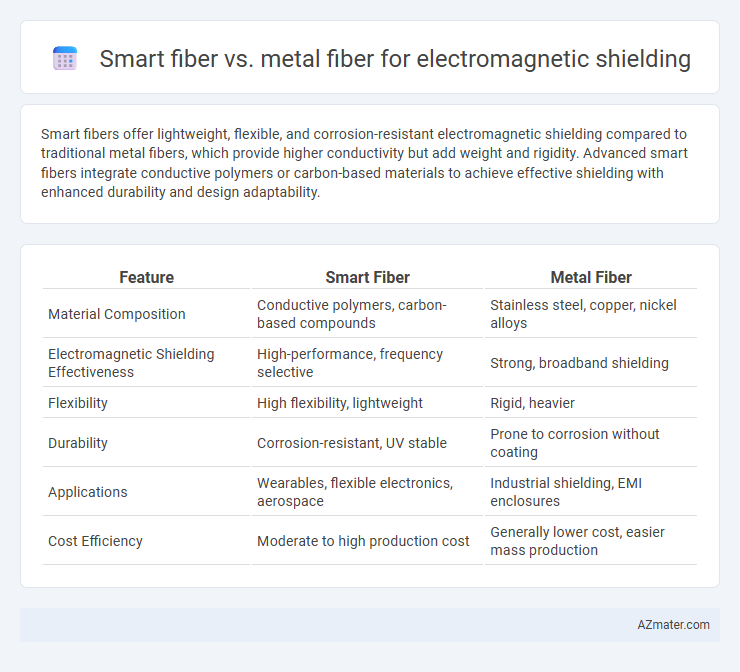
Smart fibers offer lightweight, flexible, and corrosion-resistant electromagnetic shielding compared to traditional metal fibers, which provide higher conductivity but add weight and rigidity. Advanced smart fibers integrate conductive polymers or carbon-based materials to achieve effective shielding with enhanced durability and design adaptability.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Smart Fiber | Metal Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Conductive polymers, carbon-based compounds | Stainless steel, copper, nickel alloys |
| Electromagnetic Shielding Effectiveness | High-performance, frequency selective | Strong, broadband shielding |
| Flexibility | High flexibility, lightweight | Rigid, heavier |
| Durability | Corrosion-resistant, UV stable | Prone to corrosion without coating |
| Applications | Wearables, flexible electronics, aerospace | Industrial shielding, EMI enclosures |
| Cost Efficiency | Moderate to high production cost | Generally lower cost, easier mass production |
Introduction to Electromagnetic Shielding
Electromagnetic shielding is essential for protecting sensitive electronic devices from interference caused by electromagnetic fields. Smart fiber, composed of conductive polymers or metal-coated fibers, offers flexibility, lightweight properties, and effective attenuation of high-frequency signals, while traditional metal fibers provide robust conductivity and excellent shielding effectiveness at lower frequencies. Comparing smart fibers and metal fibers reveals a balance between mechanical adaptability and electromagnetic performance critical for diverse industrial applications.
What Are Smart Fibers?
Smart fibers are advanced materials designed for electromagnetic shielding, integrating conductive properties with flexibility and adaptability. Unlike traditional metal fibers that primarily offer static shielding through high conductivity, smart fibers incorporate responsive materials such as conductive polymers or nanomaterials to dynamically attenuate electromagnetic interference (EMI) across a broad frequency range. These fibers enable lightweight, durable, and multifunctional shielding solutions ideal for wearable electronics, aerospace, and IoT applications where real-time EMI management and enhanced mechanical performance are critical.
Overview of Metal Fibers
Metal fibers offer superior electromagnetic shielding due to their high electrical conductivity and effective attenuation of a broad spectrum of electromagnetic frequencies. Commonly made from materials such as copper, stainless steel, or aluminum, metal fibers provide durable, corrosion-resistant performance in harsh environments. Their woven or nonwoven structures ensure flexible integration into textiles and composites, making them ideal for advanced protective applications.
Key Properties Influencing Shielding Effectiveness
Smart fiber exhibits superior electromagnetic shielding effectiveness due to its high electrical conductivity and flexibility, enabling better attenuation of electromagnetic interference (EMI) across a wide frequency range. Metal fibers, typically composed of copper, aluminum, or stainless steel, offer excellent conductivity and corrosion resistance but often lack the adaptability and lightweight characteristics of smart fibers. Key properties influencing shielding effectiveness include conductivity, fiber diameter, network density, and material integration, where smart fibers provide enhanced durability and tunability compared to traditional metal fibers.
Shielding Performance: Smart Fiber vs Metal Fiber
Smart fiber composites exhibit superior shielding performance compared to traditional metal fibers due to their enhanced conductivity and flexibility, providing effective attenuation across a broader frequency range. Metal fibers offer high conductivity but are prone to corrosion and reduced efficiency in dynamic or flexible applications. Smart fibers maintain consistent electromagnetic shielding effectiveness with improved durability and lightweight properties, making them ideal for advanced electronic and aerospace applications.
Flexibility and Wearability Comparison
Smart fiber offers superior flexibility compared to metal fiber, enabling better conformity to complex shapes and improved comfort in wearable applications. Metal fibers, while excellent in electromagnetic shielding effectiveness, tend to be stiffer and heavier, which can reduce overall wearability and cause discomfort during extended use. The integration of smart fiber technology enhances durability and breathability, making it a preferred choice for lightweight, flexible, and comfortable electromagnetic shielding in textile-based wearables.
Durability and Longevity Analysis
Smart fiber materials for electromagnetic shielding exhibit superior durability compared to traditional metal fibers due to their inherent flexibility, resistance to corrosion, and enhanced mechanical strength. Metal fibers often suffer from oxidation and fatigue over time, which diminishes their shielding effectiveness and structural integrity. Long-term studies highlight smart fibers maintain consistent electromagnetic attenuation performance under harsh environmental conditions, ensuring prolonged operational lifespan.
Cost Efficiency and Scalability
Smart fiber offers superior cost efficiency compared to traditional metal fiber due to lower raw material and manufacturing expenses, making it ideal for large-scale electromagnetic shielding applications. Its scalability benefits from lightweight properties and ease of integration into flexible substrates, reducing installation costs and time. Metal fiber, while effective in shielding performance, often incurs higher costs and complexity in scaling due to weight and corrosion concerns.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Smart fiber for electromagnetic shielding offers superior sustainability through its biodegradability and lower energy consumption during production compared to traditional metal fiber, which relies heavily on mining and energy-intensive refining processes. The reduced carbon footprint and recyclability of smart fibers contribute to minimizing environmental impact while maintaining effective electromagnetic interference (EMI) protection. Metal fibers, although highly conductive, pose challenges in terms of resource depletion and waste management, making smart fibers a more eco-friendly alternative in sustainable shielding applications.
Future Trends in Electromagnetic Shielding Materials
Smart fiber technology in electromagnetic shielding is advancing with adaptive properties that dynamically respond to electromagnetic interference, offering enhanced protection compared to traditional metal fibers. Future trends emphasize the integration of smart fibers with nanomaterials and conductive polymers to improve flexibility, weight reduction, and multi-functional shielding capabilities. Research is increasingly directed toward sustainable and lightweight smart fiber composites that maintain high conductivity and corrosion resistance for next-generation shielding applications.
Infographic: Smart fiber vs Metal fiber for Electromagnetic shielding
 azmater.com
azmater.com