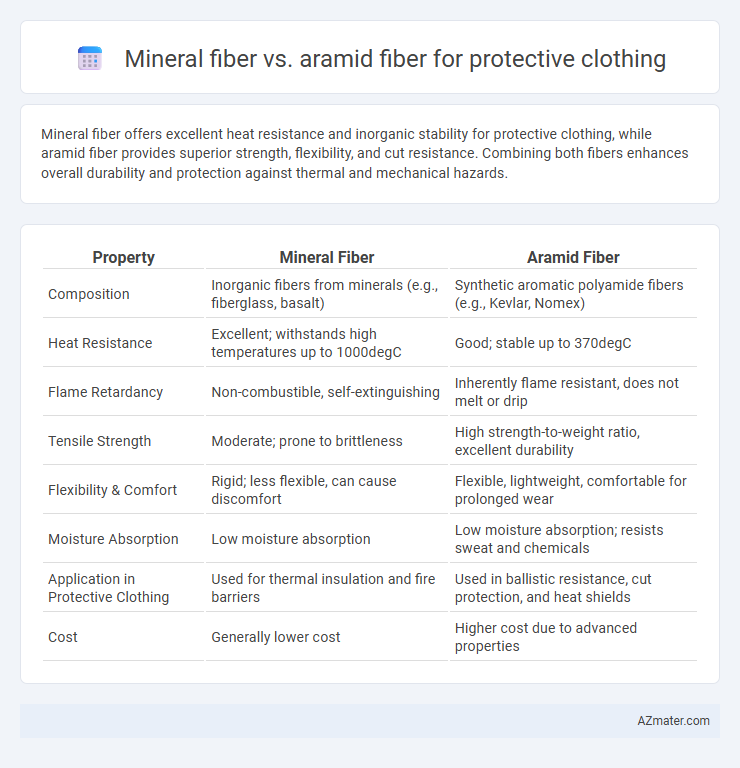
Mineral fiber offers excellent heat resistance and inorganic stability for protective clothing, while aramid fiber provides superior strength, flexibility, and cut resistance. Combining both fibers enhances overall durability and protection against thermal and mechanical hazards.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Mineral Fiber | Aramid Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Inorganic fibers from minerals (e.g., fiberglass, basalt) | Synthetic aromatic polyamide fibers (e.g., Kevlar, Nomex) |
| Heat Resistance | Excellent; withstands high temperatures up to 1000degC | Good; stable up to 370degC |
| Flame Retardancy | Non-combustible, self-extinguishing | Inherently flame resistant, does not melt or drip |
| Tensile Strength | Moderate; prone to brittleness | High strength-to-weight ratio, excellent durability |
| Flexibility & Comfort | Rigid; less flexible, can cause discomfort | Flexible, lightweight, comfortable for prolonged wear |
| Moisture Absorption | Low moisture absorption | Low moisture absorption; resists sweat and chemicals |
| Application in Protective Clothing | Used for thermal insulation and fire barriers | Used in ballistic resistance, cut protection, and heat shields |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to advanced properties |
Overview of Protective Clothing Materials
Mineral fibers like asbestos were historically used in protective clothing for their heat resistance but pose significant health risks due to fiber inhalation hazards. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar and Nomex, offer superior thermal stability, high tensile strength, and excellent cut and abrasion resistance, making them the preferred choice for modern protective garments. Advances in aramid fiber technology provide lightweight, durable, and flame-resistant materials critical for firefighter suits, industrial safety apparel, and ballistic protection.
What are Mineral Fibers?
Mineral fibers, primarily composed of inorganic materials such as basalt, glass, and ceramic fibers, offer exceptional thermal resistance and non-combustibility for protective clothing. These fibers provide high tensile strength and excellent insulation against extreme heat, making them ideal for firefighting and industrial safety applications. Mineral fibers also exhibit chemical stability and durability, enhancing protective garments against harsh environmental conditions.
What are Aramid Fibers?
Aramid fibers are synthetic fibers known for their exceptional strength, heat resistance, and durability, making them ideal for protective clothing in high-risk environments. Unlike mineral fibers such as fiberglass, aramid fibers, including Kevlar and Nomex, offer superior flexibility, lightweight comfort, and resistance to flames and cuts. These properties ensure enhanced protection against heat, abrasions, and mechanical impacts, crucial for firefighters, military personnel, and industrial workers.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Mineral fiber exhibits high thermal resistance and moderate tensile strength, making it suitable for protection against extreme heat but with limited flexibility. Aramid fiber offers superior mechanical strength, high tensile strength, and excellent impact resistance, enabling enhanced durability and abrasion resistance in protective clothing. In terms of mechanical performance, aramid fibers outperform mineral fibers by providing greater flexibility and resilience under dynamic stress conditions.
Thermal Resistance and Heat Protection
Mineral fibers exhibit exceptional thermal resistance with melting points typically above 1000degC, making them highly effective for heat protection in protective clothing. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar and Nomex, offer excellent heat resistance and thermal stability up to approximately 400degC while providing superior strength and flexibility. Protective clothing leveraging mineral fibers is ideal for environments with extreme heat exposure, whereas aramid fibers provide balanced protection with enhanced durability and comfort for mid-range thermal hazards.
Chemical Resistance Properties
Mineral fibers exhibit superior chemical resistance, particularly against acids and alkalis, making them ideal for protective clothing in highly corrosive environments. Aramid fibers offer moderate chemical resistance but excel in resisting organic solvents and high-temperature degradation. Protective garments utilizing mineral fibers provide enhanced durability and prolonged protection when exposed to aggressive chemical agents compared to aramid fiber alternatives.
Comfort and Flexibility in Wear
Mineral fibers offer excellent thermal resistance but tend to be stiffer and less breathable, impacting comfort and flexibility in protective clothing. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, provide superior flexibility and lightweight comfort while maintaining high thermal and abrasion resistance. For wear requiring extended movement and prolonged use, aramid fibers are generally preferred due to their enhanced comfort and flexibility properties.
Durability and Longevity
Mineral fiber offers exceptional heat resistance and maintains structural integrity under extreme temperatures, making it highly durable for protective clothing in high-heat environments. Aramid fiber, such as Kevlar, provides superior tensile strength and excellent abrasion resistance, enhancing longevity against mechanical wear and impacts. Both fibers deliver long-lasting protection, but mineral fibers excel in thermal durability while aramid fibers outperform in overall durability against physical stress.
Cost and Availability
Mineral fiber protective clothing is generally more cost-effective and widely available due to its established production and lower material costs. Aramid fiber, known for superior strength and heat resistance, tends to be more expensive and less readily accessible because of complex manufacturing processes and limited suppliers. Cost efficiency and material accessibility make mineral fiber a preferred choice in budget-constrained safety applications despite aramid fiber's performance advantages.
Suitability for Various Applications
Mineral fibers offer excellent heat resistance and non-flammability, making them ideal for high-temperature environments such as firefighting and foundry work. Aramid fibers provide superior tensile strength, puncture resistance, and flexibility, which are essential for ballistic protection and cut-resistant clothing. The choice between mineral and aramid fibers depends on specific application requirements, balancing heat resistance and mechanical durability for optimal protective performance.
Infographic: Mineral fiber vs Aramid fiber for Protective clothing
 azmater.com
azmater.com