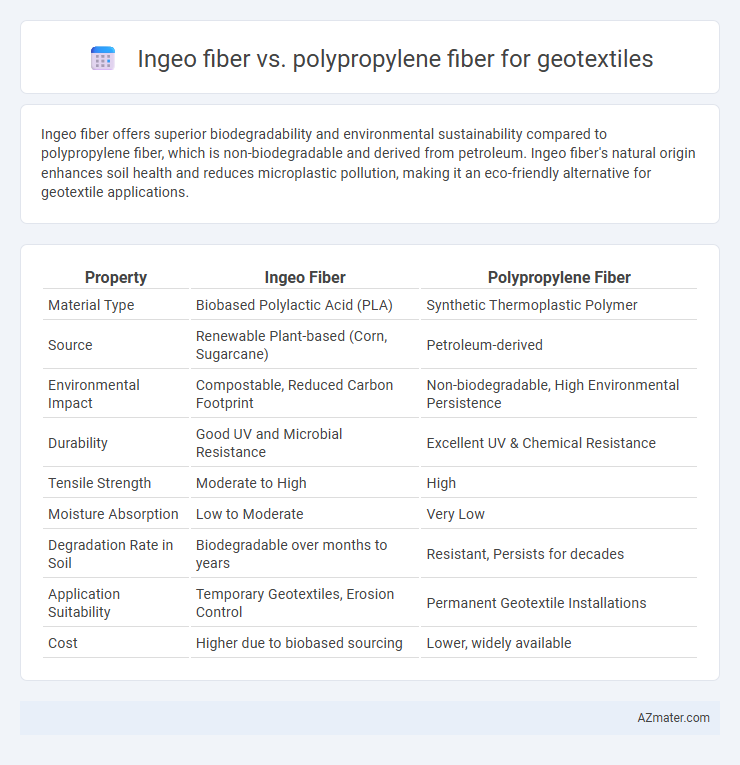
Ingeo fiber offers superior biodegradability and environmental sustainability compared to polypropylene fiber, which is non-biodegradable and derived from petroleum. Ingeo fiber's natural origin enhances soil health and reduces microplastic pollution, making it an eco-friendly alternative for geotextile applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ingeo Fiber | Polypropylene Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Biobased Polylactic Acid (PLA) | Synthetic Thermoplastic Polymer |
| Source | Renewable Plant-based (Corn, Sugarcane) | Petroleum-derived |
| Environmental Impact | Compostable, Reduced Carbon Footprint | Non-biodegradable, High Environmental Persistence |
| Durability | Good UV and Microbial Resistance | Excellent UV & Chemical Resistance |
| Tensile Strength | Moderate to High | High |
| Moisture Absorption | Low to Moderate | Very Low |
| Degradation Rate in Soil | Biodegradable over months to years | Resistant, Persists for decades |
| Application Suitability | Temporary Geotextiles, Erosion Control | Permanent Geotextile Installations |
| Cost | Higher due to biobased sourcing | Lower, widely available |
Introduction to Geotextiles and Fiber Types
Geotextiles are permeable fabrics used in civil engineering to enhance soil stability, erosion control, and drainage. Ingeo fiber, composed of polylactic acid derived from renewable resources, offers biodegradability and environmental sustainability, contrasting with polypropylene fiber, a synthetic polymer known for its durability, chemical resistance, and long lifespan. Selecting between Ingeo and polypropylene fibers depends on project requirements, balancing ecological impact with mechanical performance in geotextile applications.
Overview of Ingeo Fiber: Composition and Properties
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based resources such as corn, is a biodegradable and compostable biopolymer primarily composed of polylactic acid (PLA). It offers excellent tensile strength, UV resistance, and good moisture management, making it suitable for geotextile applications that demand environmental sustainability and durability. Unlike polypropylene fiber, which is petroleum-based and non-biodegradable, Ingeo fiber reduces carbon footprint and supports eco-friendly construction projects.
Overview of Polypropylene Fiber: Composition and Properties
Polypropylene fiber, a synthetic thermoplastic polymer derived from propylene monomers, exhibits excellent chemical resistance, low moisture absorption, and high tensile strength, making it ideal for geotextile applications. Its lightweight nature combined with UV resistance and durability ensures long-term performance in soil stabilization, erosion control, and drainage projects. The fiber's resistance to alkalis, acids, and biological degradation further enhances its suitability for diverse environmental conditions in geotechnical engineering.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Ingeo fiber exhibits superior tensile strength and elongation compared to polypropylene fiber, enhancing its durability in geotextile applications. The higher modulus of elasticity in Ingeo fibers provides better load distribution and resistance to deformation under mechanical stress. Polypropylene fibers, while cost-effective, typically show lower mechanical performance, impacting long-term structural stability in geotextile installations.
Durability and Environmental Resistance
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable polylactic acid (PLA), exhibits moderate durability and biodegradability, making it suitable for temporary geotextile applications with environmental resistance to UV and microbial degradation. Polypropylene fiber, a synthetic polymer, offers superior durability, high tensile strength, and exceptional resistance to chemicals, UV exposure, and moisture, ensuring long-term performance in geotextile installations. While Ingeo fibers promote sustainability with lower carbon footprint, polypropylene fibers dominate in applications requiring extended lifespan and robust environmental resistance.
Biodegradability and Sustainability Factors
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based sources, offers superior biodegradability compared to polypropylene fiber, which is petroleum-based and non-biodegradable. Ingeo's compostable properties reduce environmental impact by breaking down naturally, supporting sustainable geotextile applications. Polypropylene fibers, while durable and cost-effective, contribute to long-term plastic pollution due to their resistance to degradation.
Installation and Handling Differences
Ingeo fiber offers enhanced flexibility and lighter weight compared to polypropylene fiber, making installation in geotextile applications easier and faster with reduced labor effort. Polypropylene fibers are more rigid and prone to static buildup, requiring more careful handling to prevent damage or tangling during deployment. The biodegradable nature of Ingeo fiber also demands careful moisture control during installation to preserve fiber integrity, unlike the more chemically stable polypropylene fibers.
Cost Analysis: Ingeo vs Polypropylene
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based sources, generally incurs higher upfront production costs compared to polypropylene fiber, which is synthesized from petroleum-based materials and benefits from established manufacturing economies of scale. Polypropylene fiber remains the more cost-effective option for geotextile applications, offering lower raw material and processing expenses while maintaining adequate durability and performance. However, Ingeo fiber's biodegradability may reduce environmental remediation costs and align with sustainability-driven project budgets despite its higher initial price point.
Application Suitability in Geotextile Projects
Ingeo fiber offers enhanced biodegradability and environmental sustainability, making it suitable for temporary geotextile applications such as erosion control and landscaping where natural decomposition is beneficial. Polypropylene fiber provides superior chemical resistance and long-term durability, ideal for permanent structures like road stabilization, drainage systems, and soil reinforcement. Selection between Ingeo and polypropylene fibers depends on project lifespan requirements, environmental impact considerations, and exposure conditions in geotextile engineering.
Conclusion: Choosing the Optimal Fiber for Geotextiles
Ingeo fiber offers superior biodegradability and sustainability, making it an ideal choice for environmentally sensitive geotextile applications, while polypropylene fiber excels in cost-effectiveness and durability for high-strength, long-term projects. Selecting the optimal fiber depends on project requirements; Ingeo is preferable for temporary or eco-friendly installations, whereas polypropylene suits permanent infrastructure needing robust performance. Evaluating factors like environmental impact, mechanical properties, and lifecycle cost ensures the best match between fiber type and geotextile application.
Infographic: Ingeo fiber vs Polypropylene fiber for Geotextile
 azmater.com
azmater.com