Hemp fiber offers superior durability, breathability, and natural antimicrobial properties compared to bamboo fiber, making it ideal for sustainable fabric production. Bamboo fiber excels in softness and moisture-wicking, but hemp's strength and eco-friendly cultivation make it a preferred choice for long-lasting, biodegradable textiles.
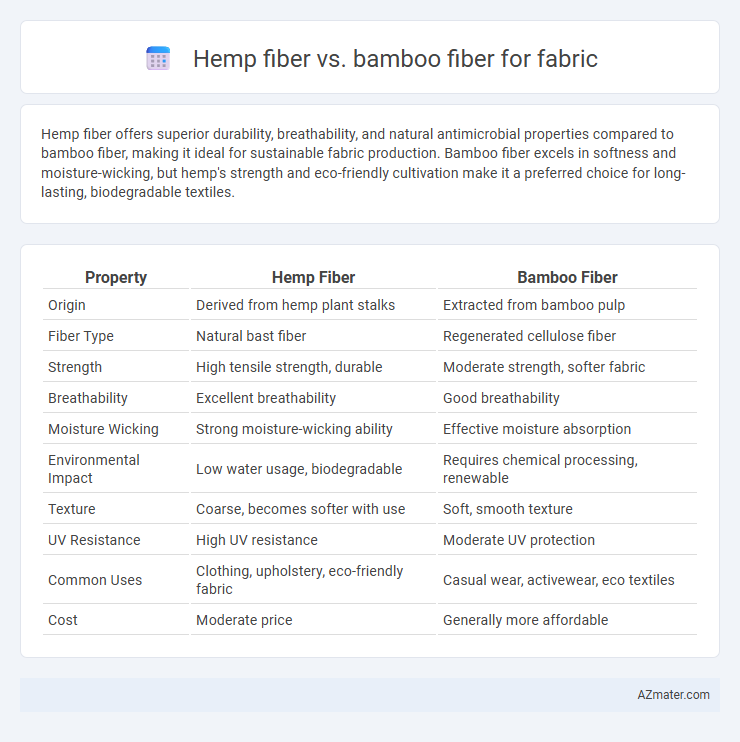
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hemp Fiber | Bamboo Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Derived from hemp plant stalks | Extracted from bamboo pulp |
| Fiber Type | Natural bast fiber | Regenerated cellulose fiber |
| Strength | High tensile strength, durable | Moderate strength, softer fabric |
| Breathability | Excellent breathability | Good breathability |
| Moisture Wicking | Strong moisture-wicking ability | Effective moisture absorption |
| Environmental Impact | Low water usage, biodegradable | Requires chemical processing, renewable |
| Texture | Coarse, becomes softer with use | Soft, smooth texture |
| UV Resistance | High UV resistance | Moderate UV protection |
| Common Uses | Clothing, upholstery, eco-friendly fabric | Casual wear, activewear, eco textiles |
| Cost | Moderate price | Generally more affordable |
Introduction to Hemp and Bamboo Fibers
Hemp fiber, derived from the stalks of the Cannabis sativa plant, is known for its durability, breathability, and resistance to mold and UV light, making it a highly sustainable option for fabric production. Bamboo fiber, extracted from the pulp of bamboo grass, offers a soft texture combined with natural antibacterial properties and excellent moisture-wicking capabilities ideal for sensitive skin. Both fibers emphasize eco-friendly cultivation with rapid growth rates, requiring minimal pesticides and water compared to conventional cotton.
Origins and Cultivation Practices
Hemp fiber originates from the stalks of the Cannabis sativa plant, which thrives in temperate climates with minimal pesticide use and requires significantly less water compared to conventional cotton. Bamboo fiber is derived from the fast-growing bamboo grass, predominantly cultivated in tropical and subtropical regions, known for its rapid growth cycle and sustainable replanting practices without the need for fertilizers or pesticides. Both fibers benefit from eco-friendly cultivation, but hemp's robustness and soil-enhancing properties distinguish it in sustainable fabric production.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Hemp fiber requires significantly less water and pesticides compared to bamboo, making it a more eco-friendly choice for sustainable fabric production. Hemp plants grow quickly and improve soil health through phytoremediation, reducing environmental degradation. Bamboo, though fast-growing and renewable, often involves energy-intensive processing and chemical treatments that can diminish its sustainability advantages.
Processing Techniques for Fabric Production
Hemp fiber processing involves retting, breaking, and scutching to separate the bast fibers, followed by carding and spinning into yarn, which results in coarse yet durable fabric ideal for textiles requiring strength. Bamboo fiber extraction employs either mechanical crushing and retting or chemical processes like viscose production, yielding softer and finer fibers suitable for smooth, breathable fabrics. The mechanical method preserves bamboo's natural qualities with eco-friendly benefits, while chemical processing enables mass production of bamboo viscose but involves more intensive chemical treatments impacting sustainability.
Texture, Softness, and Comfort Comparison
Hemp fiber offers a coarse texture with high durability, making it ideal for heavy-duty fabrics but less soft compared to bamboo fiber. Bamboo fiber boasts a fine, silky texture that provides superior softness and a smooth feel against the skin, enhancing overall comfort. Both fibers are breathable and moisture-wicking, yet bamboo's natural softness makes it preferable for sensitive skin and lightweight apparel.
Durability and Longevity of Fabrics
Hemp fiber offers exceptional durability and longevity due to its strong, coarse fibers that resist tearing and wear, making it ideal for heavy-duty fabrics and long-lasting garments. Bamboo fiber, while softer and more breathable, generally has lower tensile strength and may degrade faster under frequent washing and abrasion compared to hemp. Choosing hemp fiber fabric results in more resilient and sustainable textiles, especially for applications requiring extended use and durability.
Moisture Wicking and Breathability
Hemp fiber exhibits superior moisture-wicking properties due to its highly absorbent and breathable structure, efficiently drawing sweat away from the skin and promoting rapid evaporation. Bamboo fiber also offers excellent breathability with natural antibacterial qualities, enhancing comfort in warm and humid conditions. While both fibers excel in moisture management, hemp's coarser texture makes it more durable, whereas bamboo provides a softer feel, catering to different fabric performance preferences.
Applications in Fashion and Textiles
Hemp fiber exhibits exceptional durability and breathability, making it ideal for sustainable fashion such as casual wear, denim, and eco-friendly activewear, while bamboo fiber offers a softer texture with natural moisture-wicking properties preferred in luxury apparel and intimate wear. Hemp's coarse and strong fibers suit heavy-duty textiles like upholstery and workwear, whereas bamboo's fine fibers are commonly utilized in soft, lightweight fabrics for baby clothing and summer garments. Both fibers contribute to environmentally conscious textile production, with hemp supporting biodegradability and bamboo enhancing antimicrobial qualities in fashion applications.
Cost and Market Availability
Hemp fiber is generally more expensive than bamboo fiber due to its labor-intensive cultivation and processing methods, whereas bamboo fiber benefits from higher yield rates and faster growth cycles, reducing production costs. Market availability of bamboo fiber fabrics is broader, driven by strong consumer demand and well-established supply chains, while hemp fiber fabrics remain niche with limited but growing distribution channels. Both fibers offer sustainable alternatives, but bamboo fabric holds a competitive edge in cost efficiency and accessibility within the global textile market.
Final Verdict: Choosing Between Hemp and Bamboo Fiber
Hemp fiber offers superior durability, breathability, and eco-friendliness due to its low-impact cultivation and natural resistance to pests, making it ideal for sustainable fabric use. Bamboo fiber provides exceptional softness, moisture-wicking properties, and antibacterial benefits, favored in comfort-driven textiles like activewear and bedding. The final choice hinges on prioritizing either hemp's robust sustainability and longevity or bamboo's comfort and performance characteristics for specific fabric applications.
Infographic: Hemp fiber vs Bamboo fiber for Fabric
 azmater.com
azmater.com