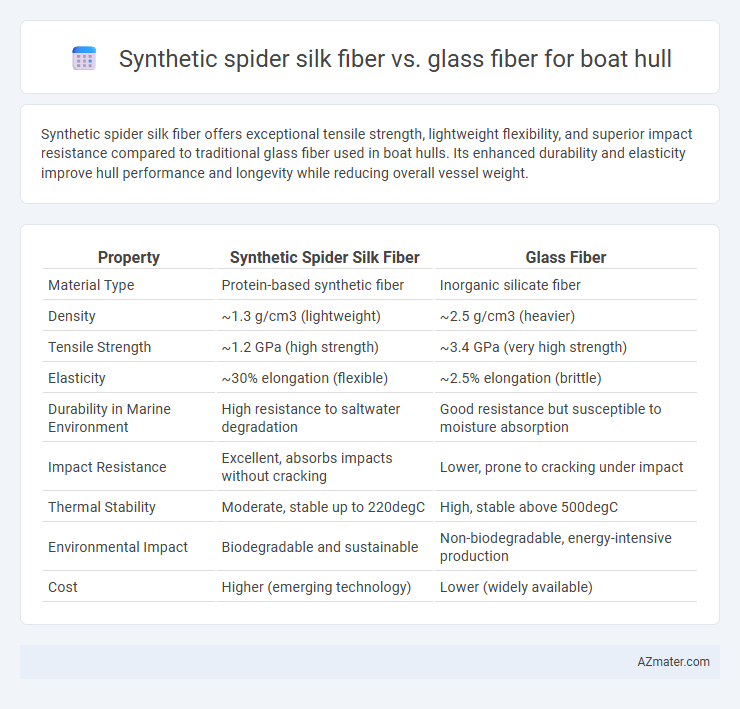
Synthetic spider silk fiber offers exceptional tensile strength, lightweight flexibility, and superior impact resistance compared to traditional glass fiber used in boat hulls. Its enhanced durability and elasticity improve hull performance and longevity while reducing overall vessel weight.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Synthetic Spider Silk Fiber | Glass Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Protein-based synthetic fiber | Inorganic silicate fiber |
| Density | ~1.3 g/cm3 (lightweight) | ~2.5 g/cm3 (heavier) |
| Tensile Strength | ~1.2 GPa (high strength) | ~3.4 GPa (very high strength) |
| Elasticity | ~30% elongation (flexible) | ~2.5% elongation (brittle) |
| Durability in Marine Environment | High resistance to saltwater degradation | Good resistance but susceptible to moisture absorption |
| Impact Resistance | Excellent, absorbs impacts without cracking | Lower, prone to cracking under impact |
| Thermal Stability | Moderate, stable up to 220degC | High, stable above 500degC |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable and sustainable | Non-biodegradable, energy-intensive production |
| Cost | Higher (emerging technology) | Lower (widely available) |
Introduction to Advanced Boat Hull Materials
Synthetic spider silk fiber exhibits remarkable tensile strength and flexibility, surpassing many conventional materials used in boat hulls. Its lightweight nature combined with exceptional impact resistance contributes to improved fuel efficiency and durability compared to traditional glass fiber composites. Innovations in advanced boat hull materials increasingly favor synthetic spider silk fiber for enhanced performance, corrosion resistance, and environmental sustainability.
Overview of Synthetic Spider Silk Fiber
Synthetic spider silk fiber exhibits exceptional tensile strength and elasticity, outperforming traditional glass fiber in durability and flexibility for boat hull applications. Its lightweight yet resilient properties contribute to improved impact resistance and enhanced fatigue life, making it an innovative alternative in marine composites. Unlike glass fiber, synthetic spider silk fiber offers superior biodegradability and environmental sustainability without compromising structural integrity.
Properties of Glass Fiber in Marine Applications
Glass fiber offers exceptional tensile strength and corrosion resistance, making it a widely preferred reinforcement material for boat hulls in marine environments. Its high durability against saltwater and UV exposure ensures longevity and structural integrity, while its cost-effectiveness and ease of fabrication enhance production efficiency. The relatively high stiffness and impact resistance of glass fiber contribute to robust hull performance under dynamic sea conditions.
Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Spider Silk vs Glass Fiber
Synthetic spider silk fiber exhibits an exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, surpassing traditional glass fiber in boat hull applications by offering superior tensile strength at a fraction of the density. This lightweight yet durable characteristic enhances fuel efficiency and improves handling due to reduced hull mass. Consequently, synthetic spider silk fibers present a revolutionary alternative for marine engineering, combining robustness with significant weight savings.
Flexibility and Impact Resistance Comparison
Synthetic spider silk fiber offers superior flexibility compared to glass fiber, enabling boat hulls to better absorb and dissipate energy from impacts without cracking. Its high tensile strength combined with elasticity allows hulls to withstand sudden shocks and pressure changes more effectively than the brittle nature of glass fiber. This enhanced impact resistance and flexibility make synthetic spider silk a promising material for durable, resilient boat hull construction.
Durability in Marine Environments
Synthetic spider silk fiber exhibits exceptional durability in marine environments due to its high tensile strength, elasticity, and resistance to saltwater corrosion, outperforming traditional glass fiber in flexible load-bearing applications. Unlike glass fiber, which can suffer from micro-cracking and degradation when exposed to prolonged moisture and UV radiation, synthetic spider silk maintains structural integrity and resists biofouling, extending boat hull lifespan. The biodegradability and lightweight nature of synthetic spider silk also contribute to improved fuel efficiency and reduced environmental impact in marine vessel construction.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Synthetic spider silk fiber offers a significant sustainability advantage over traditional glass fiber in boat hull construction due to its biodegradability and lower carbon footprint during production. While glass fiber relies on energy-intensive processes and generates non-biodegradable waste, synthetic spider silk is derived from renewable bioengineered proteins, enabling reduced environmental pollution and enhanced recyclability. The use of synthetic spider silk fiber contributes to eco-friendly marine applications by minimizing microplastic release and promoting circular economy principles.
Cost Analysis and Scalability
Synthetic spider silk fiber offers a promising alternative to glass fiber for boat hull construction, with cost analysis revealing higher initial material expenses but potential long-term savings through durability and reduced maintenance. Scalability remains a challenge for synthetic spider silk due to current production limitations and complex biofabrication processes, whereas glass fiber benefits from established large-scale manufacturing and widespread supply chains. Innovations in synthetic biology and manufacturing techniques are expected to improve scalability and drive down costs, positioning synthetic spider silk as a competitive, sustainable option in marine composite materials.
Current Limitations and Research Directions
Synthetic spider silk fiber offers exceptional tensile strength and flexibility compared to traditional glass fiber used in boat hulls, but its current limitations include high production costs and scalability challenges. Research is focused on improving biofabrication techniques to enhance yield and reduce environmental impact while maintaining durability and resistance to marine conditions. Innovations aim to optimize composite integration methods to fully exploit spider silk's lightweight and impact-resistant properties, potentially surpassing glass fiber in performance and sustainability.
Future Prospects for Boat Hull Construction
Synthetic spider silk fiber offers exceptional tensile strength and flexibility, making it a promising alternative to traditional glass fiber in boat hull construction due to its lightweight and biodegradability. Advances in bioengineering could enable scalable production of synthetic spider silk, enhancing durability and resistance to environmental stressors compared to glass fiber composites. Future boat hulls may benefit from this sustainable material through improved performance, reduced carbon footprint, and enhanced structural integrity in marine applications.
Infographic: Synthetic spider silk fiber vs Glass fiber for Boat hull
 azmater.com
azmater.com