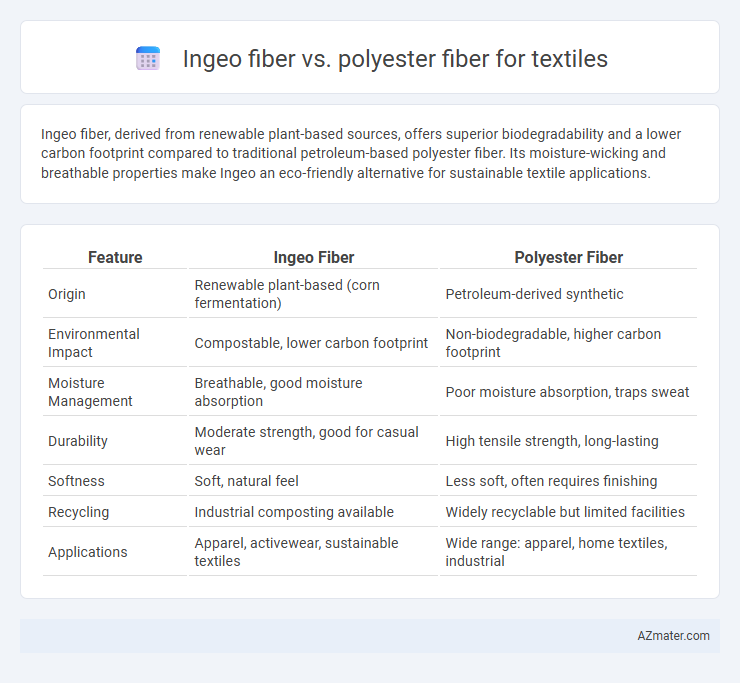
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based sources, offers superior biodegradability and a lower carbon footprint compared to traditional petroleum-based polyester fiber. Its moisture-wicking and breathable properties make Ingeo an eco-friendly alternative for sustainable textile applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ingeo Fiber | Polyester Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Renewable plant-based (corn fermentation) | Petroleum-derived synthetic |
| Environmental Impact | Compostable, lower carbon footprint | Non-biodegradable, higher carbon footprint |
| Moisture Management | Breathable, good moisture absorption | Poor moisture absorption, traps sweat |
| Durability | Moderate strength, good for casual wear | High tensile strength, long-lasting |
| Softness | Soft, natural feel | Less soft, often requires finishing |
| Recycling | Industrial composting available | Widely recyclable but limited facilities |
| Applications | Apparel, activewear, sustainable textiles | Wide range: apparel, home textiles, industrial |
Introduction to Ingeo Fiber and Polyester Fiber
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based sources like corn, offers a sustainable alternative to traditional synthetic fibers used in textiles. Polyester fiber, a petroleum-based synthetic fiber known for its strength, durability, and wrinkle resistance, dominates the textile market but poses environmental challenges due to its non-biodegradable nature. Comparing Ingeo fiber and polyester highlights the growing demand for eco-friendly textiles that balance performance with reduced environmental impact.
Composition and Source Materials
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based sources like corn starch, is composed primarily of polylactic acid (PLA), a biodegradable biopolymer offering an eco-friendly alternative to traditional fibers. Polyester fiber, made from petroleum-derived synthetic polymers such as polyethylene terephthalate (PET), relies heavily on fossil fuels and features non-biodegradable properties. The contrasting compositions and source materials directly impact sustainability, environmental footprint, and end-of-life disposal in textile applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based materials like corn, offers a significantly lower carbon footprint and biodegradability compared to petroleum-based polyester fiber, which contributes to persistent microplastic pollution and high energy consumption during production. Ingeo's manufacturing process consumes less water and relies on renewable resources, enhancing its sustainability profile in the textile industry. Polyester fiber, while durable and cost-effective, poses environmental challenges including non-biodegradability and reliance on fossil fuels, making Ingeo a more eco-friendly alternative for sustainable textile production.
Mechanical Properties and Performance
Ingeo fiber, made from polylactic acid (PLA), offers superior tensile strength and elasticity compared to conventional polyester fiber, enhancing fabric durability and comfort. Ingeo's biodegradability and moisture-wicking capabilities provide better performance in terms of breathability and environmental impact, while polyester excels in abrasion resistance and wrinkle retention. Mechanical properties such as Young's modulus and elongation at break position Ingeo as a sustainable alternative with competitive strength, though polyester remains favored for high-stress textile applications.
Comfort and Wearability in Textiles
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based materials, offers superior breathability and moisture-wicking properties compared to traditional polyester fiber, enhancing overall comfort in textiles. Polyester fiber, while durable and resistant to wrinkles, often retains heat and moisture, potentially reducing wearability during extended use. The natural origin and biodegradability of Ingeo fiber also contribute to a softer hand feel and reduced environmental impact, making it a preferred choice for sustainable comfort-focused textile applications.
Moisture Management and Breathability
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based sources, offers superior moisture management by efficiently wicking sweat away from the skin, enhancing dryness and comfort in textiles. Polyester fiber, while durable and quick-drying, tends to retain moisture on the fabric surface, potentially leading to a clammy feel during extended wear. Breathability in Ingeo fiber outperforms traditional polyester by allowing better air circulation, making it ideal for activewear and performance textiles.
Dyeability and Color Retention
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based sources, exhibits superior dyeability due to its hydrophilic nature, allowing for vibrant and uniform color absorption compared to petroleum-based polyester fiber. Polyester fiber typically requires high-energy dyeing processes and disperse dyes that can limit color fastness and vibrancy, whereas Ingeo fiber maintains strong color retention even after multiple washes and exposure to sunlight. The enhanced dye uptake and eco-friendly production of Ingeo fiber make it an increasingly preferred choice for textile manufacturers aiming for sustainable, long-lasting colored fabrics.
Cost Comparison and Market Availability
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based resources, generally carries a higher production cost compared to conventional polyester fiber, making it less price-competitive in large-scale textile manufacturing. Polyester fiber, synthesized from petrochemicals, benefits from established mass production infrastructure, resulting in lower prices and widespread availability in global textile markets. Market demand for sustainable materials is gradually boosting Ingeo fiber's accessibility, but polyester remains dominant due to its cost-effectiveness and extensive supply chain.
Applications in Textile Industry
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based sources, offers superior moisture-wicking and breathable properties ideal for sustainable activewear and casual textiles, whereas polyester fiber, synthesized from petrochemicals, provides high durability, wrinkle resistance, and cost-effectiveness widely used in upholstery, sportswear, and industrial fabrics. Ingeo fibers contribute to reduced environmental impact due to biodegradability and lower carbon footprint, making them increasingly preferred in eco-conscious fashion and performance textiles. Polyester remains dominant in mass production and high-performance applications requiring strength and quick-drying capabilities, maintaining a strong presence in both fashion and technical textile sectors.
Future Trends and Innovations
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based resources, offers a sustainable alternative to traditional polyester fiber, which relies on petrochemicals. Future trends highlight increasing innovations in Ingeo's biodegradability and moisture-wicking properties, driving its adoption in eco-conscious textile markets. Advances in polymer science and circular economy initiatives are expected to enhance the performance compatibility and recycling efficiency of both Ingeo and polyester fibers, shaping the next generation of sustainable textiles.
Infographic: Ingeo fiber vs Polyester fiber for Textile
 azmater.com
azmater.com