Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based sources, offers superior environmental sustainability and durability for upholstery compared to rayon fiber, which is chemically processed from wood pulp and tends to degrade faster. Ingeo's natural moisture-wicking and wrinkle-resistant properties enhance comfort and longevity, making it a preferable choice for eco-friendly and high-performance upholstery applications.
Table of Comparison
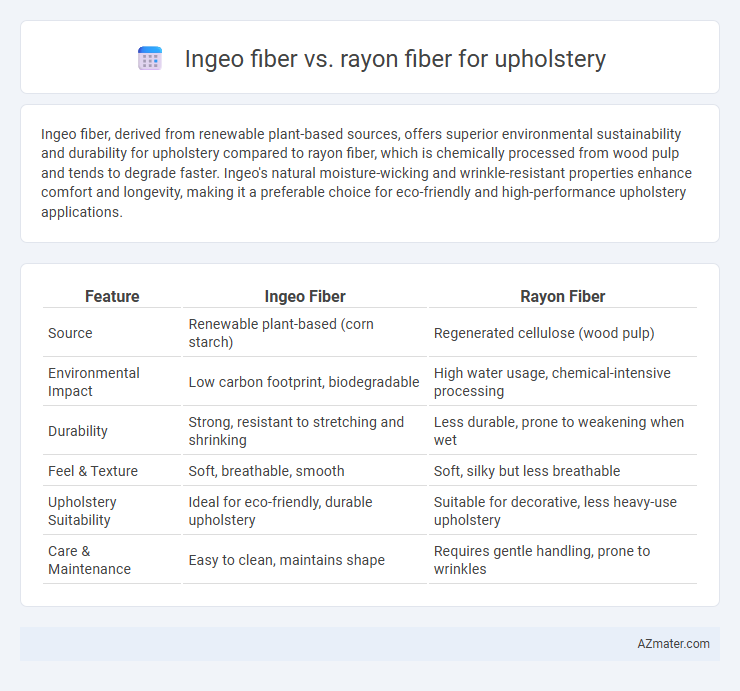
| Feature | Ingeo Fiber | Rayon Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Renewable plant-based (corn starch) | Regenerated cellulose (wood pulp) |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, biodegradable | High water usage, chemical-intensive processing |
| Durability | Strong, resistant to stretching and shrinking | Less durable, prone to weakening when wet |
| Feel & Texture | Soft, breathable, smooth | Soft, silky but less breathable |
| Upholstery Suitability | Ideal for eco-friendly, durable upholstery | Suitable for decorative, less heavy-use upholstery |
| Care & Maintenance | Easy to clean, maintains shape | Requires gentle handling, prone to wrinkles |
Introduction to Ingeo and Rayon Fibers
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based resources such as corn starch, offers a sustainable alternative to traditional fibers and is biodegradable with a low environmental footprint in upholstery applications. Rayon fiber, a semi-synthetic fiber made from regenerated cellulose obtained from wood pulp, provides a soft, smooth texture favored in upholstery but involves higher chemical processing with less eco-friendly attributes. Comparing Ingeo and Rayon fibers, key considerations include Ingeo's renewable origin and biodegradability versus Rayon's versatility and cost-effectiveness in fabric production.
Origin and Production Processes
Ingeo fiber is derived from renewable plant sources, primarily corn starch, through a fermentation and polymerization process that results in a biopolymer called polylactic acid (PLA), making it a sustainable choice for upholstery. Rayon fiber originates from cellulose found in wood pulp, which undergoes chemical treatment and spinning processes to create a semi-synthetic fiber often reliant on intensive chemical use. The production of Ingeo fiber offers lower environmental impact due to its renewable origins and reduced chemical processing compared to traditional rayon manufacturing methods.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Ingeo fiber, made from renewable plant-based materials like corn, offers significant environmental benefits over rayon fiber, which is derived from cellulose through chemical-intensive processes. Ingeo production releases fewer greenhouse gases and consumes less water, while rayon manufacturing often involves toxic chemicals such as carbon disulfide, posing risks to ecosystems and workers. Choosing Ingeo fiber for upholstery supports sustainability by reducing carbon footprint and minimizing pollution compared to conventional rayon fibers.
Physical Properties: Strength and Durability
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based materials, offers superior tensile strength and resistance to wear compared to traditional rayon fiber, making it a more durable choice for upholstery applications. Rayon fiber, though soft and breathable, tends to exhibit lower abrasion resistance and can weaken when exposed to moisture, reducing its overall longevity in high-traffic furniture. The enhanced durability and strength of Ingeo fiber contribute to extended fabric life, maintaining upholstery integrity under frequent use and stress.
Comfort and Texture Differences
Ingeo fiber offers a softer, more breathable texture compared to Rayon fiber, enhancing comfort in upholstery applications by providing better moisture-wicking properties and a cooler feel. Rayon fiber tends to have a smoother but less breathable surface, which may cause heat retention during prolonged use. Choosing Ingeo fiber can result in upholstery that feels more natural and comfortable due to its renewable plant-based origins and superior tactile softness.
Stain and Moisture Resistance
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based materials like corn, offers superior stain and moisture resistance compared to traditional Rayon fiber, which is made from regenerated cellulose and tends to absorb water more readily. The hydrophobic properties of Ingeo fibers reduce liquid absorption, making upholstery more durable and easier to clean, whereas Rayon fibers can stain and retain moisture, leading to potential mold and mildew issues. This enhanced resistance of Ingeo fiber improves the longevity and maintenance of upholstery fabrics in high-traffic or humid environments.
Color Retention and Fading
Ingeo fiber demonstrates superior color retention compared to rayon fiber in upholstery applications, maintaining vibrant hues longer under regular use and exposure to light. Rayon fibers tend to fade more quickly due to their cellulose-based composition, which is less resistant to UV degradation and washing. Choosing Ingeo fiber enhances durability and aesthetic longevity in furniture textiles where colorfastness is critical.
Cost and Market Availability
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant materials, offers a sustainable alternative to rayon fiber, which is chemically produced from regenerated cellulose. In terms of cost, Ingeo fiber generally carries a premium price due to its eco-friendly manufacturing process and lower production scale, while rayon fiber remains more affordable and widely available in the upholstery market. Market availability favors rayon fiber given its long-standing industry presence and established supply chains, whereas Ingeo fiber is gaining traction primarily in niche and eco-conscious segments.
Suitability for Upholstery Applications
Ingeo fiber offers superior durability and stain resistance compared to rayon fiber, making it more suitable for high-traffic upholstery applications. Its renewable, bio-based origin enhances sustainability without compromising fabric strength, whereas rayon tends to be less resilient and more prone to wear and moisture damage. Ingeo's resistance to fading and environmental impact gives it a distinct advantage in long-lasting, eco-friendly upholstery projects.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Fiber
Ingeo fiber offers superior sustainability, being made from renewable plant-based materials with a lower environmental impact compared to rayon, which is derived from chemically processed wood pulp. Ingeo provides enhanced durability and UV resistance, making it more suitable for long-lasting upholstery applications, while rayon tends to have a softer feel but may degrade faster under heavy use. Selecting Ingeo fiber ensures eco-friendly, robust upholstery with reduced maintenance, whereas rayon is preferred for cost-effective, softer finishes in low-traffic areas.
Infographic: Ingeo fiber vs Rayon fiber for Upholstery
 azmater.com
azmater.com