Bamboo fiber offers superior biodegradability and lightweight strength compared to traditional glass fiber in composite materials. Bamboo fiber composites provide enhanced flexibility and lower environmental impact while maintaining competitive mechanical performance.
Table of Comparison
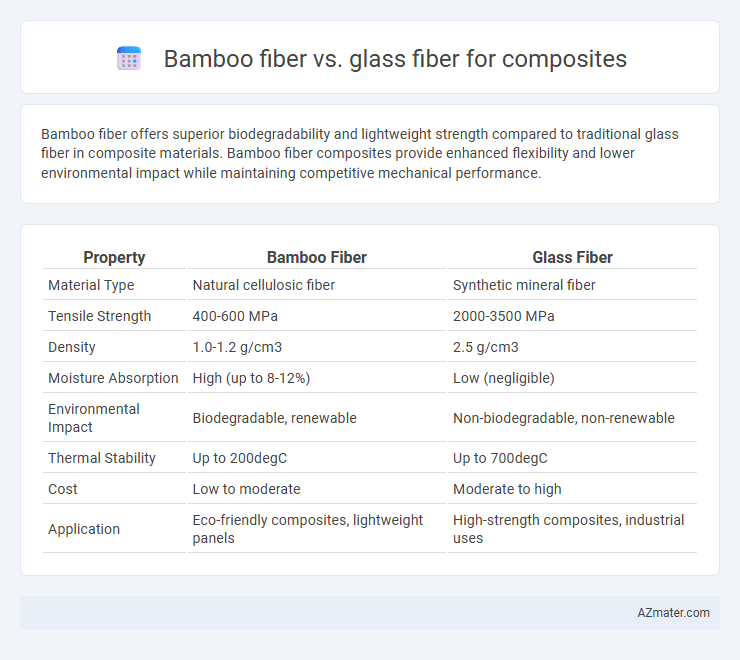
| Property | Bamboo Fiber | Glass Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Natural cellulosic fiber | Synthetic mineral fiber |
| Tensile Strength | 400-600 MPa | 2000-3500 MPa |
| Density | 1.0-1.2 g/cm3 | 2.5 g/cm3 |
| Moisture Absorption | High (up to 8-12%) | Low (negligible) |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, renewable | Non-biodegradable, non-renewable |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 200degC | Up to 700degC |
| Cost | Low to moderate | Moderate to high |
| Application | Eco-friendly composites, lightweight panels | High-strength composites, industrial uses |
Introduction to Composite Materials
Composite materials consist of two or more distinct constituents, typically a fibrous reinforcement and a matrix, combined to achieve superior mechanical properties. Bamboo fiber, a natural and sustainable reinforcement, offers lightweight, high tensile strength, and biodegradability compared to synthetic glass fiber, which provides excellent stiffness, thermal resistance, and durability. Selection between bamboo fiber and glass fiber depends on application requirements such as environmental impact, mechanical performance, and cost-efficiency in composite manufacturing.
Overview of Bamboo Fiber
Bamboo fiber is a sustainable, biodegradable natural fiber widely used in composites due to its high tensile strength and lightweight properties. Compared to glass fiber, bamboo fiber offers excellent impact resistance and better environmental benefits, reducing carbon footprint and promoting eco-friendly materials. Its cellular structure provides enhanced vibration damping and thermal insulation, making it a versatile choice for automotive and construction applications.
Overview of Glass Fiber
Glass fiber, composed primarily of fine strands of silica-based glass, serves as a dominant reinforcement material in composite manufacturing due to its high tensile strength, lightweight properties, and excellent resistance to heat and corrosion. This fiber enhances mechanical properties such as impact resistance and dimensional stability, making it suitable for automotive, aerospace, and construction applications. Its versatility and cost-effectiveness provide a performance benchmark when compared to natural fibers like bamboo.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Bamboo fiber composites exhibit high tensile strength and excellent impact resistance due to their natural cellulose structure, making them lightweight yet durable alternatives to traditional glass fiber composites. Glass fiber composites generally offer superior stiffness and higher modulus of elasticity, translating to better load-bearing capacities in structural applications. Bamboo fiber's enhanced flexibility and eco-friendly profile make it suitable for applications requiring energy absorption, while glass fiber excels in environments demanding high mechanical rigidity and thermal stability.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Bamboo fiber offers a significantly lower environmental impact compared to glass fiber due to its renewable nature, fast growth rate, and biodegradability, making it a sustainable choice for composite materials. Glass fiber production involves high energy consumption and releases greenhouse gases, while bamboo fibers sequester carbon during growth and reduce landfill waste. Incorporating bamboo fiber in composites supports circular economy principles and reduces the ecological footprint associated with traditional synthetic fibers.
Cost Analysis: Bamboo vs Glass Fiber
Bamboo fiber composites generally offer a lower material cost compared to glass fiber composites due to the abundant availability and renewable nature of bamboo. Processing bamboo fiber requires less energy-intensive methods, reducing overall manufacturing expenses, while glass fiber involves higher energy costs for extraction and production of silica-based fibers. Despite the lower upfront cost of bamboo fiber, glass fiber composites may provide longer service life and higher strength, impacting long-term cost-effectiveness in high-performance applications.
Processing and Manufacturing Techniques
Bamboo fiber composites offer eco-friendly processing advantages due to their low energy consumption and ease of natural fiber treatment, typically involving alkali treatment and mechanical extraction to enhance fiber-matrix adhesion. Glass fiber composites require more intensive manufacturing techniques such as pultrusion, filament winding, or resin transfer molding, which involve high temperatures and specialized equipment to ensure consistent fiber alignment and superior mechanical properties. The choice between bamboo and glass fibers significantly impacts production costs, processing times, and environmental sustainability in composite manufacturing.
Applications in Industry
Bamboo fiber composites are increasingly utilized in automotive interiors, construction panels, and consumer goods due to their lightweight, renewable nature, and excellent vibration dampening properties. Glass fiber composites dominate aerospace, marine, and structural applications because of their superior tensile strength, thermal resistance, and cost-effectiveness. The choice between bamboo and glass fiber in industry hinges on balancing sustainability goals with mechanical performance requirements.
Durability and Lifespan
Bamboo fiber composites offer excellent durability due to their natural flexibility and resistance to cracking, making them suitable for applications requiring moderate strength and long-term sustainability. Glass fiber composites provide superior lifespan and mechanical strength, resisting environmental degradation such as UV exposure and moisture, which extends their usability in demanding structural applications. The choice between bamboo fiber and glass fiber depends on the balance between eco-friendliness and high-performance durability requirements.
Future Trends and Innovations
Bamboo fiber composites are gaining attention for their sustainability and biodegradability, making them a key focus in future green manufacturing trends. Innovations in hybrid composites combining bamboo fiber with glass fiber enhance mechanical properties while reducing environmental impact. Advances in nanotechnology and chemical treatments are expected to improve the interface bonding and durability of bamboo fiber composites, positioning them as viable alternatives in automotive and construction industries.
Infographic: Bamboo fiber vs Glass fiber for Composite
 azmater.com
azmater.com