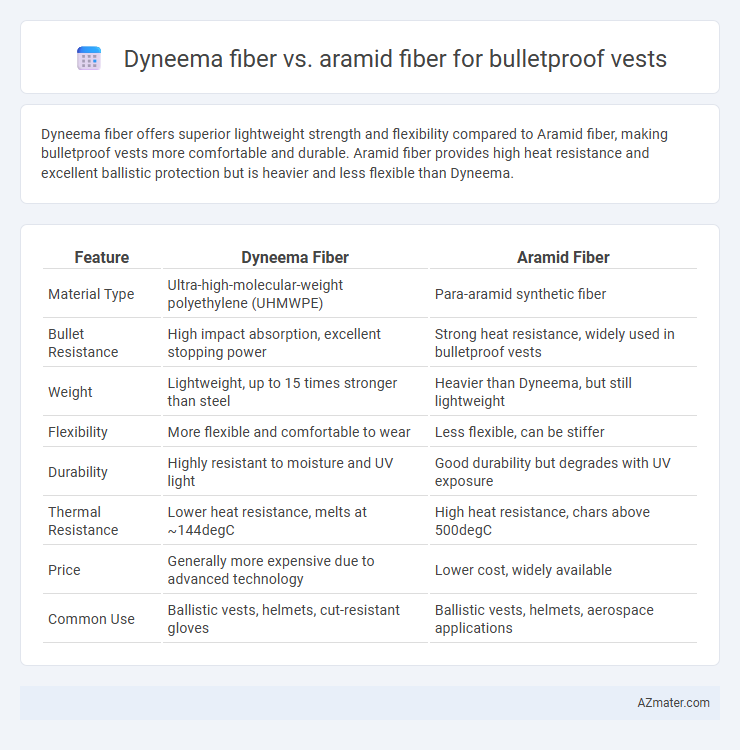
Dyneema fiber offers superior lightweight strength and flexibility compared to Aramid fiber, making bulletproof vests more comfortable and durable. Aramid fiber provides high heat resistance and excellent ballistic protection but is heavier and less flexible than Dyneema.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Dyneema Fiber | Aramid Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) | Para-aramid synthetic fiber |
| Bullet Resistance | High impact absorption, excellent stopping power | Strong heat resistance, widely used in bulletproof vests |
| Weight | Lightweight, up to 15 times stronger than steel | Heavier than Dyneema, but still lightweight |
| Flexibility | More flexible and comfortable to wear | Less flexible, can be stiffer |
| Durability | Highly resistant to moisture and UV light | Good durability but degrades with UV exposure |
| Thermal Resistance | Lower heat resistance, melts at ~144degC | High heat resistance, chars above 500degC |
| Price | Generally more expensive due to advanced technology | Lower cost, widely available |
| Common Use | Ballistic vests, helmets, cut-resistant gloves | Ballistic vests, helmets, aerospace applications |
Overview of Dyneema and Aramid Fibers
Dyneema fiber, known for its ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) composition, offers exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and superior impact resistance compared to traditional ballistic materials. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar and Twaron, are synthetic aromatic polyamides characterized by high tensile strength and excellent thermal stability but tend to be heavier and less resistant to moisture than Dyneema. Both materials are widely used in bulletproof vests, with Dyneema favored for lightweight, flexible protection and Aramid fibers preferred for heat resistance and durability in various ballistic applications.
Key Properties of Dyneema Fiber
Dyneema fiber, known as ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE), offers exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and superior cut resistance, making it a prime choice for lightweight bulletproof vests. Its high tensile strength, up to 15 times stronger than steel, provides excellent ballistic protection while enhancing wearer mobility. Dyneema's low density and excellent resistance to moisture and UV degradation contribute to longer-lasting performance and comfort compared to traditional aramid fibers like Kevlar.
Key Properties of Aramid Fiber
Aramid fiber boasts exceptional tensile strength and heat resistance, making it a prime choice for bulletproof vests requiring durability under high-stress conditions. Its superior impact resistance and ability to maintain structural integrity at elevated temperatures contribute to reliable ballistic protection. Unlike Dyneema fiber, aramid fibers such as Kevlar offer enhanced abrasion resistance and chemical stability, crucial for long-term vest performance in demanding environments.
Comparative Ballistic Performance
Dyneema fiber offers superior ballistic performance compared to Aramid fiber due to its higher tensile strength-to-weight ratio, resulting in lighter body armor with enhanced multi-hit capability. Dyneema's ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) structure efficiently disperses energy upon bullet impact, providing better blunt force trauma reduction. In contrast, Aramid fibers like Kevlar exhibit excellent heat resistance but tend to be heavier and less effective against certain high-velocity projectiles.
Weight and Comfort Differences
Dyneema fiber is significantly lighter than aramid fiber, offering enhanced comfort for bulletproof vest wearers by reducing fatigue during extended use. Its high strength-to-weight ratio allows for thinner, more flexible armor that does not sacrifice protection while improving mobility and breathability. In contrast, aramid fiber tends to be heavier and less flexible, which can result in bulkier vests that limit comfort and increase wearer heat retention.
Durability and Environmental Resistance
Dyneema fiber demonstrates superior durability compared to aramid fiber, maintaining strength and flexibility after prolonged exposure to moisture, UV radiation, and chemicals. Aramid fiber, while initially strong, degrades more quickly under environmental stressors like water absorption and UV exposure, reducing the effective lifespan of bulletproof vests. The enhanced environmental resistance of Dyneema ensures consistent ballistic performance and longer service life in diverse conditions, making it favorable for durable, weather-resistant body armor.
Flexibility and Wearability in Vests
Dyneema fiber offers superior flexibility compared to aramid fibers, allowing bulletproof vests to maintain greater comfort and freedom of movement without compromising ballistic protection. Its lightweight and moisture-resistant properties enhance overall wearability, reducing wearer fatigue during extended use. In contrast, aramid fibers, while strong, tend to be stiffer and less breathable, which can limit comfort and flexibility in tactical applications.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Dyneema fiber offers a higher cost compared to Aramid fiber due to its advanced ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene composition and specialized manufacturing process, which limits its widespread availability. Aramid fiber, such as Kevlar, remains more accessible and economically feasible for mass production, supported by established supply chains and extensive industrial use. Cost-efficiency and broad availability make Aramid a preferred choice for many bulletproof vest manufacturers despite Dyneema's superior strength-to-weight ratio.
Industry Applications and Use Cases
Dyneema fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and enhanced ballistic resistance, making it ideal for lightweight bulletproof vests used by military and law enforcement in high-mobility operations. Aramid fiber, such as Kevlar, excels in thermal stability and impact resistance, widely applied in tactical vests and protective gear for firefighting and riot control where heat and abrasion resistance are critical. Both fibers serve distinct industry needs with Dyneema preferred for lightweight, flexible protection and Aramid favored for durability in extreme environments.
Choosing the Right Fiber for Bulletproof Vests
Dyneema fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and excellent ballistic performance, making it ideal for lightweight bulletproof vests requiring high flexibility and durability. Aramid fiber, such as Kevlar, provides strong heat resistance and proven impact absorption, suitable for vests prioritizing multi-hit protection and thermal stability. Selecting the right fiber depends on application-specific needs: Dyneema excels in mobility and comfort, while Aramid is preferred for traditional toughness and resilience under harsh conditions.
Infographic: Dyneema fiber vs Aramid fiber for Bulletproof vest
 azmater.com
azmater.com