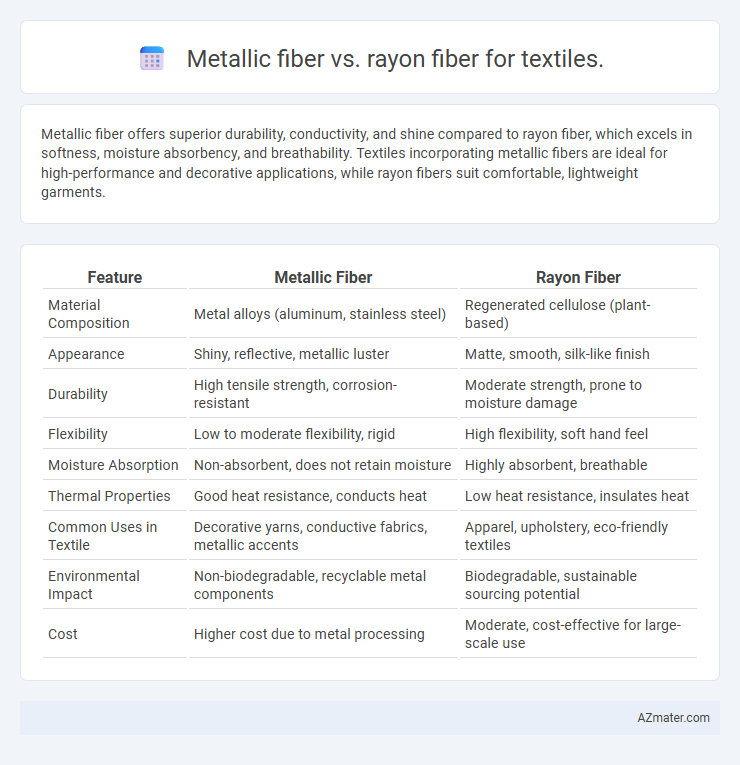
Metallic fiber offers superior durability, conductivity, and shine compared to rayon fiber, which excels in softness, moisture absorbency, and breathability. Textiles incorporating metallic fibers are ideal for high-performance and decorative applications, while rayon fibers suit comfortable, lightweight garments.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Metallic Fiber | Rayon Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Metal alloys (aluminum, stainless steel) | Regenerated cellulose (plant-based) |
| Appearance | Shiny, reflective, metallic luster | Matte, smooth, silk-like finish |
| Durability | High tensile strength, corrosion-resistant | Moderate strength, prone to moisture damage |
| Flexibility | Low to moderate flexibility, rigid | High flexibility, soft hand feel |
| Moisture Absorption | Non-absorbent, does not retain moisture | Highly absorbent, breathable |
| Thermal Properties | Good heat resistance, conducts heat | Low heat resistance, insulates heat |
| Common Uses in Textile | Decorative yarns, conductive fabrics, metallic accents | Apparel, upholstery, eco-friendly textiles |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable, recyclable metal components | Biodegradable, sustainable sourcing potential |
| Cost | Higher cost due to metal processing | Moderate, cost-effective for large-scale use |
Introduction: Comparing Metallic and Rayon Fibers in Textiles
Metallic fibers, composed of metal-coated or metal-based strands, provide textiles with enhanced durability, reflectivity, and heat resistance compared to rayon fibers, which are regenerated cellulose fibers known for their softness, breathability, and moisture absorption. Metallic fibers are commonly used in high-performance and decorative fabrics, offering unique conductivity and aesthetic appeal, whereas rayon is favored for comfort-focused apparel and home textiles due to its silk-like texture and dye retention qualities. The choice between metallic and rayon fibers significantly impacts the textile's functional properties, including strength, flexibility, and environmental resistance.
Chemical Composition of Metallic vs Rayon Fibers
Metallic fibers primarily consist of metal-coated plastics, often aluminum or stainless steel, providing durability and reflective properties. Rayon fibers are regenerated cellulose fibers derived from wood pulp, featuring a chemical composition rich in cellulose polysaccharides, which contributes to their softness and moisture absorption. The chemical composition contrast impacts their performance, with metallic fibers offering strength and luster, while rayon fibers excel in breathability and comfort.
Manufacturing Processes: Metallic Fiber vs Rayon Fiber
Metallic fiber manufacturing involves processes such as metal drawing, cutting, and sometimes plating to achieve fine filaments, whereas rayon fiber production requires the chemically intensive viscose or lyocell process, where cellulose is dissolved and regenerated into fibers. Metallic fibers are produced through metal extrusion and then mechanically processed to achieve flexibility, while rayon fibers rely on wet spinning techniques and subsequent washing, stretching, and drying stages. The distinct manufacturing pathways impact fiber properties such as durability, luster, and moisture absorption, influencing their application in textile blends.
Physical Properties and Appearance
Metallic fiber exhibits superior tensile strength, high elasticity, and excellent durability compared to rayon fiber, which is softer and more absorbent but less resilient. The appearance of metallic fiber features a shiny, reflective surface ideal for decorative and high-fashion textiles, while rayon fiber offers a smooth, silky texture with a matte or slightly lustrous finish that mimics natural fibers. Physical properties such as thermal conductivity and resistance to moisture differ significantly, with metallic fibers providing enhanced heat dissipation and moisture resistance, while rayon fibers absorb moisture and provide comfort in wearable textiles.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Metallic fibers exhibit superior durability and tensile strength compared to rayon fibers, making them ideal for textiles requiring long-lasting wear and resistance to tearing. Rayon, a semi-synthetic fiber derived from cellulose, tends to have lower abrasion resistance and is more prone to weakening when exposed to moisture. The enhanced strength of metallic fibers provides better structural integrity in high-performance or decorative fabrics, whereas rayon is favored for its softness and drapability but lacks comparable durability.
Comfort and Wearability: Which Fiber Performs Better?
Metallic fibers, often made from metals like aluminum or stainless steel, provide durability and aesthetic appeal but tend to lack breathability and softness, leading to reduced comfort in textiles. Rayon fibers, derived from cellulose, offer superior breathability, moisture absorption, and softness, enhancing overall wearability and comfort in garments. For textiles prioritizing comfort and everyday wearability, rayon fibers generally outperform metallic fibers due to their skin-friendly and flexible properties.
Applications in Fashion and Technical Textiles
Metallic fiber offers high durability, shine, and conductivity, making it ideal for fashion textiles that require glamour and futuristic aesthetics, as well as technical textiles used in electromagnetic shielding and wearable technology. Rayon fiber provides excellent moisture absorption, softness, and breathability, preferred in fashion for comfortable and drapable garments and in technical textiles for medical dressing and filtration applications. The choice between metallic and rayon fibers depends on the desired performance attributes, with metallic fibers excelling in visual impact and functionality, while rayon fibers emphasize comfort and biodegradability.
Cost and Economic Considerations
Metallic fibers generally incur higher production costs due to expensive raw materials like aluminum or stainless steel and specialized manufacturing processes, making them less economically viable for large-scale textile applications. Rayon fibers, derived from cellulose and produced through cost-effective chemical processing, offer a more affordable alternative with good versatility and softness, contributing to their widespread use in the textile industry. Cost-efficiency and scalability position rayon as a preferred choice for budget-conscious manufacturers, while metallic fibers are reserved for niche markets requiring enhanced durability or aesthetic appeal.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Metallic fibers, derived from metals such as aluminum or stainless steel, pose significant environmental challenges due to their energy-intensive production and difficulty in recycling, leading to increased landfill waste. Rayon fiber, a semi-synthetic material made from cellulose, offers better biodegradability but often involves chemical-intensive manufacturing processes that contribute to water pollution and deforestation. Sustainable textile choices favor innovative, closed-loop rayon production methods and recycled metallic fibers to minimize ecological footprints and reduce harmful emissions.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Fiber for Your Textile Needs
Metallic fiber offers exceptional durability, excellent conductivity, and a unique aesthetic ideal for high-performance and decorative textiles, whereas rayon fiber provides superior softness, breathability, and moisture absorption suitable for everyday apparel and comfortable fabrics. The choice between metallic and rayon fibers largely depends on the intended application, balancing functional benefits such as durability and conductivity against comfort and cost-efficiency. Selecting the right fiber requires evaluating the textile's end-use, whether prioritizing performance or wearability, to optimize fabric quality and user experience.
Infographic: Metallic fiber vs Rayon fiber for Textile
 azmater.com
azmater.com