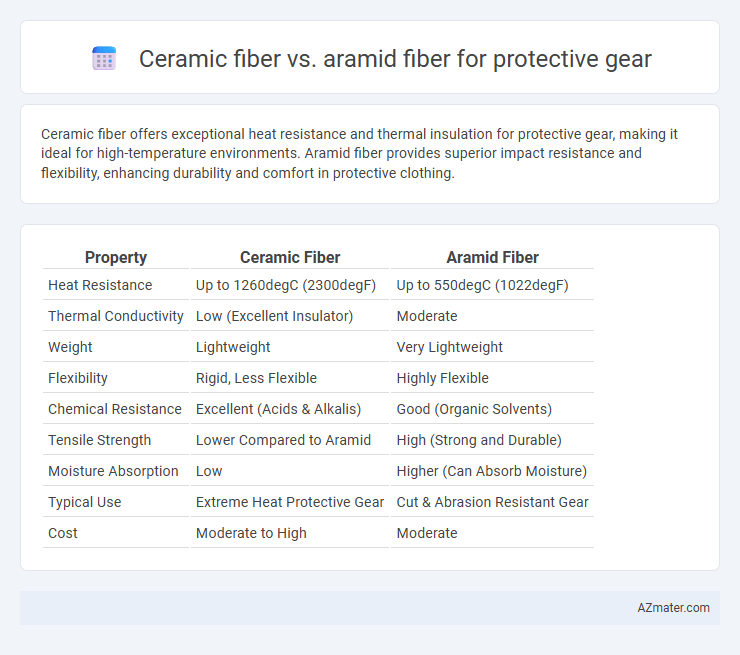
Ceramic fiber offers exceptional heat resistance and thermal insulation for protective gear, making it ideal for high-temperature environments. Aramid fiber provides superior impact resistance and flexibility, enhancing durability and comfort in protective clothing.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ceramic Fiber | Aramid Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Resistance | Up to 1260degC (2300degF) | Up to 550degC (1022degF) |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low (Excellent Insulator) | Moderate |
| Weight | Lightweight | Very Lightweight |
| Flexibility | Rigid, Less Flexible | Highly Flexible |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent (Acids & Alkalis) | Good (Organic Solvents) |
| Tensile Strength | Lower Compared to Aramid | High (Strong and Durable) |
| Moisture Absorption | Low | Higher (Can Absorb Moisture) |
| Typical Use | Extreme Heat Protective Gear | Cut & Abrasion Resistant Gear |
| Cost | Moderate to High | Moderate |
Introduction to Protective Gear Materials
Ceramic fiber offers exceptional heat resistance and insulation, making it ideal for protective gear in high-temperature environments such as firefighting and industrial applications. Aramid fiber provides superior tensile strength, flexibility, and cut resistance, commonly used in bulletproof vests and tactical equipment. Both materials are critical in designing protective gear tailored to specific threats and operational conditions, balancing thermal protection with durability and comfort.
Overview of Ceramic Fiber
Ceramic fiber offers exceptional heat resistance withstanding temperatures up to 2300degF (1260degC), making it ideal for protective gear in high-temperature environments such as firefighting and industrial applications. Its low thermal conductivity and lightweight composition provide superior insulation while maintaining flexibility and durability under thermal stress. Unlike aramid fiber, ceramic fiber excels in protecting against extreme heat and molten metal splashes but is less effective against mechanical abrasion and impact.
Overview of Aramid Fiber
Aramid fiber, a class of heat-resistant and strong synthetic fibers, excels in protective gear due to its exceptional tensile strength, low weight, and resistance to abrasion and heat up to approximately 370degC (700degF). Commonly found in ballistic vests, helmets, and firefighting apparel, aramid fibers such as Kevlar and Nomex provide excellent cut and impact resistance while maintaining flexibility. Their chemical stability and durability under harsh conditions make aramid fibers a preferred choice for advanced protective equipment requiring high performance and reliability.
Thermal Resistance Comparison
Ceramic fiber offers superior thermal resistance, withstanding temperatures up to 2300degF (1260degC), making it ideal for extreme heat protection in industrial environments. Aramid fiber, such as Kevlar, provides effective thermal resistance up to approximately 900degF (482degC) while maintaining flexibility and impact resistance suitable for protective clothing. The choice between ceramic and aramid fibers depends on the required thermal threshold and mechanical durability for specific protective gear applications.
Mechanical Strength Differences
Ceramic fibers exhibit superior mechanical strength at high temperatures, maintaining structural integrity and resistance to abrasion, making them ideal for extreme heat protection in firefighting and industrial gear. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, provide excellent tensile strength and impact resistance at ambient temperatures but degrade faster under intense heat. The mechanical strength disparity significantly influences their application, with ceramic fibers preferred for thermal insulation and aramid fibers favored for ballistic protection.
Weight and Flexibility
Ceramic fiber used in protective gear offers excellent heat resistance but is significantly heavier and less flexible compared to aramid fiber. Aramid fiber, renowned for its lightweight properties and superior flexibility, provides high tensile strength while allowing greater mobility and comfort. The combination of low weight and enhanced flexibility in aramid fiber makes it more suitable for protective clothing requiring extended wear and dynamic movement.
Chemical and Fire Resistance
Ceramic fiber offers superior fire resistance with the ability to withstand temperatures exceeding 2300degF, making it ideal for high-heat environments. Aramid fiber, known for its exceptional chemical resistance, effectively resists a wide range of acids, alkalis, and organic solvents while maintaining structural integrity. Protective gear combining ceramic and aramid fibers enhances both fire and chemical protection, optimizing safety in hazardous conditions.
Comfort and Wearability
Ceramic fiber offers excellent heat resistance and insulation but tends to be stiffer and heavier, which can reduce overall comfort and flexibility in protective gear. Aramid fiber, such as Kevlar, provides superior lightweight durability and flexibility, enhancing wearability and ease of movement during extended use. The breathable nature of aramid fibers also improves moisture management, making them preferable for comfort in various protective applications.
Cost and Availability
Ceramic fiber offers high-temperature resistance but comes at a higher cost and limited availability compared to aramid fiber, which is more widely accessible and affordable for protective gear applications. Aramid fiber, such as Kevlar, provides excellent strength and durability at a lower price point, making it a popular choice in cost-sensitive markets. Availability of aramid fiber is supported by extensive industrial production, while ceramic fiber remains specialized and less common in standard protective gear supply chains.
Best Applications for Each Fiber Type
Ceramic fiber excels in high-temperature environments, making it ideal for protective gear used in firefighting, industrial heat shields, and thermal insulation applications due to its superior heat resistance and low thermal conductivity. Aramid fiber, known for its exceptional tensile strength and cut resistance, is best suited for ballistic protection, cut-resistant gloves, and impact-resistant clothing, providing lightweight durability and flexibility. Selecting the appropriate fiber depends on the protection requirements: thermal resistance favors ceramic fibers, while mechanical strength and abrasion resistance highlight aramid fibers.
Infographic: Ceramic fiber vs Aramid fiber for Protective gear
 azmater.com
azmater.com