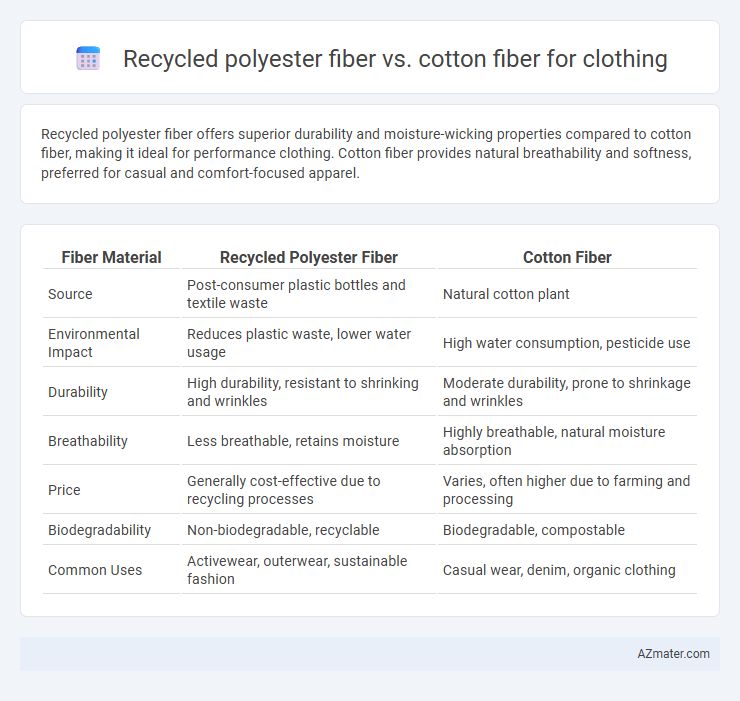
Recycled polyester fiber offers superior durability and moisture-wicking properties compared to cotton fiber, making it ideal for performance clothing. Cotton fiber provides natural breathability and softness, preferred for casual and comfort-focused apparel.
Table of Comparison
| Fiber Material | Recycled Polyester Fiber | Cotton Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Post-consumer plastic bottles and textile waste | Natural cotton plant |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces plastic waste, lower water usage | High water consumption, pesticide use |
| Durability | High durability, resistant to shrinking and wrinkles | Moderate durability, prone to shrinkage and wrinkles |
| Breathability | Less breathable, retains moisture | Highly breathable, natural moisture absorption |
| Price | Generally cost-effective due to recycling processes | Varies, often higher due to farming and processing |
| Biodegradability | Non-biodegradable, recyclable | Biodegradable, compostable |
| Common Uses | Activewear, outerwear, sustainable fashion | Casual wear, denim, organic clothing |
Introduction to Recycled Polyester Fiber and Cotton Fiber
Recycled polyester fiber is derived from post-consumer plastic waste such as PET bottles, reducing environmental impact by lowering landfill waste and energy consumption compared to virgin polyester production. Cotton fiber, a natural and biodegradable material, is cultivated from the cotton plant and prized for its breathability, softness, and moisture absorption in textile manufacturing. While recycled polyester offers durability and water resistance, cotton provides comfort and sustainability with proper farming practices, making both fibers pivotal in eco-conscious clothing production.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Recycled polyester fiber significantly reduces environmental impact by lowering greenhouse gas emissions by up to 75% compared to virgin polyester and conserving water resources relative to cotton cultivation, which requires approximately 10,000 liters of water per kilogram of fiber. Cotton fiber production contributes to soil degradation, pesticide pollution, and extensive freshwater consumption, making it one of the most resource-intensive natural fibers in the clothing industry. Choosing recycled polyester promotes circular economy principles through waste reduction and energy-efficient manufacturing, while cotton's environmental footprint remains heavily influenced by agricultural practices and land use.
Production Processes and Resource Consumption
Recycled polyester fiber is produced by melting down used plastic bottles and industrial polyester waste, significantly reducing raw material extraction and energy consumption compared to virgin polyester production. Cotton fiber cultivation requires extensive land, water, and pesticide inputs, with approximately 2,700 liters of water needed to produce one kilogram of cotton, leading to high environmental resource consumption. The production process of recycled polyester lowers greenhouse gas emissions by up to 75% relative to conventional cotton farming, making it a more sustainable choice for clothing manufacturing.
Durability and Longevity in Clothing
Recycled polyester fiber offers superior durability and resistance to wear compared to cotton fiber, making it ideal for long-lasting clothing. It retains its shape and color after multiple washes, while cotton tends to shrink and fade over time. The high tensile strength of recycled polyester also provides enhanced longevity, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
Comfort and Breathability Differences
Recycled polyester fiber offers durability and moisture-wicking properties but tends to be less breathable and can trap heat compared to cotton fiber. Cotton fiber excels in comfort and breathability due to its natural ability to absorb moisture and allow air circulation, making it ideal for warm-weather clothing. The choice between these fibers impacts garment performance, with cotton preferred for softness and ventilation, while recycled polyester suits activewear needing quick-drying and resilience.
Moisture-Wicking and Performance Attributes
Recycled polyester fiber offers superior moisture-wicking capabilities compared to cotton fiber, effectively drawing sweat away from the skin to enhance comfort during physical activities. Its synthetic structure promotes faster drying times and better breathability, making it ideal for high-performance and athletic clothing. In contrast, cotton fiber, while breathable, tends to retain moisture, which can lead to slower drying and a heavier feel during intense workouts.
Cost Analysis and Market Trends
Recycled polyester fiber generally offers a lower production cost compared to cotton fiber due to its use of post-consumer plastic waste and less water consumption, making it an economically viable material for sustainable fashion brands. Market trends indicate a growing demand for recycled polyester driven by increasing consumer awareness of environmental impact and corporate commitments to circular economy practices, whereas cotton faces challenges related to water usage and land requirements despite its natural fiber appeal. Cost volatility in raw cotton prices and advancements in recycling technologies are shaping the competitive landscape, favoring recycled polyester for mass-market apparel production.
Biodegradability and End-of-Life Considerations
Recycled polyester fiber, derived from post-consumer plastic, offers durability and reduces reliance on virgin resources but lacks biodegradability, persisting in landfills for hundreds of years. Cotton fiber, naturally biodegradable, decomposes within months to a few years under composting conditions, minimizing environmental impact after disposal. End-of-life considerations favor cotton for its rapid bio-breakdown, while recycled polyester requires advanced recycling or energy recovery methods to mitigate long-term environmental persistence.
Consumer Preferences and Brand Perspectives
Recycled polyester fiber offers durability, moisture-wicking properties, and environmental benefits that appeal to eco-conscious consumers, while cotton fiber is favored for its natural softness and breathability. Brands increasingly prioritize recycled polyester to reduce carbon footprints and promote sustainability, responding to growing demand for low-impact fashion material. Consumer preferences lean towards blended fabrics combining recycled polyester and cotton, balancing comfort with sustainability and performance.
Future Trends in Sustainable Clothing Materials
Recycled polyester fiber offers significant environmental advantages over conventional cotton fiber, including reduced water consumption and lower greenhouse gas emissions, making it a key focus in the future of sustainable clothing materials. Innovations in recycling technologies and fiber blending are enhancing the performance and recyclability of recycled polyester, positioning it as a scalable solution in eco-friendly fashion. Consumer demand for durability and eco-conscious products drives brands toward integrating recycled polyester with organic cotton blends, promoting circularity and resource efficiency in apparel production.
Infographic: Recycled polyester fiber vs Cotton fiber for Clothing
 azmater.com
azmater.com