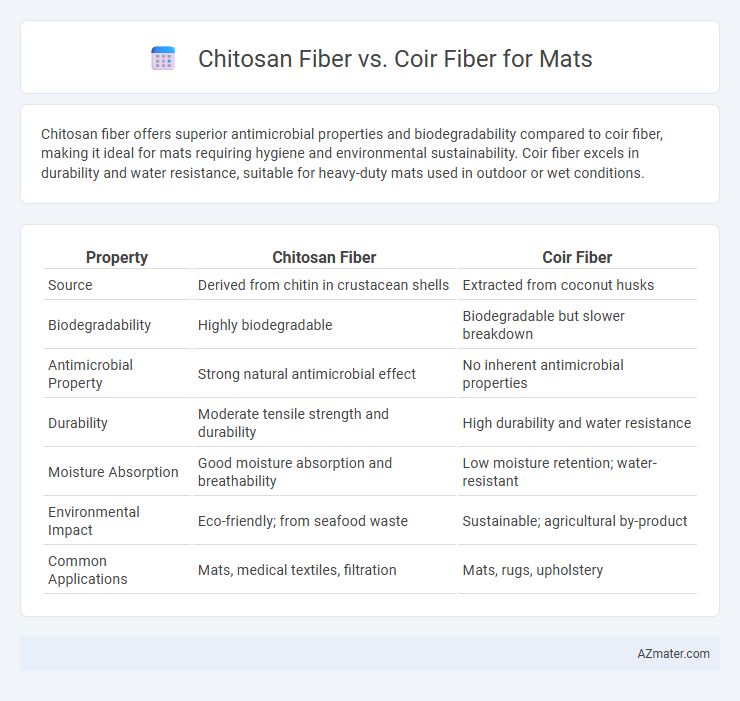
Chitosan fiber offers superior antimicrobial properties and biodegradability compared to coir fiber, making it ideal for mats requiring hygiene and environmental sustainability. Coir fiber excels in durability and water resistance, suitable for heavy-duty mats used in outdoor or wet conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Chitosan Fiber | Coir Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Derived from chitin in crustacean shells | Extracted from coconut husks |
| Biodegradability | Highly biodegradable | Biodegradable but slower breakdown |
| Antimicrobial Property | Strong natural antimicrobial effect | No inherent antimicrobial properties |
| Durability | Moderate tensile strength and durability | High durability and water resistance |
| Moisture Absorption | Good moisture absorption and breathability | Low moisture retention; water-resistant |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly; from seafood waste | Sustainable; agricultural by-product |
| Common Applications | Mats, medical textiles, filtration | Mats, rugs, upholstery |
Introduction to Chitosan and Coir Fibers
Chitosan fiber, derived from chitin in crustacean shells, offers natural antibacterial properties and biodegradability, making it an eco-friendly choice for mats. Coir fiber, obtained from coconut husks, is known for its durability, water resistance, and coarse texture, commonly used in doormats and floor mats. Both fibers provide sustainable alternatives, with chitosan emphasizing antimicrobial benefits and coir focusing on strength and moisture handling.
Origin and Production Process
Chitosan fiber is derived from chitin, primarily sourced from crustacean shells such as shrimp and crabs, and undergoes a biopolymer extraction and regeneration process involving deacetylation and fiber spinning. Coir fiber, on the other hand, originates from the husk of coconut fruits and is produced through a mechanical retting process followed by decortication and drying to extract coarse natural fibers. The distinct biological sources and extraction methods result in varying fiber properties, with chitosan offering biodegradability and antimicrobial traits, while coir provides durability and water resistance suitable for mat applications.
Physical Properties Comparison
Chitosan fiber exhibits higher tensile strength and flexibility compared to coir fiber, enhancing durability and comfort in mats. Coir fiber is known for its coarse texture and excellent water resistance, making it suitable for outdoor use. The lower moisture retention and biodegradability of chitosan fiber contribute to improved hygiene and environmental sustainability in mat applications.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Chitosan fiber exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to coir fiber, with higher tensile strength and elasticity, making it more resistant to deformation under stress. The durability of chitosan fiber mats is enhanced by its natural antimicrobial properties, which prevent microbial degradation and extend the product's lifespan. In contrast, coir fiber mats, while durable and biodegradable, tend to absorb moisture, leading to faster wear and reduced mechanical integrity over time.
Water Absorption and Retention
Chitosan fiber exhibits superior water absorption and retention properties compared to coir fiber, making it ideal for mats in humid or wet environments. Its hydrophilic nature allows it to absorb and retain moisture efficiently, preventing mold and mildew growth. In contrast, coir fiber, derived from coconut husks, offers moderate water absorption but drains quickly, making it less suitable for applications requiring prolonged moisture retention.
Biodegradability and Environmental Impact
Chitosan fiber, derived from chitin found in crustacean shells, is highly biodegradable and decomposes quickly without releasing harmful residues, making it an eco-friendly option for mats. Coir fiber, obtained from coconut husks, is also biodegradable but breaks down more slowly due to its lignin content, providing longer durability but a slightly prolonged environmental impact. Both fibers are renewable resources, but chitosan's rapid biodegradability offers a significant advantage in reducing landfill waste and supporting sustainable material cycles.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Chitosan fiber offers moderate cost efficiency due to its biodegradable properties and antimicrobial benefits, but higher manufacturing expenses limit large-scale production. Coir fiber is highly cost-effective and widely available, sourced from coconut husks, making it a preferred choice for affordable mats with durability and water resistance. In terms of availability, coir fiber dominates global markets, while chitosan fiber remains niche with limited suppliers.
Applications in Mat Manufacturing
Chitosan fiber offers superior antimicrobial properties and enhanced moisture absorption, making it ideal for mats used in healthcare and hygiene-sensitive environments. Coir fiber excels in durability and natural water resistance, often preferred for outdoor and heavy-traffic mats where robustness is crucial. Combining chitosan with coir fiber in mat manufacturing optimizes both comfort and longevity, expanding application possibilities across residential and industrial settings.
Consumer Preferences and Usability
Chitosan fiber mats attract consumers seeking eco-friendly, biodegradable products with antimicrobial properties that enhance hygiene and durability. Coir fiber mats appeal to buyers valuing natural texture, high water resistance, and excellent cushioning, making them ideal for outdoor and heavy-use areas. Usability-wise, chitosan fibers offer smoother surfaces and easier cleaning, while coir fibers provide superior roughness for effective dirt trapping and slip resistance.
Future Prospects and Innovations
Chitosan fiber exhibits significant future potential for mats due to its biodegradability, antimicrobial properties, and capacity for functional modifications enhancing durability and comfort. Innovations in blending chitosan with natural and synthetic fibers can create hybrid mats with improved mechanical strength and moisture-wicking abilities, addressing limitations of traditional coir fiber mats. Sustainable production techniques and nanotechnology integration pave the way for eco-friendly, high-performance mats that outperform coir fibers in biodegradability and user health benefits.
Infographic: Chitosan fiber vs Coir fiber for Mat
 azmater.com
azmater.com