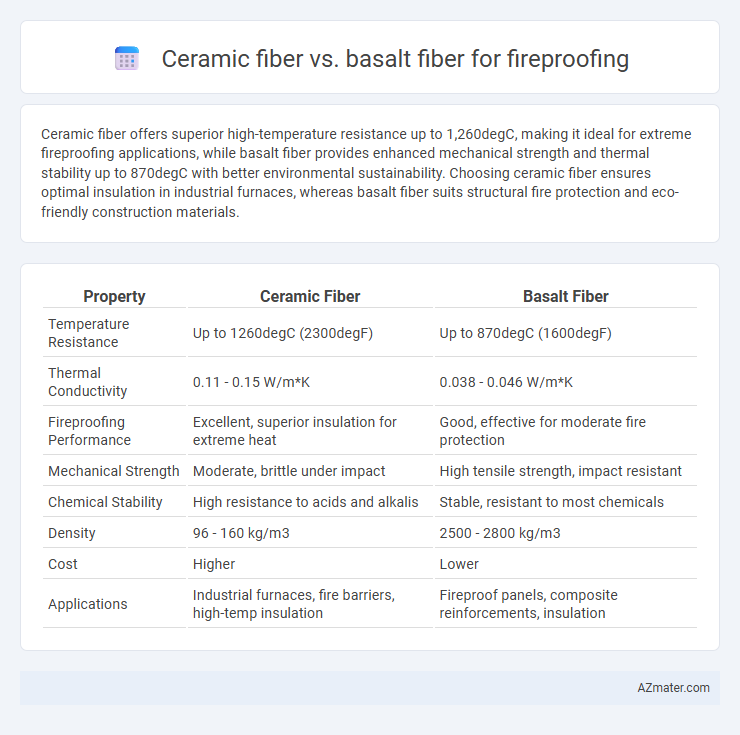
Ceramic fiber offers superior high-temperature resistance up to 1,260degC, making it ideal for extreme fireproofing applications, while basalt fiber provides enhanced mechanical strength and thermal stability up to 870degC with better environmental sustainability. Choosing ceramic fiber ensures optimal insulation in industrial furnaces, whereas basalt fiber suits structural fire protection and eco-friendly construction materials.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ceramic Fiber | Basalt Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 1260degC (2300degF) | Up to 870degC (1600degF) |
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.11 - 0.15 W/m*K | 0.038 - 0.046 W/m*K |
| Fireproofing Performance | Excellent, superior insulation for extreme heat | Good, effective for moderate fire protection |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate, brittle under impact | High tensile strength, impact resistant |
| Chemical Stability | High resistance to acids and alkalis | Stable, resistant to most chemicals |
| Density | 96 - 160 kg/m3 | 2500 - 2800 kg/m3 |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Applications | Industrial furnaces, fire barriers, high-temp insulation | Fireproof panels, composite reinforcements, insulation |
Introduction to Fireproofing Materials
Ceramic fiber and basalt fiber are critical fireproofing materials with distinct thermal properties and applications. Ceramic fiber offers superior heat resistance, typically withstanding temperatures up to 1260degC or higher, making it ideal for high-temperature insulation and fire barriers. Basalt fiber features excellent thermal stability and mechanical strength, functioning effectively in fireproof coatings and structural reinforcements.
Overview of Ceramic Fiber
Ceramic fiber is a high-temperature insulation material made from alumina and silica, offering excellent thermal stability up to 2300degF (1260degC), making it ideal for fireproofing applications. Its low thermal conductivity and lightweight nature provide superior heat resistance while maintaining structural integrity under intense fire exposure. Compared to basalt fiber, ceramic fiber delivers enhanced insulation performance and greater resistance to thermal shock, commonly used in industrial furnaces, fire barriers, and refractory linings.
Overview of Basalt Fiber
Basalt fiber, derived from volcanic basalt rock, offers superior fireproofing capabilities with a melting point around 1400degC, making it highly resistant to heat and flames in comparison to traditional ceramic fibers. Its excellent thermal stability, mechanical strength, and chemical resistance enable basalt fiber to maintain structural integrity during intense fire exposure. These qualities make basalt fiber a sustainable, durable alternative for fireproofing applications in construction, automotive, and aerospace industries.
Thermal Resistance Comparison
Ceramic fiber exhibits superior thermal resistance, typically withstanding temperatures up to 1,260degC (2,300degF), making it ideal for high-temperature fireproofing applications. Basalt fiber, while also fire-resistant, generally endures maximum temperatures around 870degC (1,600degF), offering moderate thermal protection. The higher melting point and lower thermal conductivity of ceramic fiber provide enhanced performance in extreme heat environments compared to basalt fiber.
Fireproofing Efficiency: Ceramic vs Basalt
Ceramic fiber exhibits superior fireproofing efficiency due to its exceptional thermal stability, withstanding temperatures up to 1,260degC (2,300degF) without significant degradation, making it ideal for high-temperature industrial applications. Basalt fiber offers good fire resistance, tolerating temperatures up to approximately 982degC (1,800degF), but its insulating properties are generally less effective than ceramic fiber in extreme fire scenarios. The higher melting point and lower thermal conductivity of ceramic fiber contribute to its enhanced fireproofing performance compared to basalt fiber.
Mechanical Properties and Durability
Ceramic fiber exhibits superior high-temperature resistance and low thermal conductivity, making it highly effective in fireproofing applications where extreme heat endurance and mechanical strength are critical. Basalt fiber, while offering excellent tensile strength and corrosion resistance, typically demonstrates higher thermal conductivity and lower performance under prolonged high-temperature exposure. Durability-wise, ceramic fiber maintains structural integrity in temperatures above 1200degC, whereas basalt fiber is more prone to degradation when consistently exposed to extreme heat, limiting its long-term fireproofing reliability.
Installation and Handling Differences
Ceramic fiber offers greater flexibility and lighter weight compared to basalt fiber, simplifying installation in complex geometries and reducing labor time. Basalt fiber is more rigid and dense, requiring specialized tools and careful handling to avoid damage during installation. Both materials necessitate protective equipment, but ceramic fiber poses higher respiratory risks due to finer particulates released during handling.
Cost Analysis: Ceramic Fiber vs Basalt Fiber
Ceramic fiber typically has a higher initial cost compared to basalt fiber due to its complex manufacturing process and superior high-temperature resistance, making it ideal for extreme fireproofing applications. Basalt fiber offers a more cost-effective alternative with lower raw material and production expenses, providing good thermal insulation but with slightly reduced performance at ultra-high temperatures. When budgeting for fireproofing projects, consider ceramic fiber for maximum fire resistance despite the higher price, while basalt fiber suits applications requiring moderate heat resistance and cost efficiency.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Ceramic fiber, derived from alumina and silica, offers excellent fire resistance but its manufacturing consumes high energy and produces CO2 emissions, raising environmental concerns. Basalt fiber, made from natural volcanic rock, has a lower carbon footprint due to minimal processing requirements and is fully recyclable, enhancing its sustainability profile. Both materials provide effective fireproofing, but basalt fiber stands out for its eco-friendly production and biodegradability advantages.
Applications and Best Use Cases
Ceramic fiber excels in high-temperature insulation applications such as furnace linings, fireproof blankets, and industrial kilns due to its superior heat resistance up to 1800degC, making it ideal for extreme fireproofing scenarios. Basalt fiber offers enhanced mechanical strength and chemical resistance, suited for structural reinforcement in fireproof composites, fire-resistant panels, and building insulation where moderate heat resistance up to 1000degC is required. Choosing between ceramic and basalt fiber depends on specific fireproofing needs, with ceramic fiber preferred for ultra-high-temperature environments and basalt fiber favored for reinforcement and thermal insulation in construction.
Infographic: Ceramic fiber vs Basalt fiber for Fireproofing
 azmater.com
azmater.com