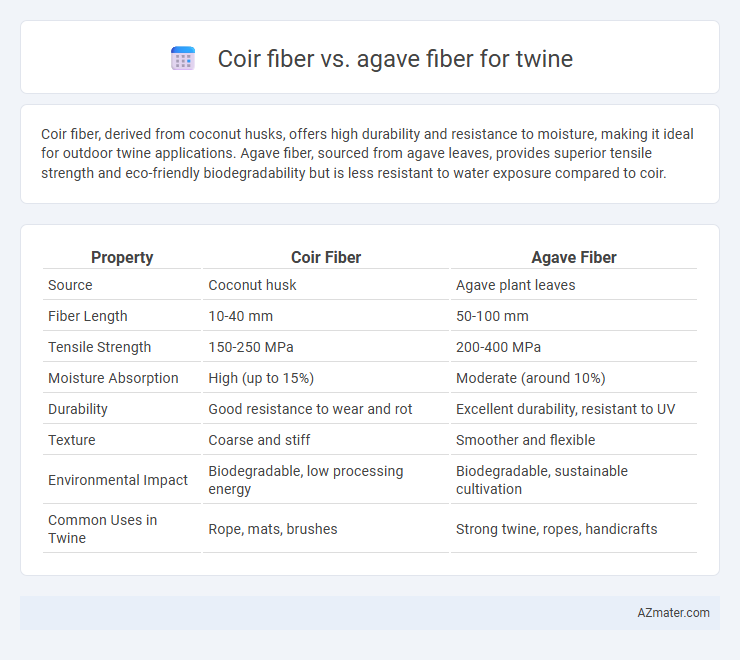
Coir fiber, derived from coconut husks, offers high durability and resistance to moisture, making it ideal for outdoor twine applications. Agave fiber, sourced from agave leaves, provides superior tensile strength and eco-friendly biodegradability but is less resistant to water exposure compared to coir.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Coir Fiber | Agave Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Coconut husk | Agave plant leaves |
| Fiber Length | 10-40 mm | 50-100 mm |
| Tensile Strength | 150-250 MPa | 200-400 MPa |
| Moisture Absorption | High (up to 15%) | Moderate (around 10%) |
| Durability | Good resistance to wear and rot | Excellent durability, resistant to UV |
| Texture | Coarse and stiff | Smoother and flexible |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, low processing energy | Biodegradable, sustainable cultivation |
| Common Uses in Twine | Rope, mats, brushes | Strong twine, ropes, handicrafts |
Introduction to Natural Twine Fibers
Coir fiber, derived from coconut husks, offers natural durability and water resistance, making it highly suitable for outdoor twine applications. Agave fiber, extracted from the leaves of agave plants, is known for its strength and flexibility, offering an eco-friendly alternative with a softer texture. Both fibers are biodegradable and sustainable, catering to growing demand for environmentally conscious natural twine products.
Overview of Coir Fiber
Coir fiber, derived from the outer husk of coconut shells, is renowned for its durability, high tensile strength, and natural resistance to water and salt, making it ideal for twine used in maritime and agricultural applications. Its coarse texture and excellent abrasion resistance provide long-lasting performance compared to other natural fibers such as agave, which tends to be softer but less resistant to environmental elements. Coir's biodegradability and renewable sourcing also contribute to its growing preference in sustainable twine production.
Overview of Agave Fiber
Agave fiber, derived from the Agave plant, is renowned for its strength, durability, and resistance to moisture, making it ideal for twine production. Unlike coir fiber, which comes from coconut husks, agave fiber offers a smoother texture and higher tensile strength, enhancing its performance in binding and packaging applications. Its natural resistance to decay and pests ensures longevity, contributing to sustainable and eco-friendly twine solutions.
Key Physical Properties Comparison
Coir fiber exhibits higher tensile strength and greater abrasion resistance than Agave fiber, making it more durable for heavy-duty twine applications. Agave fiber, however, offers superior flexibility and finer texture, allowing for smoother and more pliable twine production. The moisture absorption rate of Coir fiber is lower, which enhances its resistance to mold and rot compared to the more hydrophilic Agave fiber.
Strength and Durability Differences
Coir fiber, derived from coconut husks, exhibits superior strength and resistance to abrasion, making it highly durable for twine applications exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Agave fiber, sourced from agave leaves, offers moderate tensile strength but excels in flexibility and biodegradability, suitable for lighter-duty twine uses. The higher lignin content in coir fiber contributes to its enhanced durability compared to the softer, less dense agave fiber.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Coir fiber, derived from coconut husks, is a biodegradable and renewable resource with low environmental impact due to minimal chemical processing and high durability, making it a sustainable choice for twine production. Agave fiber, extracted from agave leaves, also boasts biodegradability and requires less water and pesticides than many traditional fibers, contributing to its eco-friendly profile and supporting sustainable agriculture. Comparing the two, coir excels in durability and waste utilization, while agave fiber offers advantages in resource efficiency and reduced environmental footprint during cultivation.
Applications in Industry and Crafts
Coir fiber, derived from coconut husks, is highly valued in the twine industry for its durability, moisture resistance, and ability to withstand heavy loads, making it ideal for agricultural, maritime, and packaging applications. Agave fiber, sourced from the agave plant, offers superior tensile strength and flexibility, frequently utilized in artisanal crafts, decorative twine, and eco-friendly packaging. Both fibers support sustainable production, with coir preferred for rugged industrial use and agave favored for fine craftwork and biodegradable products.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Coir fiber, derived from coconut husks, is widely available in tropical regions and tends to be more cost-effective due to large-scale production and established supply chains. Agave fiber, sourced primarily from Agave plants in arid zones, often incurs higher costs because of limited harvest seasons and less developed processing infrastructure. The abundant availability of coir fiber makes it a preferred choice for twine manufacturers seeking affordable and reliable raw materials.
Biodegradability and Disposal Considerations
Coir fiber, derived from coconut husks, offers excellent biodegradability with natural resistance to microbial degradation, making it ideal for twine used in environmentally sensitive applications. Agave fiber, sourced from agave leaves, decomposes faster due to its lower lignin content, promoting quicker soil enrichment when disposed of. Both fibers provide sustainable alternatives for twine, but agave fiber's rapid biodegradability supports more efficient organic waste management compared to the slower degrading coir fiber.
Choosing the Right Fiber for Your Twine Needs
Coir fiber, derived from coconut husks, offers exceptional durability and water resistance, making it ideal for outdoor twine applications requiring strength and weather tolerance. Agave fiber, sourced from agave leaves, provides a softer texture and higher flexibility, suitable for crafting and decorative twine where aesthetics and pliability are prioritized. Selecting the right fiber depends on your twine's intended use, balancing the need for toughness and environmental exposure with the desired appearance and handle.
Infographic: Coir fiber vs Agave fiber for Twine
 azmater.com
azmater.com