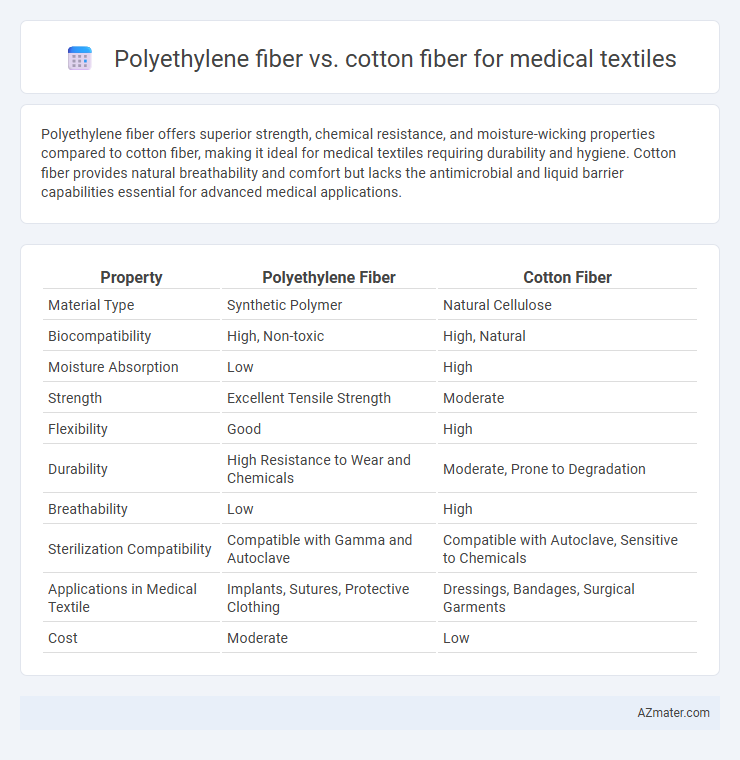
Polyethylene fiber offers superior strength, chemical resistance, and moisture-wicking properties compared to cotton fiber, making it ideal for medical textiles requiring durability and hygiene. Cotton fiber provides natural breathability and comfort but lacks the antimicrobial and liquid barrier capabilities essential for advanced medical applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyethylene Fiber | Cotton Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic Polymer | Natural Cellulose |
| Biocompatibility | High, Non-toxic | High, Natural |
| Moisture Absorption | Low | High |
| Strength | Excellent Tensile Strength | Moderate |
| Flexibility | Good | High |
| Durability | High Resistance to Wear and Chemicals | Moderate, Prone to Degradation |
| Breathability | Low | High |
| Sterilization Compatibility | Compatible with Gamma and Autoclave | Compatible with Autoclave, Sensitive to Chemicals |
| Applications in Medical Textile | Implants, Sutures, Protective Clothing | Dressings, Bandages, Surgical Garments |
| Cost | Moderate | Low |
Introduction to Medical Textiles
Polyethylene fiber in medical textiles offers superior biocompatibility, chemical resistance, and strength, making it ideal for surgical gowns, wound dressings, and implantable devices. Cotton fiber, valued for its natural breathability and absorbency, remains prominent in products like bandages, swabs, and patient gowns due to its comfort and hypoallergenic properties. The integration of these fibers in medical textiles balances durability, patient comfort, and infection control, essential for healthcare applications.
Overview of Polyethylene Fiber
Polyethylene fiber in medical textiles is renowned for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, chemical resistance, and low moisture absorption, making it ideal for surgical gowns and wound dressings. Unlike cotton fiber, which is natural and highly absorbent, polyethylene offers superior barrier properties against bacteria and fluids, enhancing infection control. Its durability and easy sterilization capabilities contribute significantly to its growing use in high-performance medical textile applications.
Overview of Cotton Fiber
Cotton fiber, a natural cellulose-based material, is widely recognized in medical textiles for its breathability, hypoallergenic properties, and excellent moisture absorption, making it ideal for bandages and surgical gowns. Its biodegradability and comfort enhance patient compliance, while its strength and softness support wound care by minimizing irritation. Compared to polyethylene fiber, cotton offers superior natural fiber characteristics essential for sensitive medical applications.
Physical and Mechanical Properties Comparison
Polyethylene fibers exhibit higher tensile strength and greater resistance to moisture absorption compared to cotton fibers, making them more durable and less prone to microbial growth in medical textiles. Cotton fibers offer superior breathability and skin comfort due to their natural cellulose composition, but they have lower abrasion resistance and tensile strength relative to polyethylene. The physical properties of polyethylene, including low density and hydrophobicity, enhance the mechanical performance of medical textiles in sterilized environments, whereas cotton fibers provide better biodegradability and softness for patient comfort.
Biocompatibility and Safety in Medical Applications
Polyethylene fiber exhibits superior biocompatibility with minimal risk of allergic reactions or immune responses, making it ideal for wound dressings and surgical implants. Cotton fiber, though natural and breathable, can harbor contaminants and triggers allergic reactions in sensitive patients, thereby limiting its safety in sterile medical environments. Medical textiles demand materials like polyethylene that ensure hypoallergenic properties, non-toxicity, and consistent sterility for patient safety and effective healing.
Breathability and Moisture Management
Polyethylene fiber in medical textiles offers superior moisture-wicking properties and enhanced breathability due to its hydrophobic nature, which helps maintain a dry microenvironment crucial for wound care. Cotton fiber excels in natural absorbency and comfort but retains moisture longer, potentially increasing microbial growth risk in medical settings. The choice between polyethylene and cotton fibers depends on the required balance of breathability and moisture management for specific medical textile applications.
Sterilization and Hygiene Considerations
Polyethylene fiber offers superior resistance to chemicals and high-temperature sterilization methods like autoclaving, maintaining its structural integrity and reducing contamination risks in medical textiles. Cotton fiber, while breathable and comfortable, tends to absorb moisture and may harbor microbes, making it less ideal for strict hygiene standards without rigorous sterilization procedures. The non-porous nature of polyethylene fibers enhances hygienic conditions, ensuring faster drying and minimizing bacterial growth compared to natural cotton fibers.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyethylene fiber in medical textiles offers significant advantages in environmental impact due to its recyclability and lower water usage during production compared to cotton fiber. Cotton cultivation requires extensive water, fertilizers, and pesticides, contributing to soil degradation and higher carbon emissions. Polyethylene fiber's durability enables longer lifespan and reduced waste generation, enhancing sustainability in medical textile applications.
Cost-Efficiency and Availability
Polyethylene fiber offers superior cost-efficiency in medical textiles due to its lower production costs and longer durability compared to cotton fiber, which requires more frequent replacement. Cotton fiber, while widely available and biodegradable, tends to be more expensive because of intensive farming and processing needs. The abundant synthetic production of polyethylene ensures consistent availability and scalability, making it a preferred choice for large-scale medical textile manufacturing.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Fiber for Medical Textiles
Polyethylene fiber offers superior chemical resistance, moisture management, and antimicrobial properties essential for medical textiles requiring durability and hygiene. Cotton fiber provides natural breathability and comfort, making it ideal for patient garments and wound dressings where softness and absorbency are critical. Selecting the right fiber depends on balancing performance needs with patient comfort, ensuring optimal functionality in medical textile applications.
Infographic: Polyethylene fiber vs Cotton fiber for Medical textile
 azmater.com
azmater.com