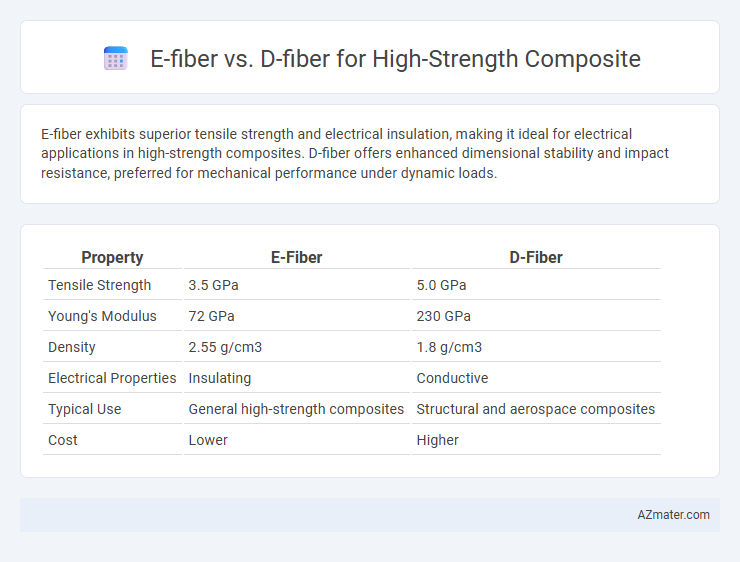
E-fiber exhibits superior tensile strength and electrical insulation, making it ideal for electrical applications in high-strength composites. D-fiber offers enhanced dimensional stability and impact resistance, preferred for mechanical performance under dynamic loads.
Table of Comparison
| Property | E-Fiber | D-Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 3.5 GPa | 5.0 GPa |
| Young's Modulus | 72 GPa | 230 GPa |
| Density | 2.55 g/cm3 | 1.8 g/cm3 |
| Electrical Properties | Insulating | Conductive |
| Typical Use | General high-strength composites | Structural and aerospace composites |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to High-Strength Composite Fibers
E-fiber and D-fiber are critical components in high-strength composite fibers, each offering unique mechanical properties essential for advanced material applications. E-fibers, primarily E-glass fibers, provide excellent tensile strength and electrical insulation, widely used in aerospace and automotive industries for their lightweight and high durability. D-fibers, or high-modulus carbon fibers, exhibit superior stiffness and fatigue resistance, making them ideal for applications requiring exceptional strength-to-weight ratios and structural integrity.
Understanding E-Fiber: Composition and Properties
E-fiber, primarily composed of alumino-borosilicate glass, exhibits high tensile strength and excellent electrical insulation properties, making it ideal for high-strength composite applications. Its low density combined with superior chemical resistance enhances composite durability under mechanical stress and harsh environmental conditions. Compared to D-fiber, E-fiber offers improved stiffness and impact resistance, critical for aerospace and automotive composite structures.
D-Fiber Overview: Key Characteristics
D-fiber, distinguished by its discontinuous and shorter filament structure, offers enhanced toughness and impact resistance compared to E-fiber in high-strength composites. It features a denser microstructure with superior thermal stability and chemical resistance, making it suitable for demanding applications. These key characteristics enable D-fiber to improve composite durability while maintaining significant strength-to-weight ratios.
Mechanical Performance Comparison: E-Fiber vs D-Fiber
E-fiber exhibits superior tensile strength and modulus compared to D-fiber, making it ideal for high-strength composite applications requiring enhanced load-bearing capacity. D-fiber offers improved impact resistance and fracture toughness, which contribute to better durability under dynamic loading conditions. Mechanical performance studies reveal that E-fiber composites deliver higher stiffness and strength-to-weight ratios, while D-fiber composites provide greater energy absorption and damage tolerance.
Durability and Environmental Resistance
E-fiber offers superior durability and environmental resistance compared to D-fiber, making it ideal for high-strength composite applications exposed to harsh conditions. E-fiber exhibits excellent resistance to moisture, UV radiation, and chemical degradation, which enhances the lifespan and structural integrity of composites. In contrast, D-fiber, while cost-effective, shows reduced performance in long-term environmental exposure, limiting its use in demanding durability-focused applications.
Cost Analysis: E-Fiber vs D-Fiber
E-fiber offers a lower cost alternative compared to D-fiber, making it attractive for budget-sensitive high-strength composite applications. The production process for E-fiber consumes less energy and raw material expenses are significantly reduced, contributing to overall cost efficiency. In contrast, D-fiber, while providing superior mechanical properties, incurs higher manufacturing and operational costs that impact the composite's final price.
Applications in High-Strength Composites
E-fiber, primarily composed of alumino-borosilicate glass, offers excellent electrical insulation and high tensile strength, making it ideal for aerospace and automotive high-strength composites where weight reduction and durability are critical. D-fiber, or dielectric fiber, provides superior dielectric properties and thermal resistance, often used in high-frequency electronics and military-grade composite materials requiring enhanced electromagnetic interference shielding. Both fibers contribute significantly to the performance and longevity of advanced composite structures in demanding industrial applications.
Manufacturing and Processing Differences
E-fiber and D-fiber differ significantly in their manufacturing and processing methods for high-strength composites; E-fibers are produced using a continuous melting process with alumino-borosilicate compositions that offer superior electrical insulation, while D-fibers are derived from more crystalline silicate materials, resulting in higher tensile strength and stiffness. The processing of E-fibers involves lower drawing temperatures and faster cooling rates, which yield finer diameters and enhanced flexibility, whereas D-fibers require higher temperatures and controlled crystallization during drawing to achieve optimal mechanical properties. These distinct manufacturing protocols directly impact the composite's performance, with E-fibers providing better impact resistance and electrical properties, and D-fibers contributing to increased load-bearing capacity and durability in structural applications.
Industry Trends: E-Fiber and D-Fiber Adoption
E-fiber and D-fiber are increasingly adopted in the high-strength composite industry due to their superior tensile properties and cost-effectiveness. E-fiber is favored for its high electrical insulating capabilities and strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for aerospace and automotive applications. D-fiber, with enhanced chemical resistance and durability, is gaining traction in industrial machinery and construction sectors seeking long-lasting composite materials.
Choosing the Right Fiber for Composite Engineering
E-fiber (E-glass fiber) offers excellent tensile strength and electrical insulation, making it ideal for high-strength composite applications requiring lightweight and corrosion resistance. D-fiber (D-glass fiber) provides superior chemical resistance and enhanced durability in harsh environments, beneficial for composites exposed to aggressive chemicals or high-moisture conditions. Selecting the right fiber depends on specific engineering requirements like mechanical performance, environmental exposure, and cost-effectiveness to optimize composite durability and strength.
Infographic: E-fiber vs D-fiber for High-Strength Composite
 azmater.com
azmater.com