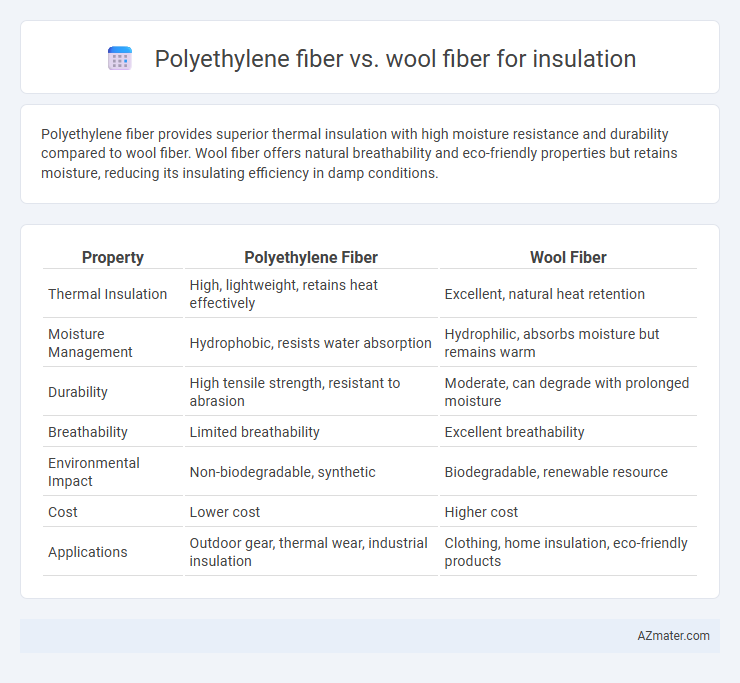
Polyethylene fiber provides superior thermal insulation with high moisture resistance and durability compared to wool fiber. Wool fiber offers natural breathability and eco-friendly properties but retains moisture, reducing its insulating efficiency in damp conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyethylene Fiber | Wool Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Insulation | High, lightweight, retains heat effectively | Excellent, natural heat retention |
| Moisture Management | Hydrophobic, resists water absorption | Hydrophilic, absorbs moisture but remains warm |
| Durability | High tensile strength, resistant to abrasion | Moderate, can degrade with prolonged moisture |
| Breathability | Limited breathability | Excellent breathability |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable, synthetic | Biodegradable, renewable resource |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Applications | Outdoor gear, thermal wear, industrial insulation | Clothing, home insulation, eco-friendly products |
Introduction to Polyethylene and Wool Fibers
Polyethylene fibers are synthetic polymers known for their high strength-to-weight ratio, excellent moisture resistance, and thermal insulation properties, making them ideal for lightweight and durable insulation applications. Wool fibers, derived from sheep, offer natural crimp and air-trapping capabilities that provide superior thermal regulation, moisture absorption, and fire resistance in insulation materials. Comparing these fibers highlights polyethylene's synthetic durability and moisture resistance against wool's renewable origin and natural thermal performance.
Thermal Insulation Properties: Polyethylene vs Wool
Polyethylene fiber offers excellent thermal insulation due to its low thermal conductivity and high moisture resistance, making it ideal for environments requiring moisture-wicking and lightweight insulation. Wool fiber provides superior thermal regulation by trapping air within its natural crimped fibers, enhancing warmth retention even when wet but tends to be heavier and more absorbent than polyethylene. Polyethylene's synthetic nature results in quicker drying times and higher durability, while wool's biodegradable properties contribute to eco-friendly insulation solutions.
Moisture Management and Breathability
Polyethylene fiber excels in moisture management due to its hydrophobic properties, effectively repelling water and drying rapidly, making it ideal for insulation in damp conditions. Wool fiber, naturally hygroscopic, absorbs and releases moisture vapor, promoting breathability and maintaining thermal comfort by regulating humidity levels. While polyethylene offers superior moisture resistance, wool provides enhanced breathability and moisture buffering, crucial for maintaining consistent insulation performance.
Durability and Longevity
Polyethylene fiber exhibits superior durability and longevity compared to wool fiber due to its resistance to moisture, mold, and mildew, making it ideal for insulation in humid or damp environments. Wool fiber, while naturally insulating and breathable, tends to degrade faster when exposed to prolonged moisture and physical wear, reducing its effective lifespan in insulation applications. Polyethylene's synthetic molecular structure maintains thermal performance over time, ensuring long-term energy efficiency in building insulation.
Weight and Comfort Comparison
Polyethylene fiber insulation is significantly lighter than wool fiber, offering enhanced ease of wear and reduced bulk without compromising thermal efficiency. Wool fiber provides superior moisture-wicking properties and natural breathability, resulting in enhanced comfort during prolonged use. Weight-wise, polyethylene is ideal for lightweight applications, while wool excels in comfort and temperature regulation, making it suitable for diverse insulation needs.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyethylene fiber insulation offers lower environmental impact due to its high recyclability and energy-efficient manufacturing processes compared to wool fiber, which is a renewable resource but requires significant land use and methane emissions from sheep farming. Wool fiber is biodegradable and naturally fire-resistant, promoting sustainability, yet its production involves higher water consumption and potential overgrazing concerns. Choosing between polyethylene and wool fiber depends on balancing recyclability and fossil fuel reliance against biodegradability and agricultural resource consumption for sustainable insulation solutions.
Fire Resistance and Safety
Polyethylene fibers exhibit low fire resistance as they melt and ignite at relatively low temperatures around 120-130degC, posing higher safety risks in insulation applications. Wool fibers inherently resist flame due to their high nitrogen and moisture content, self-extinguishing when exposed to fire and maintaining structural integrity at temperatures up to 570degC. The superior fire safety of wool fibers makes them a preferred choice for insulation in environments requiring enhanced fire retardance and minimized hazard risks.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Polyethylene fiber insulation offers superior cost efficiency due to its lower raw material and production costs compared to wool fiber, making it a budget-friendly option for large-scale applications. Availability of polyethylene fiber is higher globally, driven by synthetic manufacturing processes that ensure consistent supply, while wool fiber relies on livestock farming, which can lead to regional variability and higher prices. Polyethylene's widespread production and stable pricing contrast with wool's seasonal availability and premium market positioning, impacting overall cost-effectiveness for insulation projects.
Applications in Construction and Clothing
Polyethylene fiber, known for its high tensile strength, moisture resistance, and low thermal conductivity, is widely used in construction insulation to provide lightweight, durable, and water-resistant barriers that enhance energy efficiency. Wool fiber offers superior natural thermal regulation, breathability, and fire resistance, making it ideal for clothing insulation where comfort, moisture management, and eco-friendliness are prioritized. In construction, polyethylene fibers outperform wool in moisture-prone environments, while wool is preferred in clothing insulation for its biodegradability and ability to maintain warmth even when damp.
Maintenance and Care Considerations
Polyethylene fiber insulation requires minimal maintenance due to its resistance to moisture, mold, and pests, making it highly durable in humid environments. Wool fiber insulation, while naturally flame-retardant and moisture-regulating, demands careful care to prevent mold growth and fiber degradation in damp conditions. Both fibers benefit from regular inspection, but polyethylene's synthetic nature generally offers easier long-term upkeep compared to the organic sensitivity of wool.
Infographic: Polyethylene fiber vs Wool fiber for Insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com