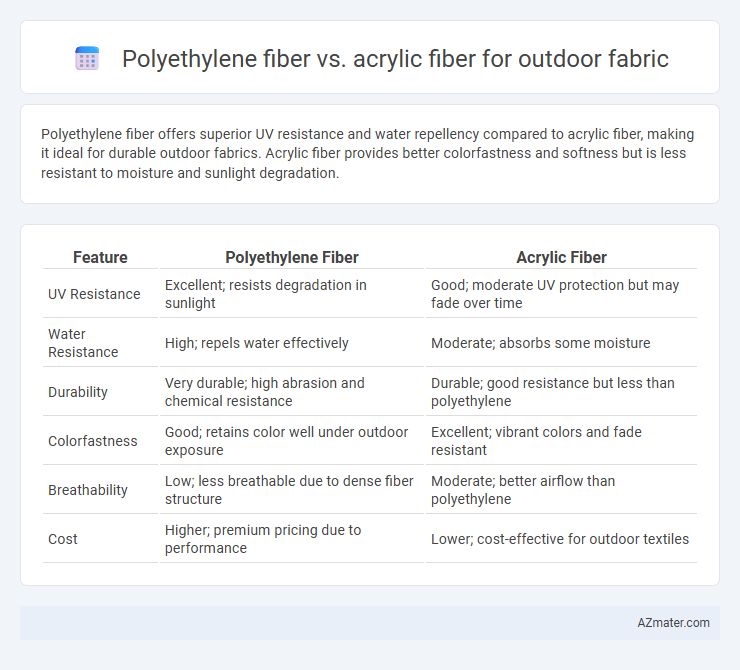
Polyethylene fiber offers superior UV resistance and water repellency compared to acrylic fiber, making it ideal for durable outdoor fabrics. Acrylic fiber provides better colorfastness and softness but is less resistant to moisture and sunlight degradation.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polyethylene Fiber | Acrylic Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| UV Resistance | Excellent; resists degradation in sunlight | Good; moderate UV protection but may fade over time |
| Water Resistance | High; repels water effectively | Moderate; absorbs some moisture |
| Durability | Very durable; high abrasion and chemical resistance | Durable; good resistance but less than polyethylene |
| Colorfastness | Good; retains color well under outdoor exposure | Excellent; vibrant colors and fade resistant |
| Breathability | Low; less breathable due to dense fiber structure | Moderate; better airflow than polyethylene |
| Cost | Higher; premium pricing due to performance | Lower; cost-effective for outdoor textiles |
Introduction to Outdoor Fabrics: Polyethylene vs Acrylic
Polyethylene fiber offers superior water resistance, UV stability, and durability, making it ideal for outdoor fabrics exposed to harsh weather conditions. Acrylic fiber provides excellent colorfastness and softness, often used for outdoor textiles requiring vibrant hues and comfort. Both materials excel in different aspects, with polyethylene prioritizing longevity and acrylic emphasizing aesthetic appeal and tactile quality.
Composition and Manufacturing of Polyethylene Fiber
Polyethylene fiber, primarily composed of high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE), boasts a highly crystalline structure that delivers exceptional strength and UV resistance ideal for outdoor fabrics. Manufactured through gel spinning or solution spinning processes, these fibers exhibit enhanced tensile strength and durability due to molecular chain alignment during extrusion. Acrylic fiber, by contrast, is produced from a polymerized acrylonitrile monomer with additives for improved weather resistance, but it generally has lower tensile strength and UV stability compared to polyethylene.
Production Process of Acrylic Fiber
Acrylic fiber production involves the polymerization of acrylonitrile monomers followed by wet or dry spinning techniques to create fine, durable fibers ideal for outdoor fabric applications. This synthetic fiber offers excellent resistance to UV radiation, weathering, and abrasion, enhancing the longevity and performance of outdoor textiles. Compared to polyethylene fiber, acrylic fibers provide superior color retention and moisture wicking properties, making them a preferred choice in outdoor fabric manufacturing.
Weather Resistance: Polyethylene vs Acrylic
Polyethylene fiber offers superior weather resistance compared to acrylic fiber, exhibiting exceptional UV stability and water resistance, which makes it highly durable for prolonged outdoor use. Acrylic fiber provides good resistance to sunlight and moisture but tends to degrade faster under intense UV exposure, leading to color fading and fiber weakening over time. The molecular structure of polyethylene enables better protection against environmental elements, ensuring longer-lasting outdoor fabrics in harsh weather conditions.
UV Protection and Colorfastness Comparison
Polyethylene fiber exhibits superior UV protection due to its inherent resistance to ultraviolet radiation, making it ideal for outdoor fabric applications exposed to prolonged sunlight. Acrylic fiber offers excellent colorfastness, retaining vibrant hues over time despite exposure to fading elements like sun and moisture. When choosing between the two, polyethylene provides enhanced UV durability, while acrylic ensures long-lasting color retention for outdoor textiles.
Durability and Longevity in Outdoor Conditions
Polyethylene fiber exhibits superior durability and resistance to UV radiation, moisture, and mildew, making it highly suitable for outdoor fabric applications. Acrylic fiber also offers good weather resistance and colorfastness but tends to degrade faster under prolonged sun exposure compared to polyethylene. The inherent strength and hydrophobic properties of polyethylene fibers ensure longer longevity and better performance in harsh outdoor environments.
Water and Mildew Resistance: Which Performs Better?
Polyethylene fiber exhibits superior water resistance due to its hydrophobic nature, making it less likely to absorb moisture and dry quickly in outdoor fabric applications. Acrylic fiber, while also water-resistant, tends to retain more moisture and is more susceptible to mildew growth under prolonged exposure to damp conditions. For enhanced outdoor durability and mildew resistance, polyethylene fiber outperforms acrylic fiber in water shedding and prevention of fungal development.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Polyethylene fiber exhibits superior resistance to moisture, mildew, and UV rays, requiring minimal maintenance and easy cleaning with mild soap and water, making it ideal for outdoor fabric. Acrylic fiber, while also durable and resistant to sunlight, often demands more frequent cleaning due to its tendency to attract dirt and may require specialized cleaners to prevent color fading. Both fibers benefit from regular brushing and prompt stain treatment, but polyethylene's hydrophobic properties significantly reduce maintenance efforts and prolong fabric longevity.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyethylene fiber demonstrates superior environmental performance in outdoor fabrics due to its high recyclability and lower energy consumption during production compared to acrylic fiber. Acrylic fiber, derived from petroleum-based chemicals, has a larger carbon footprint and releases harmful volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during manufacturing. Polyethylene's resistance to UV degradation and moisture also extends the lifespan of outdoor textiles, reducing waste and supporting sustainable product cycles.
Cost and Value Analysis for Outdoor Fabric Choices
Polyethylene fiber offers superior durability and UV resistance compared to acrylic fiber, making it a cost-effective choice for outdoor fabrics despite a higher initial price. Acrylic fiber, while more affordable upfront, tends to degrade faster under prolonged sun exposure, leading to frequent replacements and higher long-term costs. Evaluating total value, polyethylene fiber provides better longevity and weather resistance, reducing maintenance expenses and offering greater overall investment returns for outdoor applications.
Infographic: Polyethylene fiber vs Acrylic fiber for Outdoor fabric
 azmater.com
azmater.com