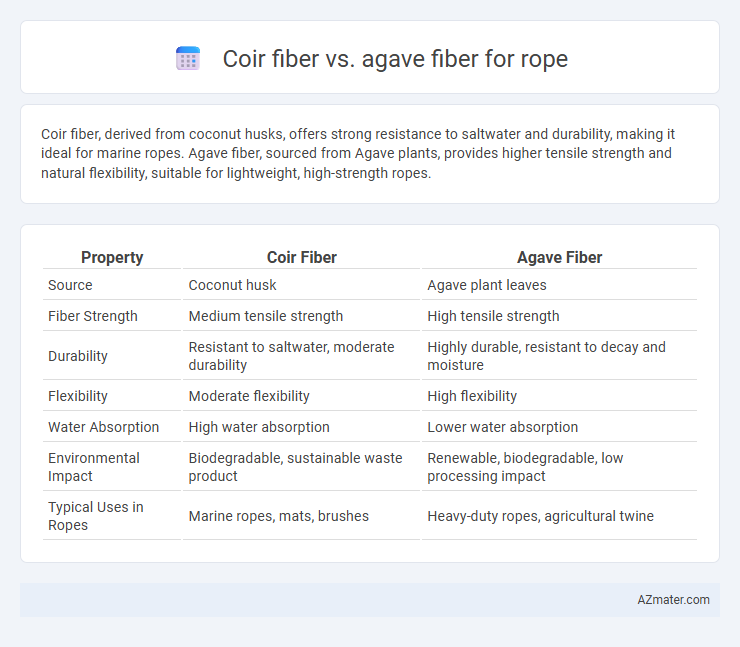
Coir fiber, derived from coconut husks, offers strong resistance to saltwater and durability, making it ideal for marine ropes. Agave fiber, sourced from Agave plants, provides higher tensile strength and natural flexibility, suitable for lightweight, high-strength ropes.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Coir Fiber | Agave Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Coconut husk | Agave plant leaves |
| Fiber Strength | Medium tensile strength | High tensile strength |
| Durability | Resistant to saltwater, moderate durability | Highly durable, resistant to decay and moisture |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility | High flexibility |
| Water Absorption | High water absorption | Lower water absorption |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, sustainable waste product | Renewable, biodegradable, low processing impact |
| Typical Uses in Ropes | Marine ropes, mats, brushes | Heavy-duty ropes, agricultural twine |
Introduction to Natural Fiber Ropes
Coir fiber, derived from coconut husks, offers excellent water resistance and durability, making it ideal for marine ropes and outdoor applications. Agave fiber, sourced from the leaves of the agave plant, provides remarkable tensile strength and flexibility, suitable for heavy-duty and industrial rope manufacturing. Both fibers serve as sustainable alternatives to synthetic ropes, emphasizing biodegradability and eco-friendly production.
Overview of Coir Fiber
Coir fiber, derived from the outer husk of coconut shells, is renowned for its coarse texture, high durability, and resistance to saltwater, making it ideal for marine rope applications. It exhibits strong tensile strength and excellent abrasion resistance, contributing to its widespread use in traditional rope manufacturing. Compared to agave fiber, coir offers greater water resistance and eco-friendly biodegradability, positioning it as a sustainable choice for various industrial uses.
Overview of Agave Fiber
Agave fiber, derived from the Agave plant's leaves, is known for its high tensile strength, durability, and resistance to saltwater, making it an excellent choice for rope production especially in marine environments. Compared to coir fiber, which comes from coconut husks and offers good water resistance and flexibility, agave fiber tends to be coarser yet more robust, providing superior longevity in heavy-duty applications. Its natural antifungal properties and biodegradability also make agave fiber ropes environmentally friendly and highly sought after in sustainable product markets.
Harvesting and Processing Methods
Coir fiber, extracted from the outer husk of coconut shells, is harvested through a labor-intensive process involving soaking the husks in water (retting) for several weeks to soften the fibers before manual or mechanical extraction. Agave fiber, derived from the leaves of agave plants, is harvested by cutting mature leaves and then subjected to a decortication process to separate the fibers, followed by washing and drying. Both fibers require specific retting and drying procedures to enhance tensile strength and durability, with coir benefiting from longer soaking times and agave fibers requiring precise decortication for optimal quality in rope making.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Coir fiber exhibits moderate tensile strength ranging from 110 to 220 MPa, making it suitable for light to medium-duty rope applications, while agave fiber demonstrates higher tensile strength, often between 300 and 500 MPa, providing superior load-bearing capacity and durability. The elongation at break for coir fiber is about 15-20%, which is lower than agave fiber's 20-25%, indicating that agave fiber ropes offer better flexibility and resistance to mechanical stress. Overall, agave fiber surpasses coir fiber in mechanical strength metrics, making it the preferred choice for heavy-duty rope manufacturing where robustness and longevity are critical.
Durability and Weather Resistance
Coir fiber, derived from coconut husks, offers moderate durability with high resistance to saltwater, making it ideal for marine and outdoor rope applications. Agave fiber, extracted from agave leaves, provides superior tensile strength and greater durability under harsh weather conditions, including UV exposure and moisture. While coir excels in water resistance, agave fibers outperform in long-term wear and weather resilience, ensuring extended rope lifespan in diverse environments.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Coir fiber, derived from coconut husks, is highly sustainable due to its natural biodegradability and the use of agricultural waste, making it an eco-friendly choice for rope production. Agave fiber, sourced from agave plant leaves, offers environmental benefits through its rapid renewability and minimal water requirements compared to conventional fiber crops. Both fibers reduce reliance on synthetic materials, but coir's ability to utilize byproducts and agave's efficient cultivation contribute significantly to lower ecological footprints in sustainable rope manufacturing.
Cost and Market Availability
Coir fiber, derived from coconut husks, is widely available and more cost-effective than agave fiber, making it a preferred choice in rope manufacturing. Agave fiber, sourced from agave plants, tends to be pricier due to limited cultivation and extraction processes, affecting its market availability. The cost-efficiency and abundant supply of coir fiber contribute to its dominance in the rope market compared to the niche demand for agave fiber.
Applications: Coir vs Agave Ropes
Coir fiber ropes excel in marine and agricultural applications due to their high resistance to saltwater and natural abrasion, making them ideal for mooring, fishing nets, and crop support. Agave fiber ropes, derived from sisal, offer superior tensile strength and durability in dry environments, commonly used in construction, packaging, and heavy-duty lifting. Both fibers provide eco-friendly alternatives to synthetic ropes, with coir favored for moisture resilience and agave for load-bearing capacity.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Fiber for Rope
Coir fiber offers exceptional water resistance and durability, making it ideal for marine and outdoor rope applications. Agave fiber provides superior strength and flexibility, suitable for heavy-duty ropes requiring high tensile strength. Selecting the right fiber depends on specific rope use cases, with coir favored for moisture-prone environments and agave preferred for load-bearing needs.
Infographic: Coir fiber vs Agave fiber for Rope
 azmater.com
azmater.com