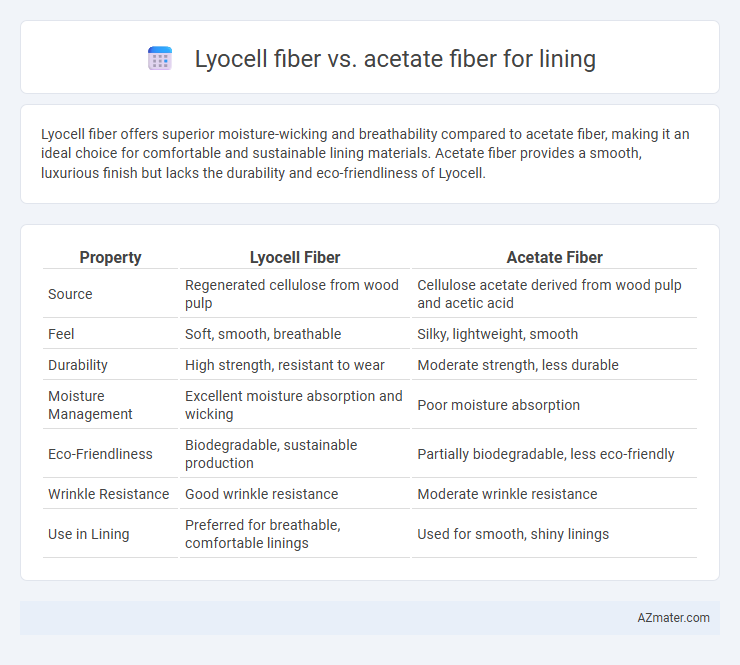
Lyocell fiber offers superior moisture-wicking and breathability compared to acetate fiber, making it an ideal choice for comfortable and sustainable lining materials. Acetate fiber provides a smooth, luxurious finish but lacks the durability and eco-friendliness of Lyocell.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Lyocell Fiber | Acetate Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Regenerated cellulose from wood pulp | Cellulose acetate derived from wood pulp and acetic acid |
| Feel | Soft, smooth, breathable | Silky, lightweight, smooth |
| Durability | High strength, resistant to wear | Moderate strength, less durable |
| Moisture Management | Excellent moisture absorption and wicking | Poor moisture absorption |
| Eco-Friendliness | Biodegradable, sustainable production | Partially biodegradable, less eco-friendly |
| Wrinkle Resistance | Good wrinkle resistance | Moderate wrinkle resistance |
| Use in Lining | Preferred for breathable, comfortable linings | Used for smooth, shiny linings |
Introduction to Lyocell and Acetate Fibers
Lyocell fiber, derived from sustainably sourced wood pulp, is known for its eco-friendly production process using non-toxic solvents and excellent moisture absorption, making it ideal for breathable garment linings. Acetate fiber, a semi-synthetic cellulosic fiber produced from cellulose acetate, offers a smooth, silky texture and high sheen, often chosen for its luxurious appearance in lining fabrics. Both fibers excel in comfort and aesthetics, with Lyocell favored for sustainability and moisture management, while Acetate emphasizes luster and softness.
Fiber Composition and Production Processes
Lyocell fiber is produced from sustainably sourced wood pulp through a closed-loop solvent spinning process, resulting in a biodegradable, cellulose-based fiber known for its strength and moisture-wicking properties. Acetate fiber originates from cellulose acetate derived by chemically modifying cellulose with acetic anhydride, using a process involving acetylation and solvent spinning, which yields a smooth, glossy fiber valued for its lustrous appearance but lower durability. The production of Lyocell prioritizes eco-friendly practices and results in a fiber with superior breathability and tensile strength, while acetate's manufacturing is more chemically intensive and produces fibers with higher susceptibility to shrinkage and chemicals.
Sustainability and Eco-Friendliness
Lyocell fiber, made from sustainably sourced wood pulp through a closed-loop process, offers superior eco-friendliness by minimizing water usage and chemical waste compared to acetate fiber, which is derived from cellulose acetate using more environmentally intensive solvents. Lyocell's biodegradability and renewable origin make it a sustainable choice for lining fabrics, whereas acetate fibers, despite their smooth finish and moisture-wicking properties, involve acetylation processes that generate harmful byproducts and rely on non-renewable solvents. The production of lyocell aligns with green textile standards by reducing environmental impact, supporting circular economy principles, and enhancing sustainability in garment linings.
Comfort and Breathability in Linings
Lyocell fiber offers superior moisture-wicking and breathability compared to acetate fiber, making it an excellent choice for linings in garments where comfort is essential. Its smooth, hypoallergenic properties reduce skin irritation, enhancing overall wearability in warm or active conditions. Acetate fiber, while offering a silky appearance, tends to retain heat and moisture, making it less breathable and potentially less comfortable for prolonged wear.
Moisture Absorption and Wicking Properties
Lyocell fiber exhibits superior moisture absorption and wicking properties compared to acetate fiber, making it highly effective for lining applications where breathability and comfort are essential. Lyocell's ability to absorb moisture up to 50% of its weight and quickly wick it away from the skin improves dryness and reduces clamminess. In contrast, acetate fiber has lower moisture absorption capacity and slower wicking performance, often resulting in less comfort in warm or humid conditions.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Lyocell fiber offers superior durability and wear resistance compared to acetate fiber, making it ideal for lining applications that require long-lasting performance. Lyocell's excellent tensile strength and abrasion resistance contribute to its ability to withstand frequent use without significant wear or damage. In contrast, acetate fiber is prone to weakening and deterioration over time, especially when exposed to moisture and friction.
Aesthetic Appeal: Texture and Finish
Lyocell fiber offers a smooth, soft texture with a subtle sheen that enhances the luxurious feel of linings, providing excellent drape and breathability. Acetate fiber is known for its high luster and silky finish, creating an elegant appearance with vibrant colors but may lack the natural softness of Lyocell. Both fibers contribute to aesthetic appeal, but Lyocell emphasizes natural matte elegance while Acetate highlights glossy sophistication in lining fabrics.
Cost Comparison for Lining Materials
Lyocell fiber lining generally costs more than acetate fiber due to its eco-friendly production process and superior moisture-wicking properties, making it a premium choice for sustainable apparel. Acetate fiber, favored for its glossy finish and affordability, remains a budget-friendly option for lining in mass production. Manufacturers often weigh the higher expense of Lyocell against its environmental benefits and enhanced comfort, whereas acetate offers a cost-effective solution with moderate performance.
Care and Maintenance Requirements
Lyocell fiber offers superior moisture-wicking and breathability compared to acetate fiber, making it easier to maintain without risk of overheating or excessive moisture buildup inside linings. Lyocell is machine washable and resistant to wrinkles, enabling straightforward care with less need for dry cleaning, whereas acetate fiber requires delicate handling and dry cleaning due to its sensitivity to heat and water. Frequent exposure of acetate linings to moisture and heat can lead to fiber weakening and loss of shape, making Lyocell a more durable and low-maintenance choice for garment linings.
Best Applications: When to Choose Lyocell vs Acetate
Lyocell fiber is best chosen for linings in high-end garments requiring moisture-wicking, breathability, and eco-friendly properties, such as luxury suits and activewear. Acetate fiber excels in linings where a smooth, glossy finish and rich color vibrancy are desired, commonly found in formalwear and bridal gowns. Selecting Lyocell ensures durability and comfort during extended wear, while Acetate is ideal for aesthetic appeal and cost-effective production in decorative linings.
Infographic: Lyocell fiber vs Acetate fiber for Lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com