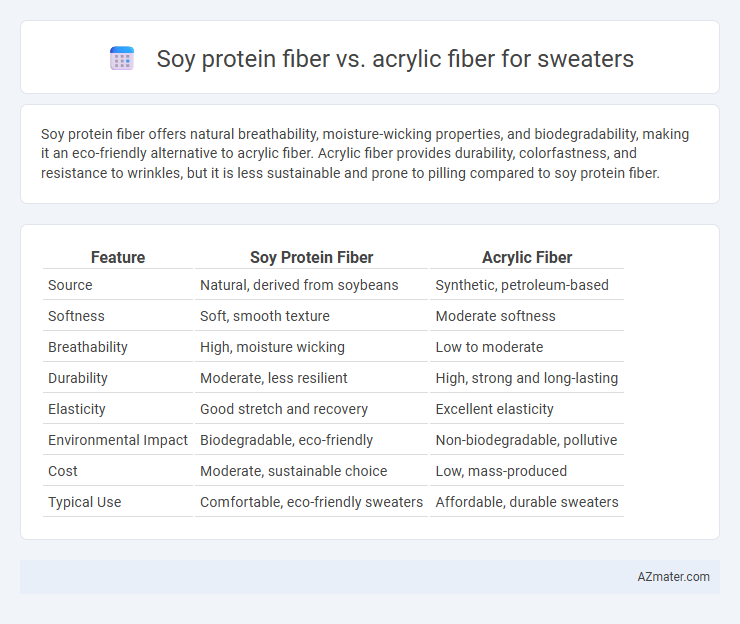
Soy protein fiber offers natural breathability, moisture-wicking properties, and biodegradability, making it an eco-friendly alternative to acrylic fiber. Acrylic fiber provides durability, colorfastness, and resistance to wrinkles, but it is less sustainable and prone to pilling compared to soy protein fiber.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Soy Protein Fiber | Acrylic Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural, derived from soybeans | Synthetic, petroleum-based |
| Softness | Soft, smooth texture | Moderate softness |
| Breathability | High, moisture wicking | Low to moderate |
| Durability | Moderate, less resilient | High, strong and long-lasting |
| Elasticity | Good stretch and recovery | Excellent elasticity |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, eco-friendly | Non-biodegradable, pollutive |
| Cost | Moderate, sustainable choice | Low, mass-produced |
| Typical Use | Comfortable, eco-friendly sweaters | Affordable, durable sweaters |
Introduction to Sweater Fibers
Soy protein fiber, derived from natural soybeans, offers superior breathability, moisture-wicking properties, and eco-friendly sustainability compared to synthetic acrylic fiber, which is created from polymer resin providing durability and lightweight warmth. Sweater fibers like soy protein enhance comfort through natural softness and biodegradability, while acrylic fibers are favored for their resistance to wrinkles, mildew, and fading during wear and washing. Selecting between soy protein and acrylic fibers impacts sweater performance, environmental impact, and wearer comfort based on fiber origin, texture, and maintenance.
Overview of Soy Protein Fiber
Soy protein fiber is a biodegradable, eco-friendly textile made from soybeans, offering a soft, smooth texture ideal for sweaters. Its excellent moisture absorption and breathability enhance comfort and skin friendliness compared to synthetic fibers like acrylic. The fiber's natural origin supports sustainability, making soy protein fiber a popular choice for environmentally conscious fashion.
Overview of Acrylic Fiber
Acrylic fiber, a synthetic polymer made from polyacrylonitrile, is widely used in sweaters for its lightweight, soft texture and excellent warmth retention. It offers high durability, resistance to moths and chemicals, and easy care with quick drying properties compared to natural fibers like soy protein fiber. Acrylic fibers also provide vibrant color retention and elasticity, making them a popular choice for affordable, versatile knitwear.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Soy protein fiber offers a more sustainable alternative to acrylic fiber for sweaters, as it is biodegradable and derived from renewable plant sources, reducing reliance on fossil fuels. Acrylic fiber production involves petroleum-based chemicals, leading to higher carbon emissions and non-biodegradable waste that contribute to long-term environmental pollution. Choosing soy protein fiber reduces environmental impact by minimizing chemical use, lowering greenhouse gas emissions, and promoting circular textile economy principles.
Comfort and Wearability
Soy protein fiber offers superior softness and breathability compared to acrylic fiber, making sweaters feel more comfortable against the skin. It naturally regulates moisture and temperature, enhancing wearability during various weather conditions. Acrylic fiber, while durable and resistant to wrinkles, often lacks the same level of comfort and can trap heat, causing discomfort during extended wear.
Durability and Longevity
Soy protein fiber, derived from natural soybeans, offers moderate durability with excellent softness and breathability, making it suitable for lightweight sweaters but prone to wear over time. Acrylic fiber, a synthetic material, provides superior durability and resistance to abrasion, pilling, and fading, ensuring longer-lasting sweaters that maintain shape and color after repeated use. Lightweight sweaters made from acrylic fibers tend to outperform soy protein blends in longevity, especially under frequent washing and heavy wear conditions.
Moisture Wicking and Breathability
Soy protein fiber exhibits superior moisture-wicking properties compared to acrylic fiber, effectively drawing sweat away from the skin to keep wearers dry. Its natural breathability enhances air circulation, providing greater comfort for sweater wearers in varying temperatures. Acrylic fiber, while durable and lightweight, tends to retain moisture and lacks the same level of ventilation, making it less effective for moisture management and breathability in sweaters.
Color Retention and Dyeability
Soy protein fiber exhibits superior dyeability due to its natural amino acid structure, allowing vibrant, long-lasting colors in sweaters. Acrylic fiber, with its synthetic polymer composition, also offers excellent color retention but may have limitations in achieving the same depth and richness of hues as soy protein fiber. Both fibers resist fading, but soy protein fiber excels in maintaining color vibrancy after multiple washes.
Price and Availability
Soy protein fiber offers a natural, biodegradable option with moderate pricing, generally falling between the cost of premium cotton and synthetic fibers, making it an affordable alternative for eco-conscious consumers. Acrylic fiber is widely available, produced at a lower cost due to synthetic manufacturing processes, resulting in cheaper pricing but less environmental sustainability. In terms of market accessibility, acrylic fibers dominate with extensive global supply chains, while soy protein fibers remain less common and often restricted to niche, sustainable textile markets.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Fiber for Sweaters
Soy protein fiber offers natural breathability, moisture-wicking properties, and biodegradability, making it an eco-friendly and comfortable choice for sweaters. Acrylic fiber provides durability, vibrant color retention, and resistance to wrinkles and moths, which enhances sweater longevity and ease of care. Selecting between soy protein and acrylic fibers depends on prioritizing sustainability and softness versus durability and vibrant appearance in sweater performance.
Infographic: Soy protein fiber vs Acrylic fiber for Sweater
 azmater.com
azmater.com