Graphene fiber offers superior thermal conductivity, lightweight strength, and enhanced durability compared to traditional asbestos fiber in brake linings. Unlike asbestos, graphene fiber is non-toxic, providing safer performance and improved heat dissipation for longer brake life.
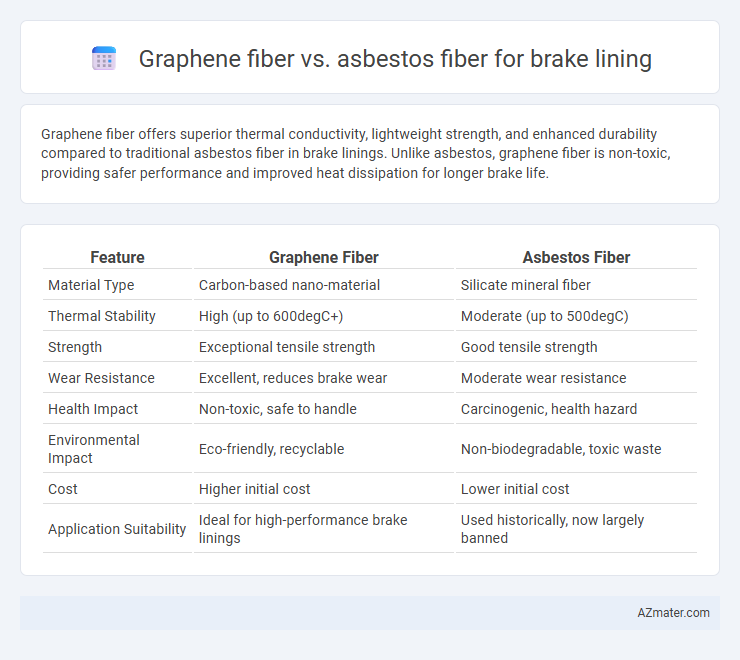
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Graphene Fiber | Asbestos Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Carbon-based nano-material | Silicate mineral fiber |
| Thermal Stability | High (up to 600degC+) | Moderate (up to 500degC) |
| Strength | Exceptional tensile strength | Good tensile strength |
| Wear Resistance | Excellent, reduces brake wear | Moderate wear resistance |
| Health Impact | Non-toxic, safe to handle | Carcinogenic, health hazard |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, recyclable | Non-biodegradable, toxic waste |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower initial cost |
| Application Suitability | Ideal for high-performance brake linings | Used historically, now largely banned |
Introduction to Brake Lining Materials
Brake lining materials play a critical role in vehicle safety and performance, requiring high thermal stability and durability under friction conditions. Graphene fiber, with its exceptional tensile strength, thermal conductivity, and lightweight properties, offers an innovative alternative to traditional asbestos fiber, which has been widely used but poses serious health risks due to its carcinogenic nature. The transition from asbestos to graphene fiber enhances brake lining performance by improving wear resistance and heat dissipation while eliminating hazardous dust generation during braking.
Overview of Graphene Fiber
Graphene fiber, known for its exceptional tensile strength and thermal conductivity, offers a lightweight and durable alternative to traditional asbestos fibers in brake lining applications. Unlike asbestos, which poses significant health hazards due to its carcinogenic properties, graphene fibers provide enhanced heat dissipation and friction stability, improving brake performance and safety. The integration of graphene fiber in brake linings leads to longer-lasting materials with superior resistance to wear and high-temperature degradation.
Overview of Asbestos Fiber
Asbestos fiber, historically used in brake linings, is a naturally occurring silicate mineral known for its high tensile strength, heat resistance, and excellent insulating properties. Despite its effectiveness in thermal stability and durability under friction, asbestos poses significant health risks due to its fibrous particles causing respiratory diseases when inhaled. Regulatory bans and safety concerns have driven the search for safer alternatives like graphene fiber, which offers comparable mechanical strength and thermal performance without the associated toxicity.
Physical and Mechanical Properties Comparison
Graphene fiber offers superior tensile strength and elasticity compared to asbestos fiber, enhancing brake lining durability and resistance to wear under high-stress conditions. Its excellent thermal conductivity and lightweight nature improve heat dissipation and reduce overall brake assembly weight, unlike asbestos which poses health risks and offers moderate thermal resistance. Additionally, graphene fiber's chemical stability ensures prolonged performance and safety, making it a preferable alternative in modern brake lining materials.
Thermal Stability and Heat Resistance
Graphene fiber exhibits superior thermal stability and heat resistance compared to asbestos fiber, making it an advanced material for brake lining applications. Its high thermal conductivity and ability to withstand temperatures exceeding 500degC enhance braking performance and durability under extreme conditions. Unlike asbestos, graphene fiber poses no health risks, offering a safer and more efficient alternative for thermal management in automotive brake systems.
Safety and Health Implications
Graphene fiber in brake lining offers significantly improved safety over asbestos fiber due to its non-toxic and biocompatible nature, reducing the risk of respiratory diseases such as asbestosis and mesothelioma linked to asbestos exposure. Graphene's enhanced mechanical strength and thermal conductivity contribute to longer brake lifespan and reduced dust emission, minimizing airborne particulate hazards. Transitioning to graphene fiber aligns with occupational health standards by eliminating carcinogenic concerns associated with asbestos in automotive braking systems.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Graphene fiber in brake linings significantly reduces environmental hazards compared to asbestos fiber, as asbestos releases carcinogenic dust harmful to both human health and ecosystems during wear and disposal. The use of graphene fibers lowers particulate emissions, enhances recyclability, and minimizes contamination risks in soil and water systems, aligning with stringent environmental regulations. Life cycle assessments demonstrate graphene's superior environmental profile, promoting sustainable manufacturing and safer end-of-life handling in automotive applications.
Performance in Brake Applications
Graphene fiber offers superior thermal conductivity and mechanical strength compared to asbestos fiber, resulting in enhanced heat dissipation and improved wear resistance in brake linings. The lightweight nature of graphene fiber contributes to reduced brake fade and longer service life under high-stress braking conditions. Unlike asbestos, graphene fibers provide safer, non-toxic performance while maintaining exceptional friction stability and durability in brake applications.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Graphene fiber offers a higher cost efficiency over asbestos fiber in brake linings due to its durability and superior thermal conductivity, reducing overall replacement frequency. Manufacturing with graphene fiber involves advanced processes such as chemical vapor deposition, which can be more complex but allows for precise material control and scalability. Although initial production costs may be higher, graphene fiber's eco-friendly profile and regulatory compliance reduce long-term liabilities compared to asbestos, which faces stringent restrictions due to health hazards and disposal costs.
Future Prospects and Industry Trends
Graphene fiber offers superior thermal conductivity and mechanical strength compared to asbestos fiber, making it a promising alternative for brake lining applications with enhanced safety and environmental compliance. The automotive industry is increasingly adopting graphene-based composites due to stricter regulations on asbestos use and growing demand for high-performance, lightweight brake materials. Future trends indicate accelerated research investment and commercial scaling of graphene fiber technologies to meet evolving standards in emission reduction and vehicle efficiency.
Infographic: Graphene fiber vs Asbestos fiber for Brake lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com