Soy protein fiber offers superior moisture-wicking and softness compared to cotton, making it ideal for sustainable and comfortable apparel. Cotton requires more water and pesticides in cultivation, whereas soy protein fiber provides an eco-friendly alternative with enhanced breathability and durability.
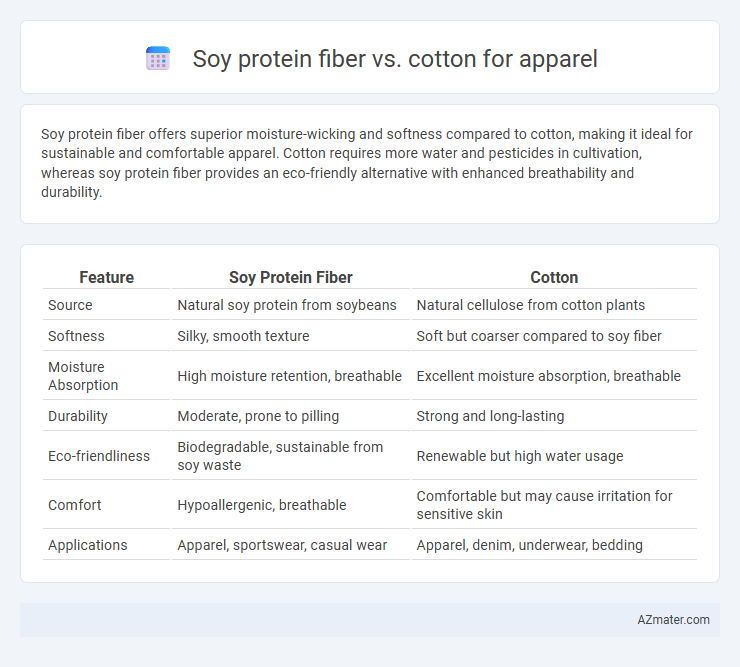
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Soy Protein Fiber | Cotton |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural soy protein from soybeans | Natural cellulose from cotton plants |
| Softness | Silky, smooth texture | Soft but coarser compared to soy fiber |
| Moisture Absorption | High moisture retention, breathable | Excellent moisture absorption, breathable |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to pilling | Strong and long-lasting |
| Eco-friendliness | Biodegradable, sustainable from soy waste | Renewable but high water usage |
| Comfort | Hypoallergenic, breathable | Comfortable but may cause irritation for sensitive skin |
| Applications | Apparel, sportswear, casual wear | Apparel, denim, underwear, bedding |
Introduction to Soy Protein Fiber and Cotton
Soy protein fiber, derived from soybean residues, offers a sustainable and biodegradable alternative to traditional natural fibers with excellent moisture absorption and softness, making it ideal for next-generation apparel textiles. Cotton, a staple in the textile industry, is widely preferred for its breathability, durability, and natural comfort, though it requires significant water resources and pesticides during cultivation. The contrast between soy protein fiber's eco-friendly production process and cotton's established market dominance highlights evolving consumer demand for sustainable and high-performance fabrics.
Environmental Impact: Soy Protein Fiber vs Cotton
Soy protein fiber significantly reduces water consumption compared to cotton, requiring up to 70% less water during cultivation. The biodegradable nature of soy protein fiber ensures minimal environmental pollution, contrasting with cotton's heavy pesticide and fertilizer use that contributes to soil degradation and water contamination. Furthermore, soy protein fiber's renewable sourcing and lower carbon footprint make it a more sustainable choice for eco-friendly apparel production.
Fiber Production Process Comparison
Soy protein fiber is produced through a process where soybean protein is extracted, dissolved, and then spun into fibers using wet spinning or dry spinning methods, resulting in a sustainable and biodegradable textile. Cotton fiber production involves harvesting cotton bolls, followed by ginning to separate fibers from seeds, and then carding and spinning the fibers into yarn, relying heavily on water and pesticides throughout cultivation. Compared to cotton, soy protein fiber production uses renewable resources with lower environmental impact and eliminates intensive agricultural requirements.
Comfort and Wearability in Apparel
Soy protein fiber offers superior softness and moisture absorption compared to cotton, enhancing comfort in apparel. Its natural elasticity improves wearability by providing better stretch and recovery, reducing fabric fatigue over time. Cotton remains breathable and durable but may lack the smooth, silky texture and thermal regulation properties found in soy protein fiber.
Moisture Management and Breathability
Soy protein fiber exhibits superior moisture management compared to cotton, efficiently wicking sweat away from the skin to maintain dryness and comfort during physical activities. Its breathable structure enhances air circulation, reducing heat buildup and promoting a cooler wearing experience. Cotton, while breathable and comfortable, absorbs moisture rather than wicking it, which can lead to a heavier, damp feel during intense exertion or humid conditions.
Durability and Longevity Differences
Soy protein fiber exhibits moderate durability due to its natural protein structure, offering good resistance to wear but lower tensile strength compared to cotton. Cotton fibers are known for their high durability and longevity, with strong abrasion resistance and resilience that withstands frequent washing and extensive use. Choosing cotton for apparel ensures longer-lasting garments, while soy protein fibers provide a softer feel but may require gentler care to maintain fabric integrity over time.
Hypoallergenic and Skin-Friendly Properties
Soy protein fiber exhibits superior hypoallergenic properties compared to cotton, making it an excellent choice for sensitive skin and allergy-prone individuals. Its natural amino acid content enhances skin hydration and breathability, reducing irritation and promoting comfort in apparel. Cotton, while breathable and soft, tends to retain moisture longer which can sometimes lead to skin irritation or allergies in sensitive wearers.
Sustainability and Biodegradability
Soy protein fiber offers superior sustainability compared to cotton, as it is derived from renewable soybean byproducts, reducing waste and lessening environmental impact. Unlike conventional cotton, which often requires extensive water and pesticide use, soy protein fiber production involves lower resource consumption and generates fewer greenhouse gas emissions. Both fibers are biodegradable, but soy protein fiber decomposes more rapidly in natural conditions, enhancing its eco-friendly appeal for sustainable apparel.
Cost and Market Availability
Soy protein fiber tends to be more expensive than cotton due to its complex production process and limited manufacturing scale, impacting its market availability. Cotton remains widely accessible and cost-effective, leveraging established agricultural infrastructure and mass production techniques. The higher cost and niche market presence of soy protein fiber restrict its use primarily to sustainable and specialty apparel segments.
Future Trends in Apparel Fabrics
Soy protein fiber offers sustainable advantages with its biodegradable and renewable properties, appealing to eco-conscious consumers in future apparel trends. Innovations in soy protein fiber enhance moisture-wicking and softness, positioning it as a competitive alternative to cotton, which remains dominant due to its breathability and durability. Increasing demand for plant-based, environmentally friendly fabrics drives the integration of soy protein fiber blends in performance and casual wear, projecting growth in sustainable textile markets.
Infographic: Soy protein fiber vs Cotton for Apparel
 azmater.com
azmater.com