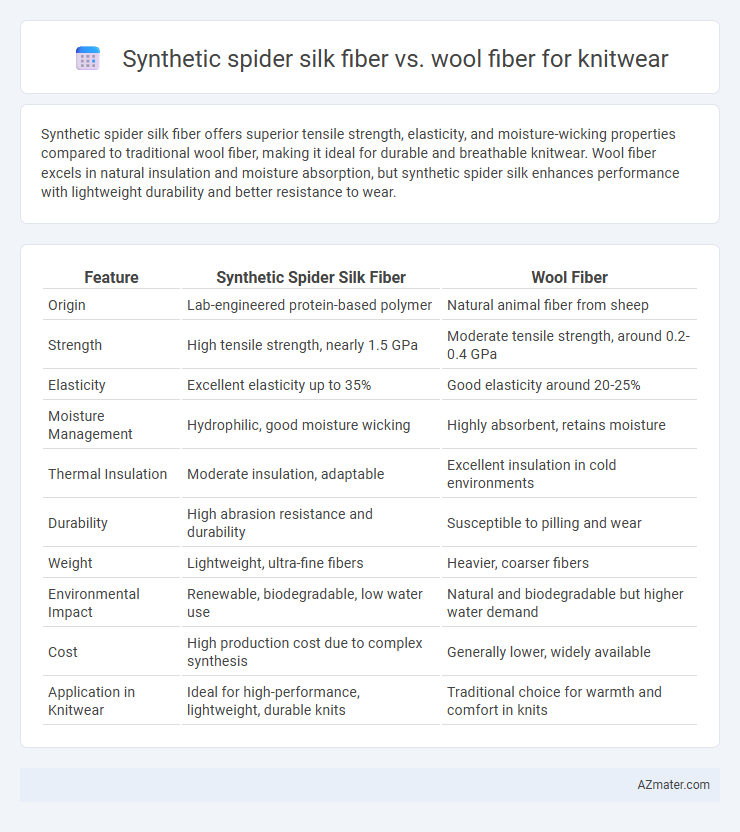
Synthetic spider silk fiber offers superior tensile strength, elasticity, and moisture-wicking properties compared to traditional wool fiber, making it ideal for durable and breathable knitwear. Wool fiber excels in natural insulation and moisture absorption, but synthetic spider silk enhances performance with lightweight durability and better resistance to wear.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Synthetic Spider Silk Fiber | Wool Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Lab-engineered protein-based polymer | Natural animal fiber from sheep |
| Strength | High tensile strength, nearly 1.5 GPa | Moderate tensile strength, around 0.2-0.4 GPa |
| Elasticity | Excellent elasticity up to 35% | Good elasticity around 20-25% |
| Moisture Management | Hydrophilic, good moisture wicking | Highly absorbent, retains moisture |
| Thermal Insulation | Moderate insulation, adaptable | Excellent insulation in cold environments |
| Durability | High abrasion resistance and durability | Susceptible to pilling and wear |
| Weight | Lightweight, ultra-fine fibers | Heavier, coarser fibers |
| Environmental Impact | Renewable, biodegradable, low water use | Natural and biodegradable but higher water demand |
| Cost | High production cost due to complex synthesis | Generally lower, widely available |
| Application in Knitwear | Ideal for high-performance, lightweight, durable knits | Traditional choice for warmth and comfort in knits |
Introduction to Synthetic Spider Silk and Wool Fibers
Synthetic spider silk fiber, engineered for exceptional strength and elasticity, offers a lightweight, durable alternative to traditional materials in knitwear. Wool fibers, derived from sheep fleece, provide natural insulation, moisture wicking, and breathability, making them a popular choice for warmth and comfort. Comparing these fibers highlights synthetic spider silk's advanced mechanical properties against wool's sustainable and thermal benefits in knitting applications.
Origins and Production Methods
Synthetic spider silk fiber is engineered through biomimetic processes using genetically modified organisms or chemical synthesis to replicate the protein structures found in natural spider silk, resulting in lightweight, highly durable fibers with exceptional tensile strength. Wool fiber originates from the fleece of sheep, harvested through shearing, and undergoes cleaning, carding, and spinning to produce natural, insulating, and elastic yarns favored for knitwear. The production of synthetic spider silk emphasizes advanced biotechnology and controlled laboratory conditions, whereas wool fiber relies on traditional agricultural practices and mechanical processing methods.
Physical and Mechanical Properties
Synthetic spider silk fiber exhibits superior tensile strength and elasticity compared to wool fiber, making it highly resilient and durable for knitwear applications. Its moisture-wicking properties surpass those of wool, enhancing breathability and comfort in garments. Wool fiber, though naturally insulating and flame-resistant, lacks the exceptional mechanical robustness and elongation capacity characteristic of synthetic spider silk.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Synthetic spider silk fiber offers superior sustainability compared to wool fiber due to its renewable production process and minimal land use, significantly reducing water consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. Wool fiber, while biodegradable and naturally insulating, requires extensive grazing land, contributing to methane emissions and habitat disruption. Innovations in synthetic spider silk manufacturing promote eco-friendly knitwear by lowering dependency on animal agriculture and minimizing environmental footprints.
Comfort and Wearability
Synthetic spider silk fiber offers exceptional softness and breathability, making knitwear highly comfortable for extended wear, while its moisture-wicking properties enhance temperature regulation. Wool fiber provides natural insulation and excellent elasticity, ensuring warmth and ease of movement, but may cause itchiness for sensitive skin types. The durability and lightweight nature of synthetic spider silk fibers often result in longer-lasting knitwear with superior wearability compared to traditional wool garments.
Versatility in Knitwear Applications
Synthetic spider silk fiber offers exceptional versatility in knitwear applications due to its superior strength, elasticity, and moisture-wicking properties compared to traditional wool fiber. Unlike wool, which is limited by its natural fiber structure, synthetic spider silk can be engineered for specific performance characteristics such as enhanced durability, lightweight comfort, and thermal regulation. This adaptability makes synthetic spider silk an ideal choice for a wide range of knitwear products, from high-performance activewear to luxury fashion items.
Durability and Longevity
Synthetic spider silk fiber exhibits superior durability and longevity compared to wool fiber in knitwear applications due to its high tensile strength and resistance to abrasion and environmental degradation. Wool fiber, while naturally elastic and moisture-wicking, tends to degrade faster with repeated washing and exposure to friction, leading to pilling and fiber breakage. The advanced molecular structure of synthetic spider silk enables it to maintain knitwear shape and integrity over extended use, making it a more resilient choice for long-lasting garments.
Care and Maintenance Requirements
Synthetic spider silk fiber offers superior durability and resistance to stretching and shrinking compared to wool fiber, making it easier to maintain with less frequent washing. Wool fiber requires gentle care, such as hand washing or delicate machine cycles with mild detergents, and careful drying to prevent felting and shrinkage. Synthetic spider silk fibers dry quickly and resist wrinkles, reducing the need for ironing and specialized storage, while wool demands careful storage to avoid moth damage and mildew.
Cost and Market Availability
Synthetic spider silk fiber offers a higher production cost compared to traditional wool fiber due to advanced biotechnology processes, impacting its pricing in the knitwear market. Wool fiber remains more widely available and affordable, supported by established global supply chains and natural sourcing methods. Market availability of synthetic spider silk is currently limited but growing, with innovations driving gradual adoption in premium knitwear segments seeking sustainable and high-performance alternatives.
Future Prospects in Textile Innovation
Synthetic spider silk fiber exhibits exceptional tensile strength, elasticity, and biodegradability, positioning it as a revolutionary material for knitwear innovation. Wool fiber remains valued for its natural insulation and moisture-wicking properties, but synthetic spider silk promises enhanced durability and sustainability in textile applications. Advancements in bioengineering and scalable production methods are accelerating the integration of synthetic spider silk into eco-friendly, high-performance knitwear for the future fashion industry.
Infographic: Synthetic spider silk fiber vs Wool fiber for Knitwear
 azmater.com
azmater.com