PLA fiber offers biodegradable and moisture-wicking properties ideal for eco-friendly socks, while nylon fiber provides superior durability and elasticity, enhancing sock lifespan and fit. Choosing PLA fiber supports sustainability, whereas nylon ensures long-lasting performance in everyday wear.
Table of Comparison
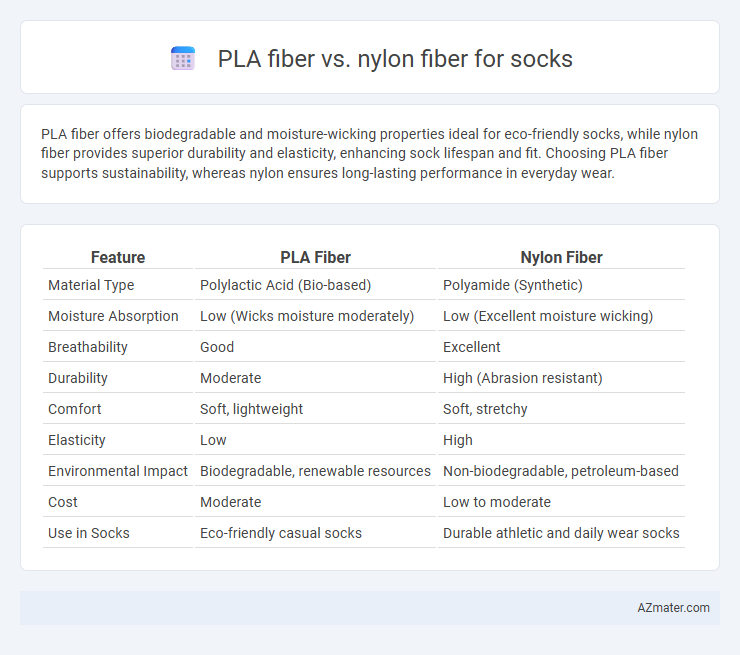
| Feature | PLA Fiber | Nylon Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Polylactic Acid (Bio-based) | Polyamide (Synthetic) |
| Moisture Absorption | Low (Wicks moisture moderately) | Low (Excellent moisture wicking) |
| Breathability | Good | Excellent |
| Durability | Moderate | High (Abrasion resistant) |
| Comfort | Soft, lightweight | Soft, stretchy |
| Elasticity | Low | High |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, renewable resources | Non-biodegradable, petroleum-based |
| Cost | Moderate | Low to moderate |
| Use in Socks | Eco-friendly casual socks | Durable athletic and daily wear socks |
Introduction to PLA and Nylon Fibers
PLA fiber, derived from renewable resources such as corn starch or sugarcane, offers eco-friendly and biodegradable properties ideal for sustainable sock production. Nylon fiber, a synthetic polymer made from petrochemicals, is renowned for its exceptional strength, elasticity, and abrasion resistance, enhancing sock durability and fit. Comparing PLA and nylon fibers highlights the trade-off between environmental impact and performance characteristics crucial for sock manufacturing.
Key Differences Between PLA and Nylon Fibers
PLA fiber, derived from renewable resources like corn starch, offers biodegradability and excellent moisture-wicking properties, making it eco-friendly and comfortable for socks. Nylon fiber, a synthetic polymer, provides superior strength, elasticity, and abrasion resistance, enhancing durability and fit in sock applications. While PLA fibers excel in sustainability and breathability, nylon fibers outperform in mechanical strength and longevity, influencing the choice based on performance versus environmental impact.
Environmental Impact: PLA vs Nylon
PLA fiber, derived from renewable resources like corn starch, offers a significantly lower carbon footprint compared to petroleum-based Nylon fiber, reducing greenhouse gas emissions during production. Its biodegradability contributes to less environmental pollution and waste accumulation, whereas Nylon persists in ecosystems for decades, posing risks to marine and soil health. Despite Nylon's durability and recyclability, the reliance on fossil fuels and the release of microplastics make PLA a more sustainable choice for eco-conscious sock manufacturing.
Comfort and Wearability in Socks
PLA fiber offers excellent moisture-wicking properties and natural breathability, enhancing comfort for sock wearers by keeping feet dry and cool. Nylon fiber provides superior durability and elasticity, ensuring a snug fit and long-lasting wear without losing shape. Combining PLA with nylon in socks often balances comfort with wearability, delivering breathable performance along with enhanced strength and stretch.
Moisture Management and Breathability
PLA fiber offers superior moisture-wicking properties compared to nylon, efficiently drawing sweat away from the skin to keep feet dry. Its natural biodegradability enhances breathability, allowing better air circulation within socks for improved thermal regulation. Nylon fiber tends to retain more moisture and has lower airflow, which can lead to discomfort and increased risk of odor buildup during extended wear.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
PLA fiber offers moderate durability but tends to degrade faster under repeated stress and moisture exposure compared to Nylon fiber. Nylon fiber is renowned for its superior tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and elasticity, making it more suitable for socks designed for long-term use and high-performance activities. The longevity of Nylon fiber socks significantly surpasses PLA fiber counterparts due to Nylon's ability to maintain structural integrity and resist wear over extended periods.
Biodegradability and Sustainability Factors
PLA fiber, derived from renewable resources like corn starch, offers superior biodegradability compared to conventional nylon fiber, which is petroleum-based and non-biodegradable. PLA socks break down naturally under industrial composting conditions, reducing environmental impact and landfill accumulation. Nylon's sustainability challenges stem from energy-intensive production and microplastic pollution, whereas PLA fibers contribute to a lower carbon footprint and sustainable textile solutions.
Cost and Market Availability
PLA fiber for socks is generally more cost-effective due to its renewable, bio-based origins and lower processing expenses compared to nylon. Nylon fiber remains widely available in global markets, benefiting from well-established manufacturing and distribution networks that ensure consistent supply and competitive pricing. Consumer demand for sustainable textiles is increasing PLA fiber market presence, but nylon continues to dominate due to its durability and moisture-wicking properties.
Applications and Performance in Socks
PLA fiber offers excellent moisture-wicking and biodegradability, making it ideal for eco-friendly socks designed for casual wear and light activities. Nylon fiber provides superior elasticity, durability, and abrasion resistance, enhancing comfort and lifespan in athletic and high-performance socks. Combining PLA with nylon can optimize breathability and strength, catering to diverse sock applications from everyday use to intense sports.
Choosing the Right Fiber for Sustainable Socks
PLA fiber, derived from renewable resources like corn starch, offers excellent biodegradability and moisture-wicking properties ideal for eco-friendly socks. Nylon fiber, while durable and stretchy for long-lasting comfort, relies on petroleum-based materials and has a slower decomposition rate, impacting sustainability. Selecting PLA fiber over nylon supports reducing environmental footprint through compostability and renewable sourcing in sustainable sock production.
Infographic: PLA fiber vs Nylon fiber for Socks
 azmater.com
azmater.com