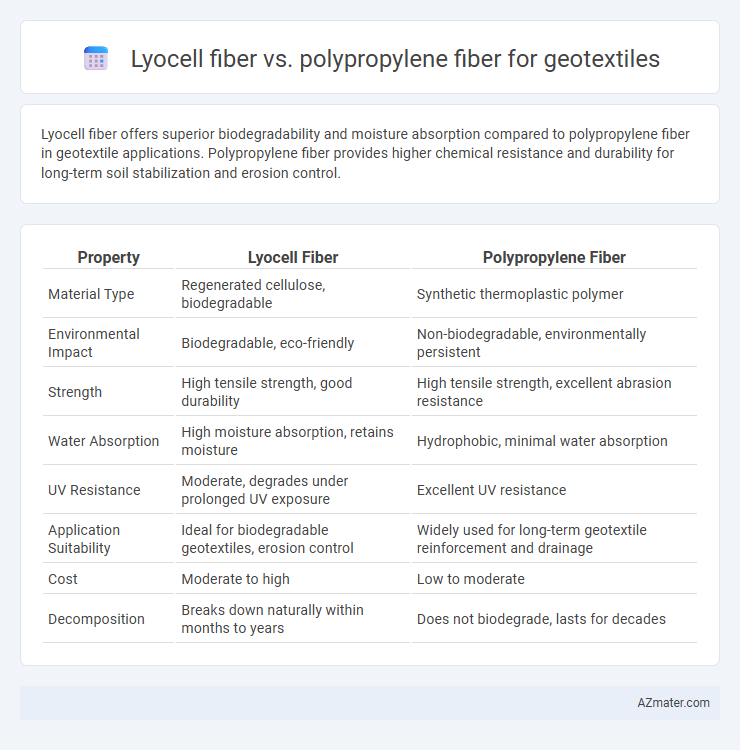
Lyocell fiber offers superior biodegradability and moisture absorption compared to polypropylene fiber in geotextile applications. Polypropylene fiber provides higher chemical resistance and durability for long-term soil stabilization and erosion control.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Lyocell Fiber | Polypropylene Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Regenerated cellulose, biodegradable | Synthetic thermoplastic polymer |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, eco-friendly | Non-biodegradable, environmentally persistent |
| Strength | High tensile strength, good durability | High tensile strength, excellent abrasion resistance |
| Water Absorption | High moisture absorption, retains moisture | Hydrophobic, minimal water absorption |
| UV Resistance | Moderate, degrades under prolonged UV exposure | Excellent UV resistance |
| Application Suitability | Ideal for biodegradable geotextiles, erosion control | Widely used for long-term geotextile reinforcement and drainage |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Low to moderate |
| Decomposition | Breaks down naturally within months to years | Does not biodegrade, lasts for decades |
Introduction to Geotextile Fibers
Geotextile fibers, such as Lyocell and Polypropylene, serve critical roles in civil engineering and construction for soil stabilization, erosion control, and filtration. Lyocell fiber, derived from cellulose, offers biodegradability, high moisture absorption, and excellent tensile strength, making it suitable for environmentally sensitive applications. Polypropylene fiber, a synthetic polymer, excels in chemical resistance, durability, and cost-effectiveness, positioning it as a dominant choice for long-term geotextile installations under harsh conditions.
Overview of Lyocell Fiber Properties
Lyocell fiber, derived from cellulose in wood pulp, exhibits high tensile strength, excellent biodegradability, and superior moisture absorbency, making it a sustainable choice for geotextile applications. Its natural fiber structure enhances soil stabilization and erosion control while promoting environmental compatibility compared to synthetic polypropylene fibers. The fiber's resistance to UV degradation and microbial attack contributes to its durability in various geotechnical environments.
Overview of Polypropylene Fiber Properties
Polypropylene fiber exhibits exceptional chemical resistance, high tensile strength, and excellent abrasion resistance, making it ideal for geotextile applications requiring durability and longevity. Its hydrophobic nature ensures minimal water absorption, enhancing stability and preventing degradation in wet environments. The fiber's lightweight characteristic combined with UV resistance improves performance in outdoor geotextile installations, differentiating it from Lyocell fiber, which is less resistant to moisture and chemicals.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Lyocell fibers exhibit superior tensile strength and elongation properties compared to polypropylene fibers, making them more durable under dynamic loads in geotextile applications. The higher modulus of elasticity in Lyocell contributes to enhanced resistance against deformation and mechanical stress, whereas polypropylene fibers tend to have lower tensile strength and stiffness. This improved mechanical strength in Lyocell fibers results in better performance for soil reinforcement, erosion control, and stability in geotechnical engineering projects.
Durability and Lifespan Analysis
Lyocell fiber in geotextiles offers moderate durability with natural biodegradability, making it suitable for temporary erosion control but limiting its lifespan under prolonged environmental exposure. Polypropylene fiber exhibits superior durability and longevity due to its chemical resistance, UV stability, and moisture repellency, ensuring extended performance in long-term geotechnical applications. The lifespan of polypropylene-based geotextiles can exceed 20 years, whereas lyocell-based materials typically degrade within a few years, impacting their suitability for permanent infrastructure projects.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Lyocell fiber, derived from sustainably managed wood pulp through a closed-loop production process, offers superior biodegradability and lower carbon emissions compared to polypropylene fiber, which is petroleum-based and non-biodegradable. Polypropylene geotextiles contribute to microplastic pollution and have a longer environmental persistence, while Lyocell fibers decompose naturally, reducing landfill burden and ecosystem contamination. The renewable nature and recyclability of Lyocell make it a more sustainable choice for environmentally conscious geotextile applications.
Water Absorption and Permeability
Lyocell fiber exhibits superior water absorption compared to polypropylene fiber, enabling enhanced moisture retention in geotextile applications. This hydrophilic nature of Lyocell improves the permeability of geotextile fabrics, facilitating efficient water flow and drainage. In contrast, polypropylene fiber's hydrophobic properties result in lower water absorption and reduced permeability, affecting its suitability for moisture management in geotextiles.
Cost-Effectiveness in Geotextile Applications
Lyocell fiber offers moderate cost-effectiveness in geotextile applications due to its sustainable production and biodegradability, which reduce long-term environmental costs but come with higher initial material prices compared to polypropylene. Polypropylene fiber dominates with low upfront costs, high durability, and resistance to chemicals and UV radiation, making it a more economically viable option for large-scale or long-term civil engineering projects. When factoring lifecycle costs, polypropylene's longevity and widespread availability often provide superior value, whereas Lyocell is preferred for eco-sensitive projects prioritizing sustainability over cost.
Typical Use Cases and Performance
Lyocell fiber in geotextiles offers superior biodegradability and moisture management, making it ideal for temporary erosion control and environmental restoration projects. Polypropylene fiber is favored for permanent applications due to its exceptional chemical resistance, tensile strength, and durability in soil stabilization and drainage systems. Performance-wise, Lyocell provides excellent biodegradability and softness, while polypropylene excels in longevity and resistance to UV degradation and microbial attack.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Fiber for Geotextiles
Lyocell fiber offers superior biodegradability and moisture absorption, making it ideal for environmentally sensitive geotextile applications. Polypropylene fiber provides excellent chemical resistance, high tensile strength, and cost-effectiveness suited for long-term erosion control and drainage projects. Selecting between Lyocell and Polypropylene depends on project requirements prioritizing sustainability or durability in geotextile performance.
Infographic: Lyocell fiber vs Polypropylene fiber for Geotextile
 azmater.com
azmater.com