Smart fiber insulation offers superior thermal regulation and energy efficiency compared to traditional glass fiber, enhancing indoor comfort and reducing heating costs. Glass fiber remains cost-effective and widely used but lacks the adaptive properties of smart fibers in managing temperature fluctuations.
Table of Comparison
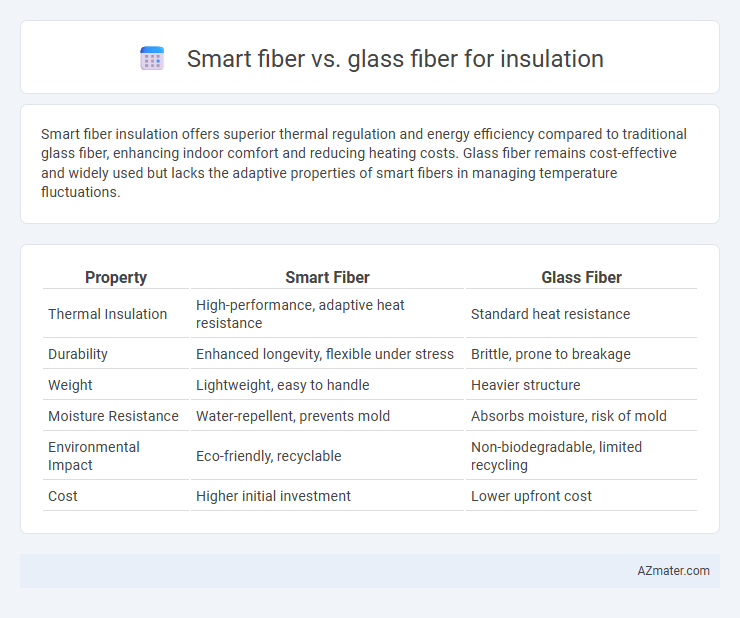
| Property | Smart Fiber | Glass Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Insulation | High-performance, adaptive heat resistance | Standard heat resistance |
| Durability | Enhanced longevity, flexible under stress | Brittle, prone to breakage |
| Weight | Lightweight, easy to handle | Heavier structure |
| Moisture Resistance | Water-repellent, prevents mold | Absorbs moisture, risk of mold |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, recyclable | Non-biodegradable, limited recycling |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower upfront cost |
Introduction to Insulation Materials
Smart fiber insulation integrates advanced synthetic fibers engineered for enhanced thermal resistance, moisture control, and durability, optimizing energy efficiency in buildings. Glass fiber insulation, composed of fine strands of glass, offers excellent thermal and acoustic insulation with high fire resistance and affordability, making it a widely used traditional choice. Both materials play critical roles in modern construction, with smart fibers often providing adaptive insulation properties tailored to specific environmental conditions.
What is Smart Fiber?
Smart fiber insulation integrates advanced materials like phase change substances or nanotechnology to enhance thermal regulation and energy efficiency beyond traditional glass fiber. Unlike conventional glass fiber, which mainly provides passive thermal resistance, smart fiber actively adapts to temperature changes, improving insulation performance and comfort. Innovations in smart fiber contribute to reduced energy consumption in buildings by dynamically managing heat flow and moisture control.
Understanding Glass Fiber Insulation
Glass fiber insulation consists of tiny glass fibers woven into a mat or batt, offering exceptional thermal resistance with an R-value typically ranging from 2.9 to 3.8 per inch, making it highly effective in reducing heat transfer. It is non-combustible, moisture-resistant, and provides sound-dampening properties, suitable for residential and commercial buildings. Smart fiber insulation, by comparison, integrates advanced materials for enhanced adaptability and energy efficiency but glass fiber remains a cost-effective, widely-used solution for reliable thermal insulation.
Thermal Efficiency Comparison
Smart fiber insulation offers superior thermal efficiency compared to traditional glass fiber due to its advanced material composition that reduces heat transfer more effectively. Its enhanced thermal resistance (R-value) preserves indoor temperatures better, resulting in lower energy consumption for heating and cooling. Glass fiber provides decent insulation but generally exhibits higher thermal conductivity, making smart fiber a more cost-effective solution for energy-efficient building design.
Moisture Resistance and Durability
Smart fiber insulation, engineered with hydrophobic treatments, offers superior moisture resistance compared to traditional glass fiber, reducing mold growth and maintaining thermal performance in humid environments. Glass fiber insulation, while durable and cost-effective, tends to absorb moisture, potentially diminishing its insulating properties and lifespan over time. Advanced smart fibers also exhibit enhanced structural integrity, providing long-term durability that outperforms conventional glass fiber under fluctuating temperature and moisture conditions.
Installation and Flexibility
Smart fiber insulation offers superior flexibility, allowing for easier installation in tight or irregular spaces compared to traditional glass fiber. Its lightweight and bendable structure reduces labor time and minimizes gaps that could compromise thermal performance. Glass fiber, while effective in thermal insulation, tends to be rigid and brittle, making installation more challenging and less adaptable to complex architectural designs.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Smart fiber insulation, often made from recycled materials and engineered for superior thermal performance, significantly reduces energy consumption and carbon footprint compared to traditional glass fiber insulation. Glass fiber, while effective in thermal resistance, requires energy-intensive manufacturing processes that emit higher levels of greenhouse gases and are less recyclable. Choosing smart fiber promotes sustainability by lowering environmental impact through enhanced energy efficiency and reduced resource depletion.
Safety and Health Considerations
Smart fiber insulation excels in safety by being non-toxic, hypoallergenic, and resistant to mold and mildew, reducing respiratory risks and enhancing indoor air quality compared to traditional glass fiber insulation. Glass fiber, while effective in thermal performance, can release microscopic glass particles that may irritate skin, eyes, and lungs, posing health hazards during installation and over time. Choosing smart fiber insulation prioritizes occupant health through safer material composition and improved air purity, making it a superior option for residential and commercial buildings.
Cost Analysis: Smart Fiber vs Glass Fiber
Smart fiber insulation offers a higher initial cost compared to traditional glass fiber, but its superior thermal performance often leads to greater long-term energy savings. Glass fiber remains the more affordable option upfront, making it popular for budget-conscious projects, yet it typically requires more maintenance and replacement over time. Evaluating total cost of ownership, smart fiber's durability and enhanced insulation efficiency can provide better value despite the higher upfront investment.
Choosing the Right Insulation for Your Needs
Smart fiber insulation offers enhanced thermal performance and moisture resistance compared to traditional glass fiber, making it ideal for energy-efficient homes and humid climates. Glass fiber remains a cost-effective solution with proven fire resistance and ease of installation, suitable for standard residential and commercial applications. Selecting insulation depends on factors like climate, budget, and specific thermal requirements, with smart fiber preferred for superior energy savings and glass fiber favored for affordability and widespread availability.
Infographic: Smart fiber vs Glass fiber for Insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com