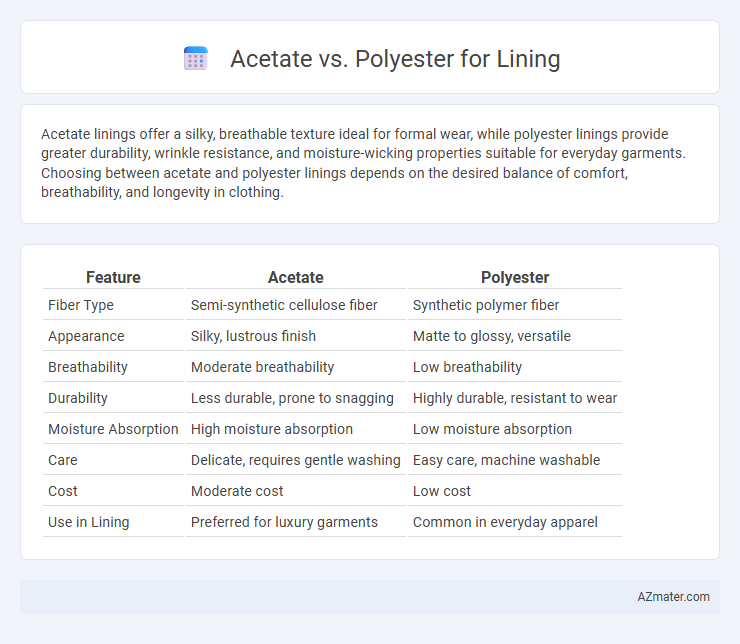
Acetate linings offer a silky, breathable texture ideal for formal wear, while polyester linings provide greater durability, wrinkle resistance, and moisture-wicking properties suitable for everyday garments. Choosing between acetate and polyester linings depends on the desired balance of comfort, breathability, and longevity in clothing.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Acetate | Polyester |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber Type | Semi-synthetic cellulose fiber | Synthetic polymer fiber |
| Appearance | Silky, lustrous finish | Matte to glossy, versatile |
| Breathability | Moderate breathability | Low breathability |
| Durability | Less durable, prone to snagging | Highly durable, resistant to wear |
| Moisture Absorption | High moisture absorption | Low moisture absorption |
| Care | Delicate, requires gentle washing | Easy care, machine washable |
| Cost | Moderate cost | Low cost |
| Use in Lining | Preferred for luxury garments | Common in everyday apparel |
Introduction: Why Lining Material Matters
Lining materials like acetate and polyester significantly impact garment comfort, durability, and appearance by controlling breathability, moisture-wicking, and texture against the skin. Acetate offers a silky, luxurious feel with excellent drape and resistance to static, making it ideal for high-end clothing linings. Polyester provides greater durability, wrinkle resistance, and cost-effectiveness, commonly used in everyday fashion and outerwear linings.
What is Acetate? Key Properties and Uses
Acetate is a semi-synthetic fiber derived from cellulose, known for its smooth, silky texture and excellent draping qualities, making it a popular choice for garment linings. Its key properties include a lustrous appearance, good moisture absorption, and resistance to shrinking, though it is less durable and heat-sensitive compared to polyester. Common uses of acetate lining include formal wear, dresses, and suits, where its softness enhances comfort and fabric appearance.
What is Polyester? Key Properties and Uses
Polyester is a synthetic fiber derived from petrochemical processes, known for its durability, resistance to shrinking and stretching, and quick-drying qualities. Its key properties include high tensile strength, wrinkle resistance, and excellent color retention, making it a popular choice for clothing linings. Common uses of polyester linings range from jackets and coats to pants and skirts, offering enhanced shape retention and moisture-wicking capabilities compared to acetate.
Comfort Comparison: Acetate vs Polyester Linings
Acetate linings offer a silky, breathable feel that enhances comfort by allowing better moisture absorption compared to polyester. Polyester linings, while durable and resistant to wrinkles, tend to trap heat and moisture, potentially causing discomfort during prolonged wear. Choosing acetate over polyester results in smoother, cooler interiors, ideal for garments intended for warmer climates or extended use.
Breathability and Moisture Management
Acetate linings offer moderate breathability and a smooth, luxurious feel but tend to trap moisture, making them less effective at moisture management compared to polyester. Polyester linings excel in wicking moisture away from the body and drying quickly, enhancing comfort in active or warm conditions. Breathable polyester fabrics facilitate airflow, reducing sweat buildup and improving overall garment ventilation.
Durability and Longevity
Acetate lining offers a smooth, silk-like feel but tends to have lower durability and can degrade faster with moisture and heat exposure compared to polyester. Polyester lining is highly durable, resistant to wrinkles, abrasions, and moisture, making it ideal for long-lasting garments. Choosing polyester enhances the longevity of clothing by maintaining structure and appearance even after frequent wear and cleaning.
Ease of Care and Maintenance
Acetate lining offers moderate ease of care, often requiring dry cleaning to maintain its smooth texture and prevent shrinkage, while polyester lining is highly durable and wrinkle-resistant, allowing for simple machine washing and quick drying. Polyester's stain resistance and color retention contribute to low maintenance compared to acetate, which may degrade under harsh washing conditions. Choosing polyester for lining ensures long-lasting fabric integrity and a convenient care routine, ideal for everyday wear and frequent laundering.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Acetate linings, derived from cellulose fibers, offer better biodegradability and a lower carbon footprint compared to petroleum-based polyester linings, which rely on fossil fuels and contribute to microplastic pollution. Polyester is more durable and resistant to moisture, but its production involves energy-intensive processes and generates non-biodegradable waste that persists in landfills and oceans. Choosing acetate for linings aligns with sustainable fashion goals by promoting renewable resources and reducing long-term environmental harm.
Cost and Affordability
Acetate linings generally cost less than polyester, making them a more budget-friendly option for affordable garment production. Polyester offers greater durability and resistance to wrinkles, which can lead to longer-lasting garments despite a higher initial cost. Choosing between acetate and polyester lining depends on balancing upfront affordability with long-term wear and maintenance expenses.
Best Applications: When to Choose Acetate or Polyester
Acetate linings are best suited for formal wear and lightweight garments due to their smooth, luxurious feel and excellent drape, offering breathability and moisture-wicking properties ideal for suits and evening dresses. Polyester linings provide superior durability, wrinkle resistance, and are cost-effective, making them ideal for everyday wear, jackets, and work uniforms where longevity and easy care are priorities. Choosing acetate enhances comfort and elegance in high-end apparel, while polyester is preferred for practicality and resilience in frequently worn or structured clothing.
Infographic: Acetate vs Polyester for Lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com