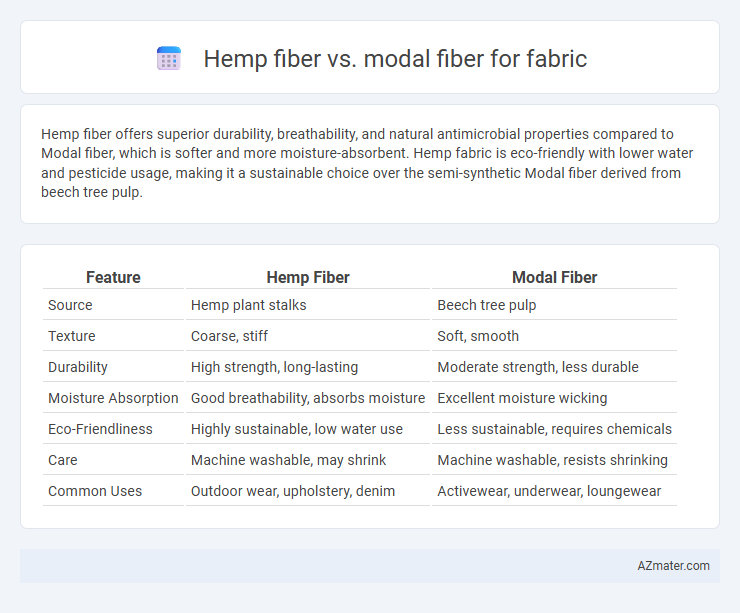
Hemp fiber offers superior durability, breathability, and natural antimicrobial properties compared to Modal fiber, which is softer and more moisture-absorbent. Hemp fabric is eco-friendly with lower water and pesticide usage, making it a sustainable choice over the semi-synthetic Modal fiber derived from beech tree pulp.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Hemp Fiber | Modal Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Hemp plant stalks | Beech tree pulp |
| Texture | Coarse, stiff | Soft, smooth |
| Durability | High strength, long-lasting | Moderate strength, less durable |
| Moisture Absorption | Good breathability, absorbs moisture | Excellent moisture wicking |
| Eco-Friendliness | Highly sustainable, low water use | Less sustainable, requires chemicals |
| Care | Machine washable, may shrink | Machine washable, resists shrinking |
| Common Uses | Outdoor wear, upholstery, denim | Activewear, underwear, loungewear |
Introduction to Hemp and Modal Fibers
Hemp fiber, derived from the stalks of the Cannabis sativa plant, is renowned for its durability, breathability, and natural resistance to pests and UV rays, making it a sustainable choice for eco-friendly fabrics. Modal fiber, a type of rayon made from beech tree cellulose, offers exceptional softness, high moisture absorbency, and a smooth texture, ideal for comfortable, luxurious textiles. Both fibers serve distinct purposes in fabric production, with hemp emphasizing strength and environmental benefits, while modal prioritizes comfort and softness.
Source and Production Processes
Hemp fiber is derived from the stalks of the Cannabis sativa plant, where the fibers are extracted through retting and decortication, resulting in a durable, coarse material ideal for sustainable textiles. Modal fiber originates from beech tree pulp, produced via a chemically intensive process involving enzymatic treatment to create a soft and flexible fabric praised for its breathability and smooth texture. The natural sourcing of hemp emphasizes environmental sustainability, while modal's production relies on industrial processing for enhanced fabric softness and drape.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Hemp fiber offers significant environmental benefits due to its rapid growth, minimal water requirements, and natural resistance to pests, reducing the need for harmful pesticides and fertilizers. Modal fiber, derived from beech trees through a chemically intensive process, involves higher water consumption and chemical use, raising concerns about its ecological footprint. Choosing hemp fiber over modal fabric supports sustainable agriculture and lower environmental degradation, making it a more eco-friendly option for textile production.
Fiber Strength and Durability
Hemp fiber exhibits exceptional strength and durability, often surpassing modal fiber in tensile strength and resistance to wear, making it ideal for long-lasting fabric applications. Modal fiber, derived from beech trees, is softer and more flexible but tends to have lower tensile strength compared to hemp, which affects its durability under heavy use. Fabrics made from hemp fiber maintain structural integrity over time, while modal fabrics require more careful handling to prevent pilling and tearing.
Comfort and Breathability
Hemp fiber offers exceptional breathability and natural moisture-wicking properties, making it highly comfortable for warm-weather clothing. Modal fiber, derived from beech trees, provides a soft, silky texture with excellent moisture absorption and smooth drape, enhancing comfort for sensitive skin. Both fibers deliver superior breathability, but hemp is more durable and eco-friendly, while modal excels in softness and flexibility.
Moisture Absorption and Wicking
Hemp fiber exhibits high moisture absorption and superior wicking properties, making it ideal for breathable and quick-drying fabrics. Modal fiber also offers excellent moisture management with a soft texture, but its absorption rate is slightly lower than hemp, which affects drying time. Fabrics blended with hemp typically maintain better moisture regulation for activewear and eco-friendly textiles.
Dyeability and Color Retention
Hemp fiber exhibits excellent dyeability due to its natural cellulose content, allowing vibrant and long-lasting colors with both reactive and vat dyes. Modal fiber, a type of semi-synthetic cellulose fiber, absorbs dyes effectively, offering rich color depth and smooth texture, but may show slight fading over extended wash cycles. Both fibers provide good color retention, with hemp being more resistant to UV degradation, enhancing fabric durability in outdoor use.
Cost and Market Availability
Hemp fiber is generally more cost-effective due to its low cultivation expenses and high yield per acre, making it widely accessible in sustainable textile markets. Modal fiber, derived from beech tree pulp, tends to be more expensive because of its complex manufacturing process and limited production regions. Market availability favors hemp in eco-friendly fabric segments, while modal is popular in premium, soft-to-the-touch apparel fabrics but remains less widespread overall.
Sustainability and Eco-Friendliness
Hemp fiber ranks higher in sustainability due to its rapid growth, low water usage, and ability to enrich soil through phytoremediation, making it an eco-friendly choice for fabric production. Modal fiber, derived from beech tree cellulose, offers biodegradability and a softer texture, but its manufacturing process involves chemical treatments that can impact environmental safety if not properly managed. Choosing hemp fabric supports carbon sequestration and reduced pesticide dependency, while modal's sustainability depends on responsible sourcing and closed-loop processing technologies.
Choosing the Right Fiber for Fabrics
Hemp fiber offers superior durability and breathability, making it ideal for eco-friendly, long-lasting fabrics, while modal fiber excels in softness and moisture-wicking, perfect for comfortable, lightweight garments. When choosing the right fiber for fabrics, consider hemp's natural resistance to UV rays and mildew versus modal's silky texture and ease of dyeing. The decision should align with the desired fabric properties, sustainability goals, and end-use applications such as activewear or casual clothing.
Infographic: Hemp fiber vs Modal fiber for Fabric
 azmater.com
azmater.com