiently wicking sweat away from the skin, but tends to be denser than bamboo, resulting in slightly less airflow. Both fibers provide sustainable options for textiles, with bamboo excelling in lightweight breathability and nettle delivering robust moisture absorption and durability.
Dyeing and Color Retention
Bamboo fiber exhibits excellent dye absorption due to its porous structure, resulting in vibrant and long-lasting colors in textile applications. Nettle fiber, known for its natural gloss and strength, offers moderate dye affinity but retains colors well when treated with mordants, enhancing fabric durability. Both fibers perform effectively in dyeing processes, with bamboo excelling in initial color vibrancy and nettle providing superior colorfastness over time.
Market Trends and Consumer Preferences
Bamboo fiber is experiencing significant growth in the textile market due to its sustainable production, softness, and antimicrobial properties, appealing to eco-conscious consumers seeking comfort and hygiene. Nettle fiber, valued for its durability and natural thermal regulation, is gaining traction among consumers prioritizing eco-friendly, long-lasting fabrics with a lower environmental footprint. Market trends indicate increasing demand for both fibers in sustainable fashion, with bamboo dominating in softness and mass-market appeal, while nettle captures niche segments focused on heritage and durability.
Infographic: Bamboo fiber vs Nettle fiber for Textile
 azmater.com
azmater.com