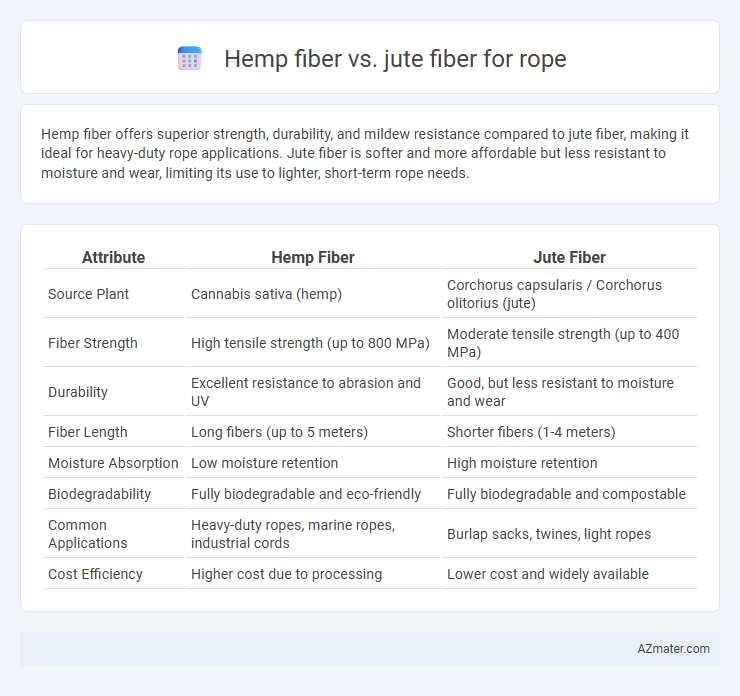
Hemp fiber offers superior strength, durability, and mildew resistance compared to jute fiber, making it ideal for heavy-duty rope applications. Jute fiber is softer and more affordable but less resistant to moisture and wear, limiting its use to lighter, short-term rope needs.
Table of Comparison
| Attribute | Hemp Fiber | Jute Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source Plant | Cannabis sativa (hemp) | Corchorus capsularis / Corchorus olitorius (jute) |
| Fiber Strength | High tensile strength (up to 800 MPa) | Moderate tensile strength (up to 400 MPa) |
| Durability | Excellent resistance to abrasion and UV | Good, but less resistant to moisture and wear |
| Fiber Length | Long fibers (up to 5 meters) | Shorter fibers (1-4 meters) |
| Moisture Absorption | Low moisture retention | High moisture retention |
| Biodegradability | Fully biodegradable and eco-friendly | Fully biodegradable and compostable |
| Common Applications | Heavy-duty ropes, marine ropes, industrial cords | Burlap sacks, twines, light ropes |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher cost due to processing | Lower cost and widely available |
Introduction to Hemp and Jute Fibers
Hemp fiber, derived from the stalk of the Cannabis sativa plant, is known for its strength, durability, and resistance to rot, making it an ideal material for rope production. Jute fiber, sourced from the Corchorus plants, is valued for its affordability, biodegradability, and coarse texture, often used in making ropes with good tensile strength but less resistance to moisture than hemp. Both fibers offer sustainable, natural alternatives to synthetic ropes, with hemp providing superior longevity and jute favored for economical and eco-friendly applications.
Historical Uses of Hemp and Jute in Rope Making
Hemp fiber has been utilized for rope making since ancient civilizations, prized for its strength, durability, and resistance to saltwater, making it the preferred material for naval ropes and ship rigging throughout history. Jute fiber, originating primarily from South Asia, became prominent in the 19th and early 20th centuries for producing affordable, biodegradable ropes used in agriculture and packaging. Both fibers exhibit unique historical importance, with hemp dominating maritime applications and jute supporting industrial and economic growth through versatile, eco-friendly rope products.
Botanical Origins and Availability
Hemp fiber, derived from the Cannabis sativa plant, is known for its superior strength and durability compared to jute fiber, which comes from the Corchorus species. Both fibers are natural and biodegradable, but hemp is cultivated globally with robust yields primarily in Europe, China, and North America, while jute is predominantly grown in the Indian subcontinent, especially Bangladesh and India. The availability of hemp fiber is increasing due to expanding agricultural regulations, whereas jute remains more regionally concentrated with seasonal limitations.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Hemp fiber exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to jute fiber, with tensile strength typically ranging from 550 to 900 MPa, whereas jute averages around 400 to 600 MPa. In terms of durability, hemp fibers resist moisture and microbial degradation better than jute, making hemp ropes more suitable for outdoor and marine applications. The enhanced abrasion resistance and longevity of hemp fiber contribute to its growing preference in heavy-duty rope manufacturing.
Water Resistance and Weathering Properties
Hemp fiber demonstrates superior water resistance compared to jute fiber, making it more durable in wet conditions and less prone to mildew and rot. Its stronger lignin content enhances weathering properties, allowing hemp ropes to maintain tensile strength and flexibility under prolonged exposure to sunlight and moisture. Jute fiber tends to absorb more water and deteriorate faster in humid or marine environments, reducing its lifespan for outdoor rope applications.
Flexibility and Handling Characteristics
Hemp fiber exhibits superior flexibility and softness compared to jute fiber, making it easier to handle and knot when used for rope production. Jute fibers tend to be coarser and less pliable, resulting in stiffer ropes that require more effort to manipulate. The enhanced elasticity and smooth texture of hemp ropes improve durability and comfort in applications demanding frequent handling.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Hemp fiber offers superior environmental benefits compared to jute fiber due to its faster growth rate, requiring less water and pesticides, which reduces soil degradation and chemical runoff. Both fibers are biodegradable and renewable, but hemp's higher yield per acre and ability to improve soil health through phytoremediation enhance its sustainability profile for rope production. Choosing hemp rope supports more sustainable agriculture and lower ecological footprints, crucial for eco-friendly industries.
Cost and Economic Considerations
Hemp fiber generally commands a higher price than jute fiber due to its sustainable cultivation practices and higher tensile strength, making it a premium choice for rope manufacturing. Jute fiber offers a more cost-effective alternative with widespread availability and lower processing costs, appealing to large-scale, budget-conscious rope producers. Economic considerations favor hemp fibers when durability and environmental impact justify the investment, while jute remains dominant in markets prioritizing affordability and mass production.
Common Applications in Rope Industry
Hemp fiber and jute fiber are widely used in the rope industry, with hemp favored for heavy-duty applications such as marine ropes, climbing ropes, and industrial lifting lines due to its superior strength, durability, and resistance to rot and UV damage. Jute fiber, softer and more flexible, is commonly employed in crafting decorative ropes, packing twine, and agricultural bindings where cost-effectiveness and biodegradability are prioritized. Both fibers contribute to eco-friendly rope production, but hemp's higher tensile strength makes it the preferred choice for demanding load-bearing uses.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Fiber for Rope
Hemp fiber offers superior tensile strength and durability, making it ideal for heavy-duty rope applications, while jute fiber provides a cost-effective, biodegradable option suited for lighter, decorative ropes. The choice between hemp and jute depends on the specific requirements of rope performance, environmental impact, and budget constraints. For demanding industrial use, hemp is preferred, whereas jute serves well for eco-friendly, low-stress uses.
Infographic: Hemp fiber vs Jute fiber for Rope
 azmater.com
azmater.com