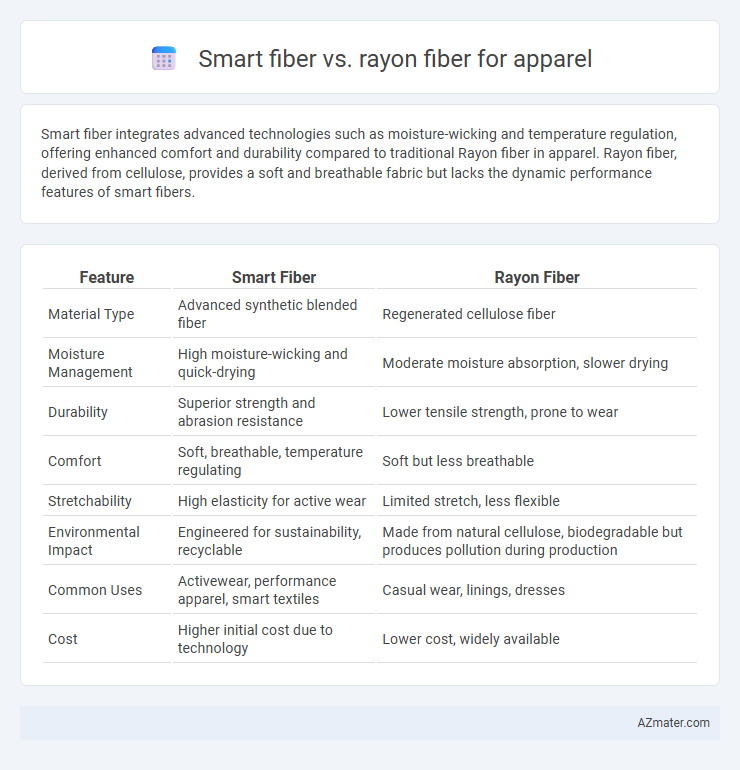
Smart fiber integrates advanced technologies such as moisture-wicking and temperature regulation, offering enhanced comfort and durability compared to traditional Rayon fiber in apparel. Rayon fiber, derived from cellulose, provides a soft and breathable fabric but lacks the dynamic performance features of smart fibers.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Smart Fiber | Rayon Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Advanced synthetic blended fiber | Regenerated cellulose fiber |
| Moisture Management | High moisture-wicking and quick-drying | Moderate moisture absorption, slower drying |
| Durability | Superior strength and abrasion resistance | Lower tensile strength, prone to wear |
| Comfort | Soft, breathable, temperature regulating | Soft but less breathable |
| Stretchability | High elasticity for active wear | Limited stretch, less flexible |
| Environmental Impact | Engineered for sustainability, recyclable | Made from natural cellulose, biodegradable but produces pollution during production |
| Common Uses | Activewear, performance apparel, smart textiles | Casual wear, linings, dresses |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to technology | Lower cost, widely available |
Introduction to Smart Fiber and Rayon Fiber
Smart fiber integrates advanced materials such as conductive polymers and nanotechnology, enabling dynamic responses to environmental stimuli like temperature, moisture, and light, making it highly functional for adaptive apparel. Rayon fiber, a semi-synthetic cellulose-based fiber derived from wood pulp, offers softness, breathability, and drape similar to natural fibers, commonly used to enhance comfort and aesthetic appeal in garments. The distinct properties of smart fiber and rayon fiber cater to different apparel needs, with smart fiber emphasizing innovation and interactivity, while rayon prioritizes comfort and natural feel.
Key Properties of Smart Fiber
Smart fiber in apparel offers enhanced moisture-wicking, temperature regulation, and odor resistance compared to traditional rayon fiber, which primarily provides softness and breathability. The advanced nanotechnology integrated into smart fibers allows them to adapt dynamically to environmental changes, improving wearer comfort and performance. These properties make smart fibers ideal for activewear and technical garments, where durability and functional benefits are paramount.
Key Properties of Rayon Fiber
Rayon fiber, made from regenerated cellulose, boasts high moisture absorbency and breathability, making it ideal for comfortable apparel. Its soft texture and excellent draping ability enhance garment aesthetics and wearability. Compared to smart fibers, rayon lacks inherent moisture management or antimicrobial properties but excels in biodegradability and dye retention.
Performance Comparison: Smart Fiber vs Rayon
Smart fiber outperforms rayon fiber in moisture-wicking, durability, and elasticity, making it ideal for high-performance apparel. Rayon excels in breathability and softness but tends to lose shape and strength when wet, unlike smart fibers engineered for enhanced resilience. Smart fibers also offer superior odor resistance and quick-drying properties, contributing to better overall comfort and longevity in activewear.
Comfort and Wearability in Apparel
Smart fiber enhances apparel comfort by providing moisture-wicking, breathability, and temperature regulation, outperforming rayon fiber in maintaining skin dryness and reducing irritation. Rayon fiber, while soft and smooth, lacks advanced moisture management, often resulting in less durability and a heavier feel during prolonged wear. Smart fiber's superior elasticity and quick-drying properties make it a preferred choice for activewear and daily clothing focused on comfort and wearability.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Smart fibers, often engineered with sustainable technologies like moisture-wicking and biodegradability, present a significant advantage over traditional Rayon fiber in apparel from an environmental perspective. Rayon, derived from cellulose but requiring heavy chemical processing and significant water use, contributes to pollution and deforestation concerns. Sustainable smart fibers reduce ecological footprints through eco-friendly production methods and enhanced durability, aligning better with the increasing demand for green textiles in the fashion industry.
Durability and Maintenance
Smart fiber exhibits superior durability compared to rayon fiber, maintaining its structural integrity through multiple washes and resisting wear and tear in apparel applications. Rayon fiber, while soft and breathable, tends to weaken when exposed to moisture and frequent laundering, leading to faster degradation and potential shrinkage. Maintenance of smart fiber fabrics is more straightforward, requiring less delicate care and offering enhanced resistance to wrinkles and stains, which extends the garment's lifespan.
Aesthetic and Design Flexibility
Smart fiber offers enhanced aesthetic appeal with its ability to incorporate advanced functionalities like color-changing and moisture-responsive properties, providing dynamic design possibilities for apparel. Rayon fiber, known for its smooth texture and excellent draping qualities, allows designers to create soft, flowing silhouettes that mimic natural fibers, ensuring classic elegance and versatility. The integration of smart fiber technology expands design flexibility beyond traditional fabrics, enabling innovative garment concepts that adapt to environmental conditions and user interaction.
Cost Considerations for Manufacturers
Smart fiber typically incurs higher initial costs than rayon fiber due to advanced technology integration and specialized manufacturing processes. Rayon fiber remains a cost-effective option, offering lower raw material and production expenses, which appeals to manufacturers prioritizing budget-friendly apparel lines. Long-term investment in smart fiber can yield value through enhanced functionality and durability, potentially offsetting higher upfront costs in competitive markets.
Future Trends in Apparel Fiber Technology
Smart fibers integrate advanced functionalities like temperature regulation, moisture sensing, and adaptive insulation, positioning them at the forefront of future apparel fiber technology. Rayon fiber, known for its softness and breathability, continues to be improved through sustainable production methods but lacks the embedded intelligence of smart fibers. The future trend in apparel fibers favors smart fibers for their ability to enhance wearer comfort and performance through responsive materials, driving innovation in wearable technology and smart textiles.
Infographic: Smart fiber vs Rayon fiber for Apparel
 azmater.com
azmater.com