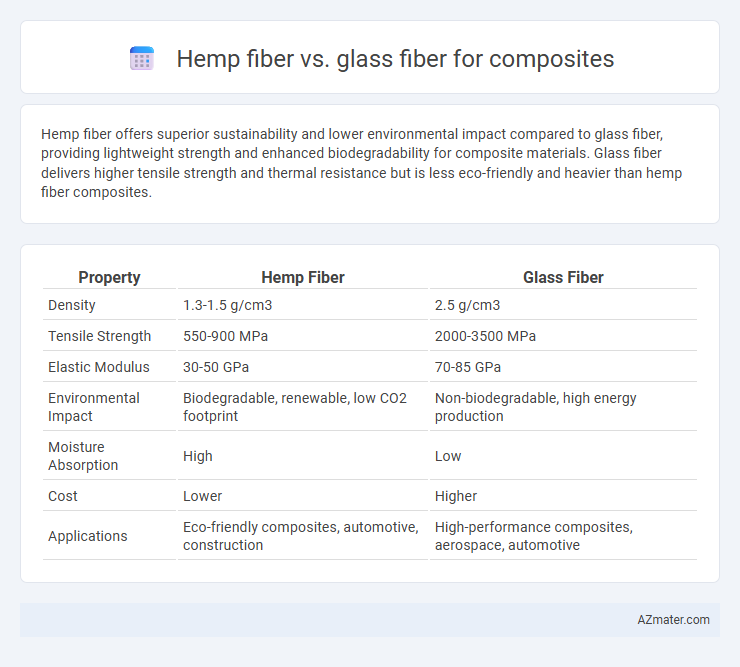
Hemp fiber offers superior sustainability and lower environmental impact compared to glass fiber, providing lightweight strength and enhanced biodegradability for composite materials. Glass fiber delivers higher tensile strength and thermal resistance but is less eco-friendly and heavier than hemp fiber composites.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hemp Fiber | Glass Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 1.3-1.5 g/cm3 | 2.5 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 550-900 MPa | 2000-3500 MPa |
| Elastic Modulus | 30-50 GPa | 70-85 GPa |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, renewable, low CO2 footprint | Non-biodegradable, high energy production |
| Moisture Absorption | High | Low |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Applications | Eco-friendly composites, automotive, construction | High-performance composites, aerospace, automotive |
Introduction to Composite Materials: Hemp Fiber vs Glass Fiber
Hemp fiber and glass fiber serve as key reinforcements in composite materials, each offering distinct mechanical and environmental benefits. Hemp fiber composites provide lightweight, biodegradable alternatives with high tensile strength and vibration damping, suitable for automotive and construction industries. Glass fiber composites deliver superior durability, thermal resistance, and structural integrity, making them ideal for aerospace, marine, and high-performance applications.
Material Properties: Comparing Hemp and Glass Fibers
Hemp fiber exhibits lower density and higher biodegradability compared to glass fiber, making it an eco-friendly alternative for composites. Glass fiber offers superior tensile strength, stiffness, and thermal resistance, which contributes to its widespread use in high-performance applications. Hemp fiber composites demonstrate improved impact resistance and vibration damping but generally have lower mechanical properties than glass fiber composites.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Hemp fiber offers significant environmental benefits over glass fiber in composite materials due to its biodegradability, renewable sourcing, and lower carbon footprint during cultivation and processing. Hemp cultivation requires less water and synthetic fertilizers while absorbing carbon dioxide, enhancing its sustainability compared to energy-intensive glass fiber production involving non-renewable resources and high greenhouse gas emissions. The end-of-life disposal of hemp fiber composites poses less ecological risk as they decompose naturally, unlike glass fiber composites that contribute to persistent waste and environmental pollution.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Hemp fiber composites exhibit lower tensile strength and stiffness compared to glass fiber composites, with hemp fibers typically offering tensile strengths around 500-900 MPa versus glass fibers exceeding 2000 MPa. Although hemp fibers provide improved impact resistance and energy absorption due to their natural fiber structure, their moisture absorption can reduce durability in humid environments, whereas glass fibers maintain higher durability and resistance to chemical and environmental degradation. The mechanical performance of hemp fiber composites is enhanced by chemical treatments and hybridization, yet glass fiber composites remain preferred for high-strength, long-lasting applications such as automotive and aerospace components.
Weight and Density Differences
Hemp fiber composites typically have a lower density of around 1.3-1.5 g/cm3 compared to glass fiber composites, which range between 2.4-2.6 g/cm3, making hemp fibers significantly lighter. The reduced weight contributes to enhanced fuel efficiency and ease of handling in automotive and aerospace applications. Weight savings with hemp fiber composites can reach up to 30-50% compared to traditional glass fiber alternatives, promoting sustainable material choices without compromising structural integrity.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Hemp fiber offers a cost-effective alternative to glass fiber in composites, with lower raw material and processing expenses due to its natural abundance and simpler extraction methods. Glass fiber remains widely available and standardized, benefiting from established supply chains and extensive industrial use, but often incurs higher costs related to energy-intensive production and health safety measures. Market availability of hemp fiber is expanding rapidly, driven by growing demand for sustainable materials, while glass fiber maintains dominance in high-performance applications with consistent quality and global accessibility.
Processing Techniques and Manufacturing
Hemp fiber composites require lower processing temperatures compared to glass fiber, making them compatible with bio-based resins and reducing energy consumption during manufacturing. Techniques like compression molding and resin transfer molding are commonly used for both fibers, but hemp fibers often demand careful pre-treatment, such as alkali treatment or enzymatic retting, to improve fiber-matrix adhesion and moisture resistance. Glass fiber composites benefit from well-established processing protocols and enable higher mechanical strength in final products, but their production involves higher environmental and health considerations due to fiber dust and energy-intensive curing cycles.
Applications in Industry: Hemp Fiber vs Glass Fiber
Hemp fiber offers sustainability and biodegradability, making it ideal for automotive interior panels and eco-friendly construction materials, while glass fiber provides superior strength and durability used extensively in aerospace, marine, and high-performance sports equipment. Industrial composites benefit from hemp fiber's lightweight nature and vibration damping, enhancing comfort and reducing emissions in vehicle manufacturing. Glass fiber's resistance to heat and chemicals ensures longevity in harsh environments, securing its role in heavy-duty applications requiring structural integrity.
Health and Safety Considerations
Hemp fiber in composites offers significant health and safety advantages due to its natural origin, reducing exposure to harmful chemicals and minimizing respiratory risks associated with synthetic fibers like glass fiber. Glass fiber can cause skin irritation, respiratory issues, and necessitates protective equipment during handling and processing, whereas hemp fiber is biodegradable and less abrasive, promoting safer working conditions. Selecting hemp fiber composites also enhances sustainability and reduces long-term environmental hazards linked to the disposal of synthetic materials.
Future Trends and Innovations in Composite Materials
Hemp fiber is emerging as a sustainable alternative to glass fiber in composite materials due to its biodegradability, lower carbon footprint, and comparable mechanical properties. Innovations in bio-based resin systems and hybrid composites enhance hemp fiber's compatibility and performance, driving its adoption in automotive and construction industries. Future trends emphasize eco-friendly composites with improved durability and recyclability, positioning hemp fiber as a key material in green manufacturing technologies.
Infographic: Hemp fiber vs Glass fiber for Composite
 azmater.com
azmater.com