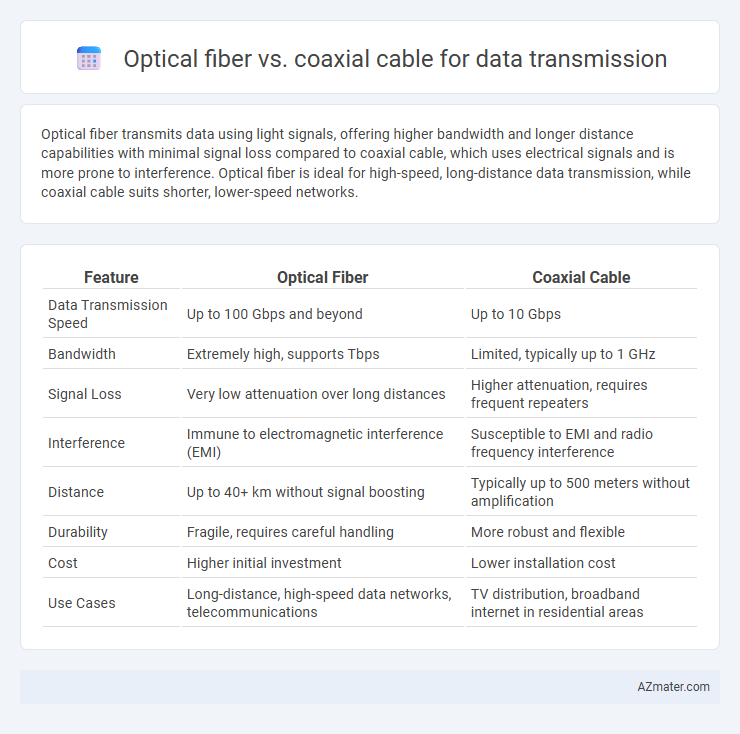
Optical fiber transmits data using light signals, offering higher bandwidth and longer distance capabilities with minimal signal loss compared to coaxial cable, which uses electrical signals and is more prone to interference. Optical fiber is ideal for high-speed, long-distance data transmission, while coaxial cable suits shorter, lower-speed networks.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Optical Fiber | Coaxial Cable |
|---|---|---|
| Data Transmission Speed | Up to 100 Gbps and beyond | Up to 10 Gbps |
| Bandwidth | Extremely high, supports Tbps | Limited, typically up to 1 GHz |
| Signal Loss | Very low attenuation over long distances | Higher attenuation, requires frequent repeaters |
| Interference | Immune to electromagnetic interference (EMI) | Susceptible to EMI and radio frequency interference |
| Distance | Up to 40+ km without signal boosting | Typically up to 500 meters without amplification |
| Durability | Fragile, requires careful handling | More robust and flexible |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower installation cost |
| Use Cases | Long-distance, high-speed data networks, telecommunications | TV distribution, broadband internet in residential areas |
Introduction to Data Transmission Media
Optical fiber and coaxial cable are essential data transmission media with distinct characteristics impacting performance and application. Optical fiber uses light to transmit data at high speeds over long distances with minimal signal loss and immunity to electromagnetic interference. Coaxial cable transmits electrical signals with moderate bandwidth and susceptibility to interference, commonly used in cable television and internet services.
What is Optical Fiber?
Optical fiber is a high-speed data transmission medium that uses thin strands of glass or plastic to transmit information as pulses of light, offering significantly higher bandwidth and longer transmission distances compared to coaxial cable. Its immunity to electromagnetic interference and lower signal attenuation make it ideal for internet, telecommunications, and cable TV networks. Optical fiber supports data rates in the range of gigabits per second, making it essential for modern high-speed communication infrastructure.
What is Coaxial Cable?
Coaxial cable is a type of electrical cable consisting of a central conductive core, an insulating layer, a metallic shield, and an outer insulating layer, designed to transmit high-frequency signals with minimal interference. It is commonly used for cable television, internet connections, and radio frequency transmission due to its durability and ability to handle moderate bandwidth requirements. Compared to optical fiber, coaxial cables have higher signal attenuation over long distances and lower data transmission speeds, making them less suitable for modern high-speed networks.
Speed and Bandwidth Comparison
Optical fiber offers significantly higher speed and bandwidth compared to coaxial cable, supporting data transmission rates up to 100 Gbps and beyond, while coaxial cables typically max out at 10 Gbps. The core glass fibers in optical cables enable minimal signal loss and electromagnetic interference, ensuring consistent high-speed data flow ideal for long-distance communication. Coaxial cables, with their copper cores, face greater attenuation and limited bandwidth, making them less suitable for modern high-demand internet and network applications.
Signal Attenuation and Distance
Optical fiber exhibits significantly lower signal attenuation compared to coaxial cable, allowing it to transmit data over much longer distances without the need for signal boosters. Typical attenuation rates for single-mode optical fiber are around 0.2 dB/km, whereas coaxial cables experience attenuation rates of about 10-15 dB per 100 meters, limiting their effective range. This low signal loss and high bandwidth capacity make optical fiber the preferred choice for long-distance, high-speed data transmission networks.
Immunity to Electromagnetic Interference
Optical fiber offers superior immunity to electromagnetic interference (EMI) compared to coaxial cable due to its use of light signals instead of electrical signals for data transmission. This inherent resistance to EMI ensures more reliable and stable communication in environments with high electrical noise, such as industrial or urban areas. Coaxial cables, while shielded, remain susceptible to EMI, which can degrade signal quality and lead to data loss or errors.
Installation and Maintenance
Optical fiber offers a lightweight and flexible installation process with smaller cable diameters and higher resistance to electromagnetic interference compared to coaxial cable. While optical fiber requires specialized tools and trained technicians for splicing and connectorization, coaxial cable installation is generally less complex but prone to signal loss and degradation over long distances. Maintenance costs for optical fiber tend to be lower due to its durability and longer lifespan, whereas coaxial cables often demand more frequent repairs and signal amplification.
Cost Analysis
Optical fiber offers higher initial installation costs due to expensive materials and specialized labor but provides lower long-term maintenance and scalability expenses compared to coaxial cable. Coaxial cable has lower upfront costs and simpler installation, making it cost-effective for short-distance or legacy systems, but it incurs higher signal degradation and upgrade expenses over time. Analyzing total cost of ownership reveals optical fiber as a more economical choice for high-bandwidth, long-distance data transmission despite higher starting costs.
Security Considerations
Optical fiber offers superior security for data transmission due to its immunity to electromagnetic interference and difficulty in tapping without detection, making it less vulnerable to signal theft compared to coaxial cable. Coaxial cables are more susceptible to electromagnetic interference and signal interception, raising the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches. The physical properties of optical fiber enhance data confidentiality and integrity, providing a more secure communication medium in sensitive applications.
Choosing the Right Medium for Applications
Optical fiber offers superior bandwidth, longer transmission distances, and immunity to electromagnetic interference, making it ideal for high-speed internet, telecommunications, and long-haul data transmission. Coaxial cable provides cost-effective, reliable performance for short to medium distances, commonly used in cable television and residential internet services. Selecting the right medium depends on factors like required data rate, distance, budget, and environmental conditions.
Infographic: Optical fiber vs Coaxial cable for Data transmission
 azmater.com
azmater.com