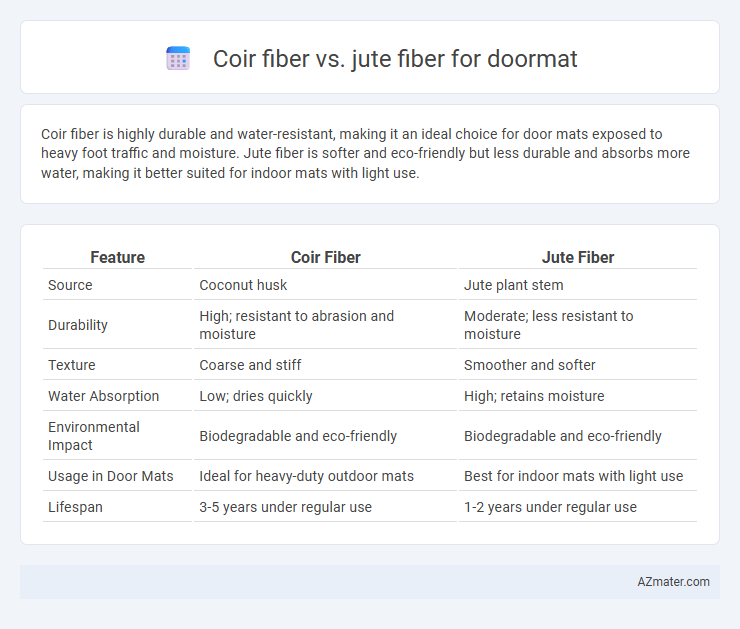
Coir fiber is highly durable and water-resistant, making it an ideal choice for door mats exposed to heavy foot traffic and moisture. Jute fiber is softer and eco-friendly but less durable and absorbs more water, making it better suited for indoor mats with light use.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Coir Fiber | Jute Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Coconut husk | Jute plant stem |
| Durability | High; resistant to abrasion and moisture | Moderate; less resistant to moisture |
| Texture | Coarse and stiff | Smoother and softer |
| Water Absorption | Low; dries quickly | High; retains moisture |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable and eco-friendly | Biodegradable and eco-friendly |
| Usage in Door Mats | Ideal for heavy-duty outdoor mats | Best for indoor mats with light use |
| Lifespan | 3-5 years under regular use | 1-2 years under regular use |
Introduction to Coir Fiber and Jute Fiber
Coir fiber, derived from the outer husk of coconut shells, is renowned for its durability and natural water resistance, making it an excellent choice for door mats exposed to heavy foot traffic and moisture. Jute fiber, obtained from the stalks of the jute plant, is softer and more biodegradable, offering eco-friendly benefits and a rustic aesthetic ideal for indoor door mats. Both fibers provide sustainable options but differ significantly in texture, resilience, and environmental impact for door mat applications.
Origin and Production Process
Coir fiber, derived from the husk of coconut shells primarily in India and Sri Lanka, undergoes a retting and decorticating process to extract coarse, durable strands ideal for door mats. Jute fiber, sourced from the stalks of Corchorus plants mainly cultivated in Bangladesh and India, is produced through retting in water, followed by stripping, washing, and drying, resulting in a softer, more pliable fiber. The robust coir fibers provide superior water resistance and durability compared to the finer, more biodegradable jute fibers commonly used for eco-friendly mats.
Physical Characteristics Comparison
Coir fiber, derived from coconut husks, exhibits coarse texture and high durability, making it highly abrasion-resistant and ideal for heavy-duty door mats. Jute fiber, sourced from the jute plant, possesses a softer, finer texture with moderate strength and moisture absorbency, suitable for indoor mats with lighter foot traffic. Both fibers differ significantly in density and flexibility, with coir offering greater rigidity and jute providing enhanced pliability in door mat applications.
Durability and Longevity
Coir fiber, derived from coconut husks, offers superior durability and resistance to wear, making it ideal for heavy-traffic door mats that require long-lasting performance. Jute fiber, though softer and biodegradable, tends to degrade faster under constant foot traffic and moisture exposure, resulting in reduced longevity. Choosing coir ensures a robust door mat with enhanced lifespan and resilience against dirt and abrasion.
Water and Moisture Resistance
Coir fiber offers superior water and moisture resistance compared to jute fiber, making it ideal for door mats exposed to wet conditions. Its natural wax content repels water, preventing mold and mildew buildup, while jute tends to absorb moisture, weakening its durability over time. Coir's robust structure ensures long-lasting performance in humid environments, whereas jute mats may deteriorate faster due to higher water retention.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Coir fiber, derived from coconut husks, boasts superior biodegradability and requires less water and chemical processing compared to jute fiber, making it a more environmentally friendly choice for door mats. Jute fiber, while also biodegradable and renewable, involves intensive water usage and pesticide application during cultivation, contributing to higher ecological footprints. Both fibers support sustainable farming, but coir's utilization of agricultural waste and minimal processing enhances its overall sustainability in eco-friendly door mat production.
Cleaning and Maintenance
Coir fiber door mats excel in dirt and moisture trapping due to their rough texture, requiring occasional shaking or hosing for efficient cleaning. Jute fiber mats are softer and more biodegradable but absorb water readily, demanding gentle brushing and air drying to prevent mold. Both materials benefit from regular maintenance, but coir's durability makes it preferable for heavy-duty cleaning needs.
Design Versatility and Aesthetics
Coir fiber offers superior durability and a natural, coarse texture that enhances rustic and traditional door mat designs, making it ideal for high-traffic areas. Jute fiber provides a softer, smoother finish with greater flexibility, allowing intricate patterns and vibrant dye absorption for aesthetically versatile mats. Both fibers support eco-friendly production, but coir's resilience contrasts with jute's elegant appearance, influencing the choice based on design demands and visual appeal.
Cost Analysis
Coir fiber door mats generally have a higher initial cost compared to jute fiber mats due to the more labor-intensive extraction and processing of coir from coconut husks. However, coir mats offer greater durability and water resistance, potentially reducing replacement frequency and long-term expenses. Jute fiber mats are more affordable upfront but absorb moisture easily, which may lead to quicker wear and higher maintenance costs over time.
Choosing the Right Fiber for Door Mats
Coir fiber offers superior durability and water resistance, making it ideal for door mats exposed to heavy foot traffic and outdoor conditions. Jute fiber provides a softer texture and is more eco-friendly, suitable for indoor mats where comfort is prioritized. Selecting between coir and jute depends on balancing the need for resilience against environmental exposure and the desired aesthetic or tactile experience.
Infographic: Coir fiber vs Jute fiber for Door mat
 azmater.com
azmater.com