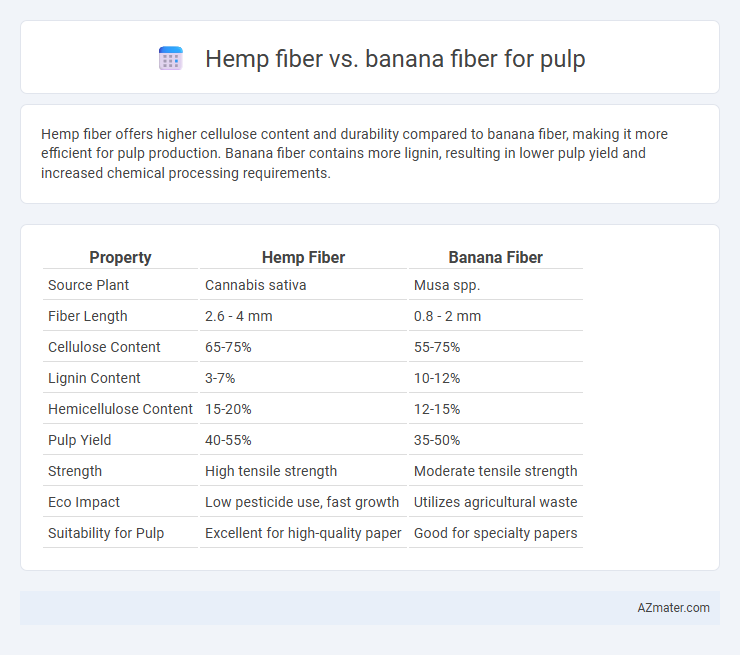
Hemp fiber offers higher cellulose content and durability compared to banana fiber, making it more efficient for pulp production. Banana fiber contains more lignin, resulting in lower pulp yield and increased chemical processing requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hemp Fiber | Banana Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source Plant | Cannabis sativa | Musa spp. |
| Fiber Length | 2.6 - 4 mm | 0.8 - 2 mm |
| Cellulose Content | 65-75% | 55-75% |
| Lignin Content | 3-7% | 10-12% |
| Hemicellulose Content | 15-20% | 12-15% |
| Pulp Yield | 40-55% | 35-50% |
| Strength | High tensile strength | Moderate tensile strength |
| Eco Impact | Low pesticide use, fast growth | Utilizes agricultural waste |
| Suitability for Pulp | Excellent for high-quality paper | Good for specialty papers |
Introduction: Comparing Hemp and Banana Fibers for Pulp
Hemp fiber exhibits superior tensile strength and higher cellulose content compared to banana fiber, making it more efficient for pulp production. Banana fiber, while abundant and sustainable, tends to have higher lignin levels, which require more intensive chemical processing. Both fibers offer eco-friendly alternatives to wood pulp, but hemp's faster growth cycle and better fiber quality provide distinct advantages in pulp manufacturing.
Botanical Background of Hemp and Banana Fibers
Hemp fiber, derived from the stalks of Cannabis sativa, is known for its high cellulose content and long bast fibers, making it ideal for pulp production due to its strength and durability. Banana fiber, extracted from the pseudostem of Musa plants, offers a rich source of lignocellulosic material with shorter fibers compared to hemp, influencing its pulp quality and texture. Both fibers exhibit distinctive botanical structures that affect pulping efficiency, with hemp's dense vascular bundles contrasting banana's layered fiber architecture.
Fiber Extraction Methods: Hemp vs. Banana
Hemp fiber extraction typically involves chemical retting or enzymatic processes to separate cellulose fibers efficiently, resulting in high-quality pulp suitable for paper production. Banana fiber extraction relies on mechanical decortication followed by water retting to remove non-cellulosic materials, but this method can yield shorter fibers with higher lignin content, affecting pulp quality. Comparing these methods, hemp's enzymatic retting offers more consistent fiber purity, while banana fiber extraction is more labor-intensive and variable, impacting overall pulp performance.
Chemical Composition Differences: Hemp and Banana
Hemp fiber contains approximately 60-70% cellulose, 5-12% hemicellulose, and 5-8% lignin, making it highly suitable for pulp production with strong fiber bonds and durability. Banana fiber typically has a lower cellulose content of around 40-60%, higher hemicellulose up to 25%, and lignin content ranging from 10-20%, which affects its strength and bleaching requirements in pulp processing. The higher lignin and hemicellulose in banana fiber result in increased chemical consumption and processing time compared to hemp fiber, influencing pulp yield and quality.
Pulp Yield: Efficiency Analysis
Hemp fiber demonstrates a higher pulp yield efficiency, typically producing 40-50% of usable fiber from raw material, compared to banana fiber, which yields around 30-40%. The superior lignin and cellulose composition in hemp contributes to more efficient pulping processes and better fiber quality. Consequently, hemp pulp is favored for industrial applications requiring stronger, durable paper products.
Physical Properties of Resulting Pulps
Hemp fiber pulp exhibits superior tensile strength and higher tear resistance compared to banana fiber pulp, making it ideal for producing durable paper products. Banana fiber pulp typically has a coarser texture and lower brightness, resulting in a more fibrous and less smooth paper surface. The higher lignin content in banana fiber also affects its pulping efficiency and results in a darker pulp compared to the lighter, more refined hemp pulp.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Hemp fiber for pulp production offers a significantly lower environmental impact compared to banana fiber due to its rapid growth rate, higher yield per acre, and minimal need for pesticides or herbicides, making it a sustainable choice for eco-friendly paper manufacturing. Banana fiber, while biodegradable and derived from agricultural waste, often requires intensive processing and water use, which can reduce its overall sustainability in large-scale pulp applications. The carbon footprint of hemp pulp is generally lower, supporting sustainable forestry practices and reducing deforestation pressures linked to traditional wood pulp sources.
Industrial Applications and Adaptability
Hemp fiber demonstrates superior tensile strength and chemical resistance, making it highly suitable for industrial pulp applications such as paper production and biocomposites. Banana fiber offers high cellulose content and biodegradability, which enhances its adaptability for eco-friendly packaging and textile industries. Both fibers provide sustainable alternatives to traditional wood pulp, with hemp excelling in durability and banana fiber favoring environmental impact and versatility.
Cost Comparison: Production and Processing
Hemp fiber production for pulp involves higher initial cultivation costs due to extensive agricultural inputs but benefits from faster growth cycles, making overall annual yield cost-effective. Banana fiber extraction requires intensive manual labor for processing pseudostems and has lower mechanization potential, increasing operational expenses despite lower raw material costs. When compared, hemp's mechanized processing reduces long-term production costs, whereas banana fiber's labor-intensive steps elevate processing expenses, affecting total cost competitiveness in pulp manufacturing.
Future Prospects and Innovations in Pulp Industry
Hemp fiber offers a higher cellulose content and faster growth cycle compared to banana fiber, making it a promising raw material for sustainable pulp production in the future. Innovations in enzymatic treatment and bio-refining techniques are improving the extraction efficiency and environmental footprint of hemp-based pulp. Research into hybrid fiber blends combining hemp and banana fibers aims to enhance paper strength and reduce processing costs, driving advancements in the pulp industry's eco-friendly alternatives.
Infographic: Hemp fiber vs Banana fiber for Pulp
 azmater.com
azmater.com