Recycled fiber offers enhanced sustainability by minimizing waste and reducing environmental impact in bag manufacturing, while jute fiber provides natural biodegradability and strong durability. Choosing recycled fiber supports circular economy goals, whereas jute fiber emphasizes eco-friendly cultivation and renewable sourcing.
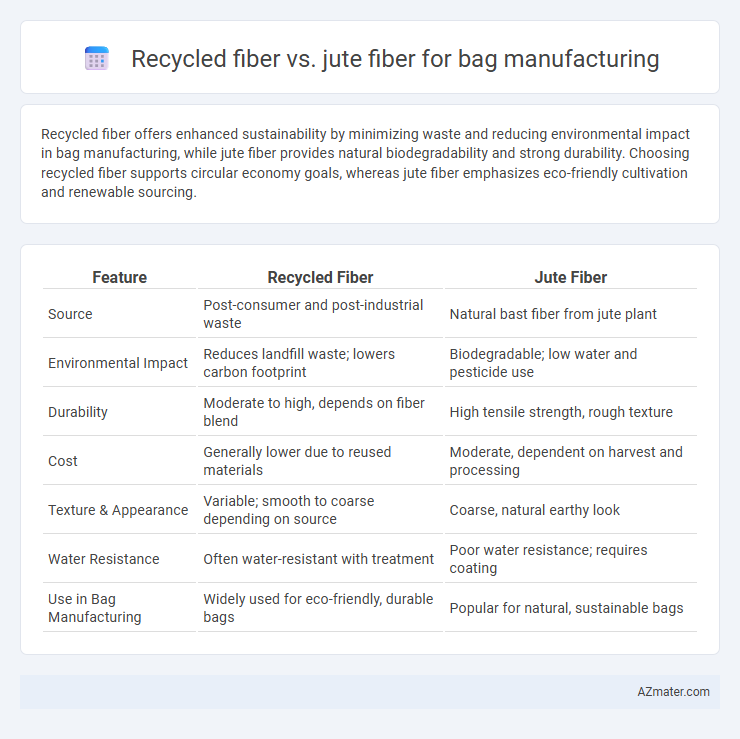
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Recycled Fiber | Jute Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Post-consumer and post-industrial waste | Natural bast fiber from jute plant |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces landfill waste; lowers carbon footprint | Biodegradable; low water and pesticide use |
| Durability | Moderate to high, depends on fiber blend | High tensile strength, rough texture |
| Cost | Generally lower due to reused materials | Moderate, dependent on harvest and processing |
| Texture & Appearance | Variable; smooth to coarse depending on source | Coarse, natural earthy look |
| Water Resistance | Often water-resistant with treatment | Poor water resistance; requires coating |
| Use in Bag Manufacturing | Widely used for eco-friendly, durable bags | Popular for natural, sustainable bags |
Introduction to Sustainable Bag Materials
Recycled fiber and jute fiber are prominent sustainable materials in bag manufacturing due to their eco-friendly properties and renewability. Recycled fibers reduce waste by repurposing materials such as plastic bottles or old textiles, lowering environmental impact through resource conservation and decreased landfill use. Jute fiber, derived from the jute plant, offers biodegradability, natural strength, and minimal water and pesticide requirements, establishing it as a renewable alternative that supports sustainable fashion and packaging industries.
What are Recycled Fibers?
Recycled fibers are materials reclaimed from waste textiles, paper, or plastics that are processed and spun into new fibers for manufacturing, providing an eco-friendly alternative to virgin fibers. These fibers reduce environmental impact by minimizing landfill waste, lowering energy consumption, and conserving natural resources compared to traditional fibers like jute. In bag manufacturing, recycled fibers offer versatility and durability while supporting sustainable production practices.
Understanding Jute Fiber Properties
Jute fiber is a natural, biodegradable material known for its high tensile strength, durability, and moisture resistance, making it ideal for eco-friendly bag manufacturing. Compared to recycled fibers, jute offers superior breathability and a coarse texture that enhances the bag's structural integrity and aesthetic appeal. Its renewable nature and lower carbon footprint contribute to sustainable production practices within the textile industry.
Environmental Impact: Recycled Fiber vs Jute Fiber
Recycled fiber reduces landfill waste and conserves resources by reusing existing materials, significantly lowering carbon emissions compared to virgin fibers. Jute fiber, a natural and biodegradable material, offers sustainability through its rapid growth and minimal agricultural inputs like pesticides and fertilizers. While recycled fibers mitigate waste through circularity, jute fibers contribute to soil health and carbon sequestration, making both environmentally advantageous with different ecological benefits.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Recycled fiber offers moderate strength and durability, making it suitable for lightweight and eco-friendly bag manufacturing, but it generally lacks the tensile strength of jute fiber. Jute fiber is renowned for its high tensile strength and natural durability, providing superior resistance to wear and tear, which ensures longer-lasting bags. Bags made from jute fiber are ideal for heavy-duty use due to their robust and biodegradable properties, whereas recycled fiber bags prioritize sustainability with a compromise on long-term strength.
Cost Analysis: Recycled Fiber vs Jute Fiber Bags
Recycled fiber bags generally offer lower material costs compared to jute fiber bags due to the utilization of post-consumer or industrial waste, reducing raw material expenses. Jute fiber, being a natural and biodegradable resource, often incurs higher costs linked to cultivation, harvesting, and processing, impacting the overall price of jute bags. When assessing long-term cost efficiency, recycled fiber bags may provide savings in production, but jute fiber bags command premium pricing due to sustainability and durability factors.
Aesthetics and Design Flexibility
Recycled fiber offers superior design flexibility for bag manufacturing due to its ability to blend with various materials and easily take on different colors and textures, enabling innovative and customized aesthetics. Jute fiber, while limited by its natural coarse texture and earthy tones, provides a rustic, eco-friendly appeal highly valued in sustainable fashion markets. Both fibers deliver unique visual qualities, with recycled fiber excelling in versatility and jute fiber in natural, organic charm.
Production Process and Energy Consumption
Recycled fiber production for bag manufacturing involves reprocessing waste textiles or plastics, significantly reducing raw material extraction and minimizing energy use by up to 50% compared to virgin fibers. Jute fiber extraction is a natural process involving retting, stripping, and drying, which is labor-intensive and consumes moderate amounts of water and energy, although often less mechanized energy than synthetic fiber production. The overall energy consumption for recycled fibers can be lower due to avoided raw material cultivation, while jute relies on agricultural inputs and manual processing stages that define its environmental footprint.
Consumer Preferences and Market Trends
Consumer preferences for recycled fiber bags emphasize environmental sustainability and reduced carbon footprint, appealing to eco-conscious buyers. Jute fiber bags gain popularity due to their natural biodegradability, durability, and traditional aesthetic, meeting demands for organic and artisanal products. Market trends indicate a growing segment favoring recycled fibers in urban markets, while jute remains dominant in regions valuing heritage and natural textures.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Fiber for Eco-Friendly Bags
Recycled fiber offers a sustainable option by reducing waste and conserving resources, while jute fiber provides natural biodegradability and strong durability. Eco-friendly bag manufacturing benefits from recycled fibers' versatility and lower environmental footprint, whereas jute contributes to soil health and carbon sequestration during cultivation. Selecting the best fiber depends on balancing performance requirements with environmental impact, making recycled fiber ideal for circular economy goals and jute fiber preferable for renewable, compostable products.
Infographic: Recycled fiber vs Jute fiber for Bag manufacturing
 azmater.com
azmater.com