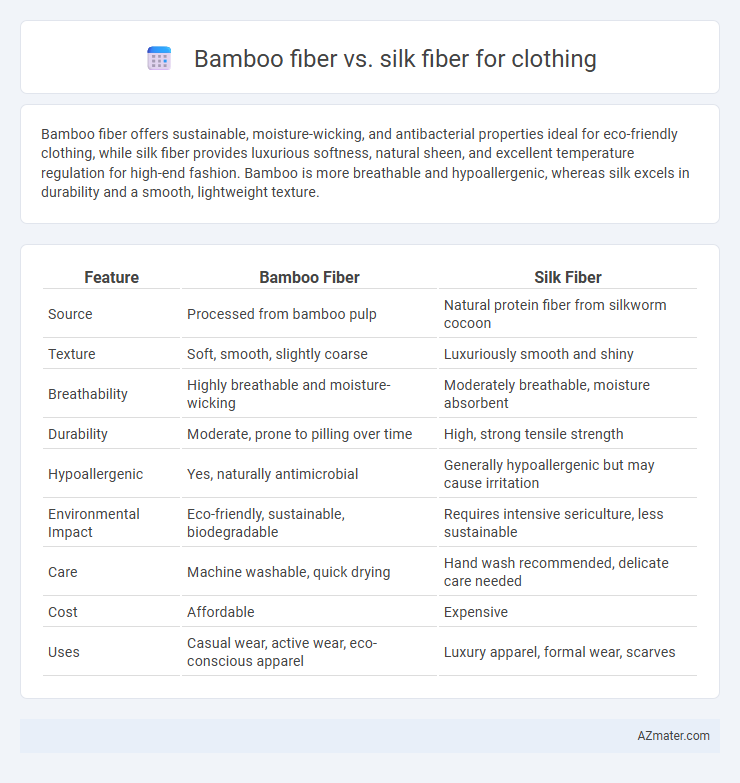
Bamboo fiber offers sustainable, moisture-wicking, and antibacterial properties ideal for eco-friendly clothing, while silk fiber provides luxurious softness, natural sheen, and excellent temperature regulation for high-end fashion. Bamboo is more breathable and hypoallergenic, whereas silk excels in durability and a smooth, lightweight texture.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bamboo Fiber | Silk Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Processed from bamboo pulp | Natural protein fiber from silkworm cocoon |
| Texture | Soft, smooth, slightly coarse | Luxuriously smooth and shiny |
| Breathability | Highly breathable and moisture-wicking | Moderately breathable, moisture absorbent |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to pilling over time | High, strong tensile strength |
| Hypoallergenic | Yes, naturally antimicrobial | Generally hypoallergenic but may cause irritation |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, sustainable, biodegradable | Requires intensive sericulture, less sustainable |
| Care | Machine washable, quick drying | Hand wash recommended, delicate care needed |
| Cost | Affordable | Expensive |
| Uses | Casual wear, active wear, eco-conscious apparel | Luxury apparel, formal wear, scarves |
Introduction to Bamboo and Silk Fibers
Bamboo fiber, derived from the pulp of bamboo grass, offers natural antibacterial properties, moisture-wicking abilities, and eco-friendly biodegradability, making it a sustainable choice for clothing manufacturing. Silk fiber, harvested from the cocoons of Bombyx mori silkworms, is renowned for its luxurious smooth texture, high tensile strength, and excellent breathability, often used in high-end apparel. Both fibers provide unique benefits in textile production, with bamboo favored for sustainability and silk celebrated for elegance and durability.
Origin and Production Process
Bamboo fiber originates from the pulp of bamboo plants, processed through either mechanical crushing and retting or chemical treatment to extract soft cellulose fibers suitable for fabric production. In contrast, silk fiber is produced naturally by silkworms that spin cocoons, which are then harvested and carefully unwound to obtain long, continuous silk threads. Bamboo fiber production emphasizes sustainability and rapid renewability, while silk fiber production relies on sericulture, involving labor-intensive cultivation of silkworms and precise harvesting techniques.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Bamboo fiber offers significant environmental benefits due to its rapid growth, requiring minimal water and no pesticides, making it a highly renewable resource compared to silk, which involves labor-intensive sericulture and high water consumption. Silk production relies on the cultivation of mulberry trees and the harvesting of silkworm cocoons, often raising ethical concerns and generating more greenhouse gases. Bamboo's biodegradability and lower carbon footprint make it a more sustainable choice for eco-conscious clothing manufacturers aiming to reduce environmental impact.
Texture and Softness Comparison
Bamboo fiber boasts a smooth, silky texture that rivals natural silk while offering superior breathability and moisture-wicking properties, making it ideal for sensitive skin. Silk fiber, renowned for its luxuriously soft and glossy feel, provides a natural sheen and exceptional smoothness that enhances garment elegance. Bamboo fiber tends to be softer over time with washing, whereas silk retains its delicate softness but requires more delicate care to maintain texture.
Moisture-Wicking and Breathability
Bamboo fiber outperforms silk fiber in moisture-wicking due to its highly absorbent and breathable structure, which efficiently pulls moisture away from the skin to keep the wearer dry. Bamboo fabric's natural micro-gaps enhance airflow, providing superior breathability compared to the smoother surface of silk that traps heat and moisture. Both fibers offer comfort, but bamboo's combination of moisture management and ventilation makes it ideal for activewear and hot climates.
Durability and Longevity
Bamboo fiber offers exceptional durability due to its natural tensile strength and resistance to wear, making it ideal for long-lasting clothing. Silk fiber, while renowned for its luxurious texture, tends to be more delicate and prone to damage from abrasion and sunlight, reducing its overall longevity. When comparing durability and lifespan, bamboo fiber outperforms silk by maintaining fabric integrity under frequent use and washing.
Allergenicity and Skin Friendliness
Bamboo fiber exhibits low allergenicity due to its natural antimicrobial properties, making it highly suitable for sensitive skin and individuals prone to allergies. Silk fiber, known for its smooth texture and hypoallergenic qualities, also offers excellent skin compatibility but can sometimes cause irritation in people with protein-based allergies. Both fibers are breathable and moisture-wicking, enhancing comfort, though bamboo's inherent antibacterial effects provide a superior option for minimizing skin irritation and allergic reactions.
Care and Maintenance Requirements
Bamboo fiber clothing requires gentle washing with mild detergent and air drying to maintain its softness and durability, while avoiding bleach and high heat that can weaken the fibers. Silk fiber garments demand delicate hand washing or dry cleaning, using cold water and silk-specific detergents, with careful handling to prevent snagging and prolonged exposure to sunlight that can cause fading. Both fibers benefit from proper storage in a cool, dry place to preserve texture and longevity, but silk's natural protein structure necessitates greater caution against moisture and pests.
Cost and Market Availability
Bamboo fiber offers a cost-effective alternative to silk fiber, typically priced lower due to its rapid renewability and simpler production process. While silk remains a premium fabric with limited availability due to labor-intensive harvesting from silkworms, bamboo fiber is more widely accessible in the textile market. The increased market availability of bamboo fiber supports its growing use in sustainable and affordable clothing lines compared to the niche, high-cost silk fiber segment.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Fiber for Clothing
Bamboo fiber offers exceptional moisture-wicking, antibacterial properties, and sustainability, making it ideal for activewear and eco-conscious consumers. Silk fiber excels in luxury, softness, temperature regulation, and durability, suited for formal wear and high-end garments. Selecting between bamboo and silk depends on priorities such as environmental impact, comfort, and garment purpose.
Infographic: Bamboo fiber vs Silk fiber for Clothing
 azmater.com
azmater.com