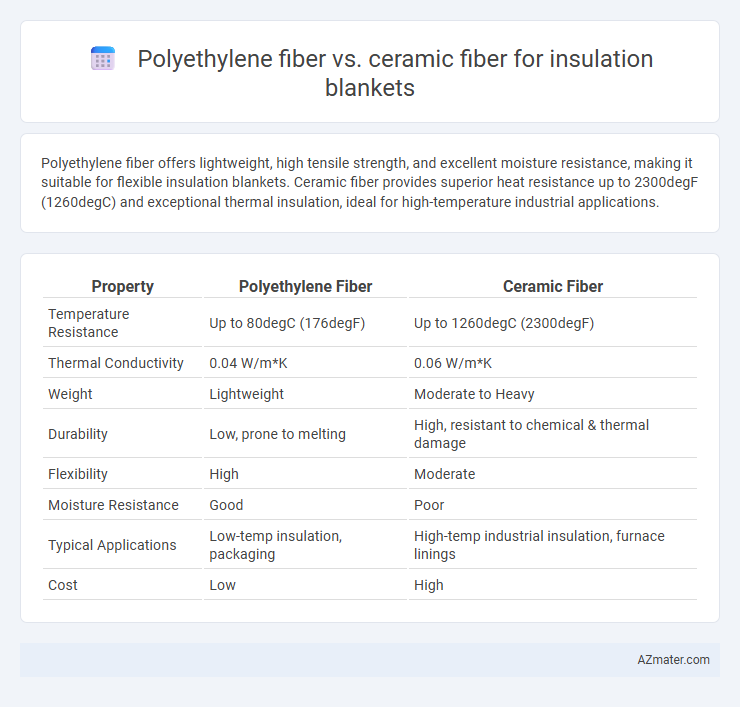
Polyethylene fiber offers lightweight, high tensile strength, and excellent moisture resistance, making it suitable for flexible insulation blankets. Ceramic fiber provides superior heat resistance up to 2300degF (1260degC) and exceptional thermal insulation, ideal for high-temperature industrial applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyethylene Fiber | Ceramic Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 80degC (176degF) | Up to 1260degC (2300degF) |
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.04 W/m*K | 0.06 W/m*K |
| Weight | Lightweight | Moderate to Heavy |
| Durability | Low, prone to melting | High, resistant to chemical & thermal damage |
| Flexibility | High | Moderate |
| Moisture Resistance | Good | Poor |
| Typical Applications | Low-temp insulation, packaging | High-temp industrial insulation, furnace linings |
| Cost | Low | High |
Introduction to Insulation Blankets
Insulation blankets are crucial for thermal management, providing efficient heat resistance and energy savings in industrial applications. Polyethylene fiber insulation blankets offer lightweight, flexible, and moisture-resistant properties with moderate thermal stability suitable for lower temperature settings. Ceramic fiber blankets deliver superior heat resistance up to 2300degF (1260degC), excellent thermal insulation, and chemical stability, making them ideal for high-temperature environments and refractory applications.
Overview of Polyethylene Fiber
Polyethylene fiber offers exceptional tensile strength and durability, making it a lightweight yet robust option for insulation blankets in various industrial applications. Its excellent chemical resistance and low moisture absorption enhance thermal insulation performance and longevity compared to ceramic fiber. Polyethylene fiber insulation blankets provide improved flexibility and easier handling, making them ideal for environments requiring frequent installation and removal.
Overview of Ceramic Fiber
Ceramic fiber is an inorganic, non-metallic insulation material composed primarily of alumina and silica, known for its exceptional thermal resistance up to 2300degF (1260degC). It offers superior durability, low thermal conductivity, and excellent chemical stability, making it ideal for high-temperature applications where polyethylene fiber cannot perform due to its lower melting point around 248degF (120degC). Ceramic fiber blankets provide lightweight, flexible insulation solutions with long service life in furnaces, kilns, and industrial pipelines.
Thermal Insulation Performance: Polyethylene vs Ceramic Fiber
Polyethylene fiber insulation blankets exhibit lower thermal resistance with operating temperatures typically below 100degC, making them suitable for lightweight, low-heat applications. Ceramic fiber insulation blankets offer superior thermal insulation performance, withstanding temperatures up to 1260degC, providing excellent heat retention and resistance in high-temperature environments. The choice between polyethylene and ceramic fiber hinges on the specific thermal requirements, where ceramic fiber is preferred for industrial and high-heat insulation needs due to its exceptional thermal stability and low thermal conductivity.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Polyethylene fiber insulation blankets offer high tensile strength and excellent flexibility, making them resistant to mechanical damage during handling and installation. Ceramic fiber blankets provide superior thermal stability and withstand extreme temperatures but tend to have lower mechanical strength and are more brittle, which can reduce durability under mechanical stress. For applications requiring robust mechanical performance and flexibility, polyethylene fiber insulation blankets are more durable, while ceramic fiber blankets excel in high-temperature resistance but may require careful handling to avoid damage.
Fire and Heat Resistance Capabilities
Polyethylene fiber insulation blankets provide limited fire resistance due to their low melting point and susceptibility to combustion, making them unsuitable for high-temperature applications. Ceramic fiber insulation blankets offer exceptional heat resistance, withstanding temperatures up to 2300degF (1260degC) and providing excellent non-combustible properties ideal for fire protection and industrial furnaces. The superior thermal stability and refractory nature of ceramic fibers ensure enhanced insulation performance in extreme heat conditions compared to polyethylene fibers.
Weight and Flexibility Considerations
Polyethylene fiber insulation blankets offer significantly lower weight, typically around 0.9 g/cm3, enhancing ease of handling and installation in applications requiring lightweight materials. Ceramic fiber blankets, with densities ranging from 96 to 384 kg/m3, tend to be heavier but provide superior thermal insulation and chemical resistance in high-temperature environments. Flexibility favors polyethylene fibers, which exhibit greater pliability and resilience, while ceramic fibers are more rigid and prone to brittleness under mechanical stress.
Health, Safety, and Environmental Impact
Polyethylene fiber insulation blankets offer low toxicity and excellent chemical resistance, making them safer for indoor air quality compared to ceramic fiber, which can release respirable crystalline silica and ceramic dust linked to respiratory issues. Polyethylene fibers are non-corrosive and pose minimal fire hazards, whereas ceramic fibers, while highly heat-resistant, can cause skin and lung irritation during handling without proper protective equipment. Environmentally, polyethylene fibers are often recyclable and produce fewer hazardous byproducts, whereas ceramic fibers require careful disposal due to their potential carcinogenic classification and limited biodegradability.
Cost and Installation Factors
Polyethylene fiber insulation blankets offer a lower upfront cost compared to ceramic fiber, making them a cost-effective solution for budget-sensitive projects. Installation of polyethylene fiber is generally easier and faster due to its lightweight and flexible nature, reducing labor time and associated expenses. In contrast, ceramic fiber blankets, although more expensive, provide superior thermal resistance and durability but require specialized handling and protective gear during installation to avoid health hazards.
Applications and Industry Recommendations
Polyethylene fiber insulation blankets are widely used in lightweight applications such as thermal protection in automotive and packaging industries due to their excellent flexibility and moisture resistance. Ceramic fiber insulation blankets excel in high-temperature environments like furnace linings and industrial kilns, offering superior thermal stability and chemical resistance up to 1400degC. Industry recommendations favor polyethylene fibers for low to moderate temperature insulation needs, while ceramic fibers are preferred for demanding high-heat applications requiring durability and fire resistance.
Infographic: Polyethylene fiber vs Ceramic fiber for Insulation blanket
 azmater.com
azmater.com