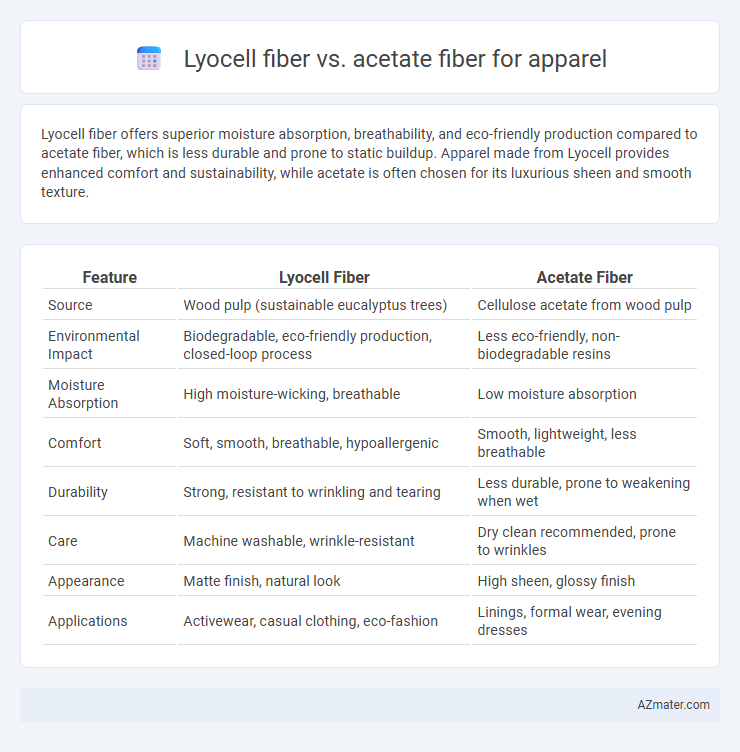
Lyocell fiber offers superior moisture absorption, breathability, and eco-friendly production compared to acetate fiber, which is less durable and prone to static buildup. Apparel made from Lyocell provides enhanced comfort and sustainability, while acetate is often chosen for its luxurious sheen and smooth texture.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Lyocell Fiber | Acetate Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Wood pulp (sustainable eucalyptus trees) | Cellulose acetate from wood pulp |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, eco-friendly production, closed-loop process | Less eco-friendly, non-biodegradable resins |
| Moisture Absorption | High moisture-wicking, breathable | Low moisture absorption |
| Comfort | Soft, smooth, breathable, hypoallergenic | Smooth, lightweight, less breathable |
| Durability | Strong, resistant to wrinkling and tearing | Less durable, prone to weakening when wet |
| Care | Machine washable, wrinkle-resistant | Dry clean recommended, prone to wrinkles |
| Appearance | Matte finish, natural look | High sheen, glossy finish |
| Applications | Activewear, casual clothing, eco-fashion | Linings, formal wear, evening dresses |
Introduction to Lyocell and Acetate Fibers
Lyocell fiber is a sustainable, biodegradable cellulose fiber derived from wood pulp, known for its softness, strength, and moisture-wicking properties, making it ideal for comfortable and eco-friendly apparel. Acetate fiber, a semi-synthetic fiber made from cellulose acetate, offers a luxurious sheen, excellent drape, and quick-drying characteristics, often used in linings and elegant garments. Both fibers serve distinct roles in apparel, with Lyocell emphasizing sustainability and comfort, while Acetate focuses on aesthetic appeal and smooth texture.
Manufacturing Processes: Lyocell vs Acetate
Lyocell fiber manufacturing involves a closed-loop process using non-toxic solvents, primarily N-Methylmorpholine N-oxide (NMMO), which dissolves cellulose from wood pulp, minimizing environmental impact and solvent recovery at over 99%. Acetate fiber production chemically modifies cellulose through acetylation with acetic anhydride, followed by solvent spinning using acetone, generating higher emissions and solvent recovery challenges. The sustainable, energy-efficient Lyocell process contrasts with the more chemically intensive and emission-prone acetate fiber manufacturing, influencing apparel production decisions based on ecological and safety considerations.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Lyocell fiber, derived from sustainably sourced wood pulp using a closed-loop production process, offers significant environmental advantages such as low water consumption and biodegradability, making it a highly sustainable choice for apparel. Acetate fiber, produced from cellulose acetate through chemical-intensive processes, generally involves higher environmental impact due to toxic solvent use and limited recyclability. Consumers and manufacturers increasingly favor Lyocell for eco-friendly apparel solutions promoting reduced carbon footprint and resource conservation.
Comfort and Feel: Wearability Comparison
Lyocell fiber exhibits superior moisture-wicking properties and breathability compared to acetate fiber, offering enhanced comfort and a soft, smooth feel against the skin. Acetate fiber, while lightweight and glossy, tends to retain heat and moisture, making it less breathable and potentially less comfortable for extended wear. Wearability-wise, lyocell's natural cellulosic composition promotes a cooler, more comfortable experience, especially in active or warm conditions, while acetate is favored for elegant draping but may lack the same level of comfort over long periods.
Moisture Management and Breathability
Lyocell fiber exhibits superior moisture management due to its hydrophilic nature, absorbing up to 50% more moisture than cotton and releasing it efficiently, enhancing wearer comfort. Its breathable structure allows excellent air permeability, promoting rapid drying and reducing heat retention in apparel. In contrast, acetate fiber offers moderate moisture wicking but tends to trap heat and moisture, resulting in lower breathability and less effective moisture management for active or warm-weather clothing.
Durability and Longevity in Apparel
Lyocell fiber exhibits superior durability and longevity in apparel due to its strong molecular structure and resistance to wear, making it ideal for long-lasting garments. Acetate fiber, while offering a smooth and luxurious feel, tends to have lower tensile strength and is more prone to degradation over time when exposed to heat and moisture. For apparel requiring frequent washing and extended use, Lyocell's resilience and ability to retain shape and color make it a more durable choice than Acetate.
Dyeing Properties and Color Retention
Lyocell fiber exhibits superior dyeing properties with excellent absorbency, allowing vibrant, uniform color uptake and enhanced colorfastness compared to acetate fiber. Acetate fiber, while capable of producing bright colors, tends to have lower wet and light fastness, often leading to color fading and bleeding over time. The strong molecular structure and moisture management of lyocell contribute to its improved color retention and longevity in apparel applications.
Cost and Market Availability
Lyocell fiber offers a higher production cost compared to acetate fiber due to its environmentally friendly manufacturing process, yet it benefits from increasing market demand driven by sustainable apparel trends. Acetate fiber remains more affordable and widely available in mass-market apparel, supported by its established supply chain and cost-efficient production methods. The growing consumer preference for eco-friendly textiles is gradually shifting market availability toward Lyocell despite its premium pricing.
Common Applications in Fashion
Lyocell fiber is widely used in fashion for sustainable apparel such as casual wear, activewear, and eco-friendly dresses due to its softness, breathability, and moisture-wicking properties. Acetate fiber finds common application in formal and evening wear, linings, and luxury garments because of its silky appearance, vibrant dyeability, and smooth texture. Both fibers offer distinct advantages, with Lyocell favored for comfort and sustainability, while Acetate emphasizes aesthetic appeal and drape quality.
Summary: Which Fiber is Better for Apparel?
Lyocell fiber offers superior moisture-wicking, breathability, and sustainability compared to acetate fiber, making it ideal for comfortable and eco-friendly apparel. Acetate fiber provides a luxurious sheen and smooth texture but lacks durability and moisture management, limiting its performance in active or long-lasting garments. For versatile, high-performance clothing, lyocell is generally the better choice due to its strength, biodegradability, and comfort properties.
Infographic: Lyocell fiber vs Acetate fiber for Apparel
 azmater.com
azmater.com