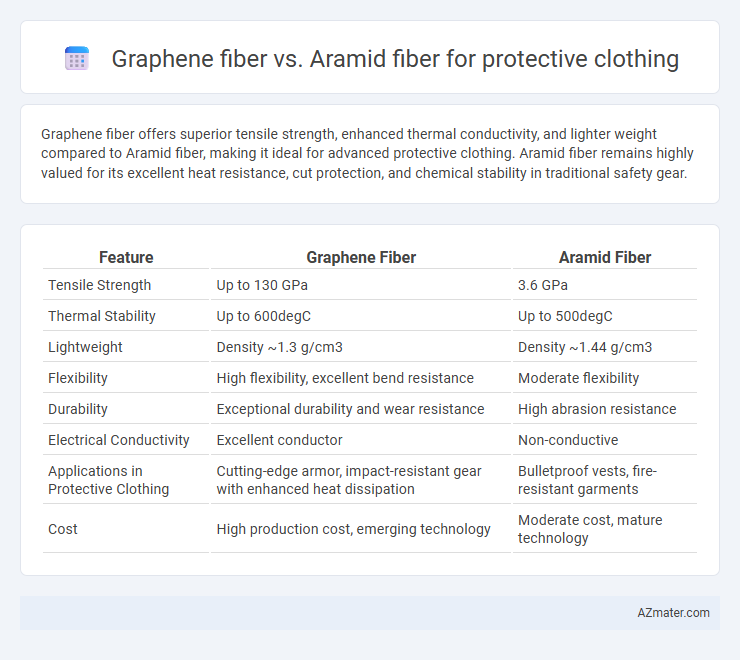
Graphene fiber offers superior tensile strength, enhanced thermal conductivity, and lighter weight compared to Aramid fiber, making it ideal for advanced protective clothing. Aramid fiber remains highly valued for its excellent heat resistance, cut protection, and chemical stability in traditional safety gear.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Graphene Fiber | Aramid Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | Up to 130 GPa | 3.6 GPa |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 600degC | Up to 500degC |
| Lightweight | Density ~1.3 g/cm3 | Density ~1.44 g/cm3 |
| Flexibility | High flexibility, excellent bend resistance | Moderate flexibility |
| Durability | Exceptional durability and wear resistance | High abrasion resistance |
| Electrical Conductivity | Excellent conductor | Non-conductive |
| Applications in Protective Clothing | Cutting-edge armor, impact-resistant gear with enhanced heat dissipation | Bulletproof vests, fire-resistant garments |
| Cost | High production cost, emerging technology | Moderate cost, mature technology |
Introduction to Advanced Protective Fibers
Graphene fiber offers exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and superior thermal conductivity compared to traditional aramid fibers, enhancing the durability and comfort of protective clothing. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, provide high tensile strength and excellent resistance to abrasion and heat, making them a reliable choice for ballistic and flame-resistant gear. Advanced protective fibers integrate the mechanical resilience of aramid with the innovative properties of graphene to optimize performance in extreme environments.
Understanding Graphene Fiber Properties
Graphene fiber exhibits exceptional tensile strength, thermal conductivity, and flexibility, making it highly suitable for protective clothing applications. Its unique atomic lattice structure enables superior resistance to cuts and abrasions while maintaining lightweight comfort compared to traditional Aramid fibers. Enhanced electrical conductivity and breathability further distinguish graphene fiber, providing advanced protection and improved wearer comfort in high-performance protective garments.
Key Features of Aramid Fiber
Aramid fiber, known for exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and high thermal resistance, is widely used in protective clothing to provide durable, flame-retardant, and impact-resistant properties. It offers superior cut and abrasion resistance compared to many synthetics, maintaining structural integrity under extreme conditions. Unlike graphene fiber, aramid fibers such as Kevlar and Twaron are well-established in ballistic protection and heat shielding, making them crucial for occupational safety applications.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Graphene fiber exhibits superior tensile strength, often surpassing Aramid fibers like Kevlar with a tensile strength reaching up to 130 GPa compared to Aramid's 3.6 GPa. Its exceptional durability stems from graphene's atomic structure, offering remarkable resistance to wear, chemical degradation, and UV exposure, which enhances the longevity of protective clothing. Aramid fibers remain widely used for impact resistance and heat tolerance, but graphene fiber's combination of extreme strength and durability positions it as a transformative material for next-generation protective gear.
Weight and Flexibility Analysis
Graphene fiber exhibits superior lightweight characteristics compared to aramid fiber, making it ideal for protective clothing that demands minimal weight without sacrificing durability. Its exceptional flexibility surpasses that of aramid fibers, allowing for enhanced wearer mobility and comfort during extended use. High tensile strength combined with low density enables graphene fiber to deliver protective performance with significantly reduced bulk, outperforming traditional aramid-based materials in weight and flexibility metrics.
Thermal and Chemical Resistance
Graphene fiber exhibits superior thermal conductivity and enhanced heat dissipation compared to aramid fiber, making it highly effective for protective clothing in extreme temperature environments. Its molecular structure provides exceptional chemical resistance, particularly against solvents and corrosive agents, surpassing traditional aramid fibers. Aramid fibers, while robust in impact resistance, tend to degrade under prolonged chemical exposure and high temperatures, limiting their protective capabilities in hazardous conditions.
Comfort and Wearability in Protective Clothing
Graphene fiber offers superior breathability and thermal regulation compared to aramid fiber, enhancing comfort during prolonged wear in protective clothing. Its lightweight and flexible nature reduces fatigue and improves overall wearability, making it ideal for dynamic environments. Aramid fiber, while durable and heat-resistant, tends to be stiffer and less breathable, which can limit comfort and mobility in extended use scenarios.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Graphene fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and enhanced thermal conductivity compared to aramid fiber, but its high production costs and complex manufacturing processes currently limit widespread adoption in protective clothing. Aramid fiber remains more cost-effective due to established large-scale manufacturing techniques and lower raw material expenses, making it the preferred choice for budget-sensitive applications. Manufacturers must weigh graphene's performance advantages against aramid's affordability and scalability when selecting materials for protective garments.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Graphene fiber outperforms aramid fiber in environmental impact due to its superior biodegradability and lower energy consumption during production, reducing ecological footprint in protective clothing manufacturing. Aramid fibers, while highly durable and resistant, rely on petrochemical processes that generate significant greenhouse gas emissions and are less recyclable, challenging sustainability efforts. Integrating graphene fiber into protective textiles offers a more sustainable solution by combining high-performance protection with eco-friendly lifecycle management.
Future Innovations in Protective Fiber Technology
Graphene fiber exhibits exceptional tensile strength, lightweight properties, and superior thermal conductivity compared to traditional Aramid fibers used in protective clothing, signaling a shift toward enhanced durability and comfort. Innovations in functionalizing graphene fibers with nanoscale coatings aim to improve impact resistance and electrical conductivity for smart protective gear. The integration of graphene into fiber composites promises next-generation protective textiles offering improved flexibility, heat dissipation, and multi-threat defense against ballistic and chemical hazards.
Infographic: Graphene fiber vs Aramid fiber for Protective clothing
 azmater.com
azmater.com