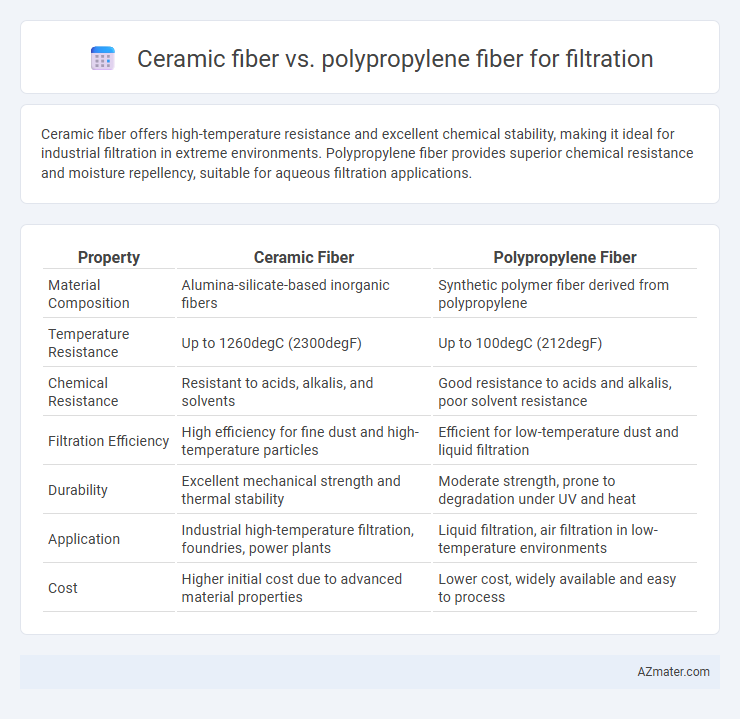
Ceramic fiber offers high-temperature resistance and excellent chemical stability, making it ideal for industrial filtration in extreme environments. Polypropylene fiber provides superior chemical resistance and moisture repellency, suitable for aqueous filtration applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ceramic Fiber | Polypropylene Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Alumina-silicate-based inorganic fibers | Synthetic polymer fiber derived from polypropylene |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 1260degC (2300degF) | Up to 100degC (212degF) |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to acids, alkalis, and solvents | Good resistance to acids and alkalis, poor solvent resistance |
| Filtration Efficiency | High efficiency for fine dust and high-temperature particles | Efficient for low-temperature dust and liquid filtration |
| Durability | Excellent mechanical strength and thermal stability | Moderate strength, prone to degradation under UV and heat |
| Application | Industrial high-temperature filtration, foundries, power plants | Liquid filtration, air filtration in low-temperature environments |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to advanced material properties | Lower cost, widely available and easy to process |
Overview of Ceramic Fiber and Polypropylene Fiber
Ceramic fiber offers excellent high-temperature resistance up to 1400degC and chemical stability, making it ideal for filtration in harsh industrial environments such as metal smelting and power plants. Polypropylene fiber, on the other hand, provides cost-effective filtration with superior resistance to acids and alkalis, along with hydrophobic properties suitable for liquid filtration in wastewater treatment. Both fibers deliver unique advantages depending on temperature tolerance, chemical compatibility, and application-specific filtration needs.
Material Composition and Structure
Ceramic fiber is composed primarily of alumina and silica, offering high thermal stability and resistance to chemical corrosion, which makes it ideal for high-temperature filtration applications. Polypropylene fiber, made from a synthetic polymer, features a lightweight, hydrophobic structure with excellent chemical resistance but is limited by lower melting points and mechanical strength. The porous, nonwoven arrangement of polypropylene fibers provides effective particulate capture at lower temperatures, whereas the rigid, woven or needled structure of ceramic fibers excels in extreme heat environments.
Filtration Efficiency Comparison
Ceramic fiber exhibits superior filtration efficiency compared to polypropylene fiber due to its high-temperature resistance and ability to capture fine particulate matter down to submicron levels. Polypropylene fiber, while cost-effective and lightweight, shows lower efficiency in filtering ultrafine particles and degrades at elevated temperatures above 100degC. The structural properties of ceramic fiber enhance durability and filtration stability in industrial applications requiring stringent particulate capture, making it preferable for high-performance filtration systems.
Temperature Resistance and Thermal Stability
Ceramic fiber exhibits exceptional temperature resistance, withstanding operating temperatures exceeding 1000degC, making it highly suitable for high-temperature filtration applications. Polypropylene fiber, on the other hand, degrades at lower temperatures, typically around 100-130degC, limiting its use to low-temperature filtration processes. The superior thermal stability of ceramic fiber ensures consistent performance and durability under extreme heat, whereas polypropylene fiber is prone to melting or structural breakdown when exposed to elevated temperatures.
Chemical Compatibility and Corrosion Resistance
Ceramic fiber exhibits exceptional chemical compatibility and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for filtration in highly acidic or alkaline environments, withstanding temperatures up to 1260degC without degradation. Polypropylene fiber offers moderate chemical resistance, particularly effective against organic solvents and mild acids, but it degrades under strong oxidizing agents and cannot tolerate high temperatures above 100degC. Selecting ceramic fiber ensures durability and performance in aggressive chemical settings, while polypropylene fiber suits filtration applications requiring lightweight material and resistance to less harsh chemicals.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Ceramic fiber exhibits superior mechanical strength and high-temperature resistance, making it ideal for filtration applications involving extreme heat and abrasive particles. Polypropylene fiber, while offering excellent chemical resistance and flexibility, has lower mechanical strength and degrades faster under high-temperature conditions. In terms of durability, ceramic fiber maintains structural integrity longer in harsh environments, whereas polypropylene fiber is better suited for low-temperature, less aggressive filtration processes.
Applications in Industrial Filtration
Ceramic fiber offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for high-temperature industrial filtration applications such as metal melting and exhaust gas cleaning. Polypropylene fiber excels in low-temperature filtration with excellent chemical resistance to acids and alkalis, commonly used in water treatment and air filtration systems. Selecting between ceramic and polypropylene fibers depends on operating temperature, chemical exposure, and filtration efficiency requirements specific to industries like steel manufacturing, chemical processing, and wastewater treatment.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Ceramic fiber filtration offers superior environmental benefits due to its high-temperature resistance and long lifespan, which reduces waste generation compared to polypropylene fiber filters that degrade faster and require more frequent replacement. Polypropylene fiber, derived from petroleum-based sources, poses sustainability challenges including carbon footprint and microplastic pollution risks during disposal. Ceramic fiber's recyclability and inert nature contribute to a lower environmental impact and enhanced sustainability in industrial filtration applications.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Ceramic fibers exhibit higher initial costs due to raw material and manufacturing complexities but offer longer service life and superior thermal resistance in filtration applications, which can reduce replacement frequency and downtime expenses. Polypropylene fibers are significantly more economical upfront, providing effective filtration at lower temperatures but may require more frequent replacement and increased maintenance costs over time. Economic considerations should balance initial investment against lifecycle costs, operational temperature requirements, and specific filtration efficiency needs to determine the optimal fiber choice.
Choosing the Right Fiber for Filtration Needs
Ceramic fiber offers exceptional thermal stability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for high-temperature filtration applications such as industrial exhaust systems and molten metal filtration. Polypropylene fiber provides excellent chemical resistance and flexibility at a lower cost, suitable for liquid filtration and air purification in less extreme environments. Selecting the right fiber depends on operating temperature, chemical exposure, and mechanical durability requirements specific to the filtration process.
Infographic: Ceramic fiber vs Polypropylene fiber for Filtration
 azmater.com
azmater.com